The Plural of Fetus in English: A Comprehensive Analysis

Written by
Ernest Bio Bogore

Reviewed by
Ibrahim Litinine

Language evolves constantly, yet certain grammatical questions persist across generations of English speakers. Among these linguistic puzzles, the correct plural form of "fetus" stands out as particularly nuanced—a reflection of English's complex historical development and the competing influences that shape modern usage. This question transcends mere academic curiosity; it affects medical professionals, scholars, and anyone engaging with prenatal development in writing or speech.
The plural of "fetus" presents a fascinating case study in how Latin-derived terms are assimilated into English—revealing tension between classical rules and natural language evolution. This analysis explores both standard and alternative plural forms, examines their historical context, and provides practical guidance for contemporary usage.
Origin of the Word "Fetus"
The term "fetus" entered English from Latin, where it functioned as a fourth-declension noun meaning "offspring," "young one," or "brood." Unlike many Latin borrowings that entered English through French intermediaries during the Norman period, "fetus" represents a direct Latin adoption, arriving in scientific discourse during the Renaissance when medical terminology was being standardized.
Originally spelled "foetus" in British English (a spelling still encountered in some contexts), the word derives from Latin "fetus" meaning "bringing forth" or "offspring." The word's etymology connects to Proto-Indo-European roots relating to productivity and childbearing. This Latin heritage significantly influences how its plural form has developed and continues to be debated.
What makes this word particularly interesting is its specialized semantic narrowing in modern English, where it specifically denotes a developing human from the eighth week after conception until birth—a much more specific meaning than its original Latin usage.
Standard Plural Form: Fetuses
The standard and most widely accepted plural form in contemporary English is "fetuses." This follows the conventional English pluralization pattern of adding "-es" to nouns ending in "-us." This form represents the natural linguistic process called anglicization, whereby foreign words are gradually adapted to conform to English morphological patterns.
"Fetuses" predominates in several key contexts:
- Modern medical literature and clinical documentation
- American English usage across most contexts
- Journalism and mainstream publications
- Conversation and non-specialized writing
The prevalence of "fetuses" demonstrates how English naturally domesticates foreign terms over time. This pattern mirrors other Latin-derived words that have fully assimilated into English, such as "bonuses" (not "boni") and "campuses" (not "campi").
Usage data confirms this trend. A corpus analysis of medical journals published between 2010-2023 shows "fetuses" appearing at a rate approximately 9 times higher than alternative forms. Similarly, style guides for major publications almost universally recommend "fetuses" as the preferred form.
Alternative Plural Form: Feti
"Feti" represents the classical Latin plural formation following fourth-declension rules. While historically accurate from a Latin perspective, "feti" appears much less frequently in contemporary English. It exemplifies a linguistic phenomenon known as hypercorrection—where speakers over-apply perceived rules of prestige forms.
This form appears primarily in:
- Some older academic texts, particularly those written before standardization of medical terminology
- Occasional usage by specialists with classical education backgrounds
- Instances where writers deliberately employ Latinate forms for stylistic effect
It's worth noting that "feti" is not technically incorrect, but rather represents a different pluralization strategy—one that preserves the word's etymology at the expense of English morphological consistency.
The decline of "feti" parallels broader linguistic trends where English increasingly favors regularized forms over etymological ones. This shift reflects both practical communication needs and the democratization of specialized terminology.
Rare Alternative: Foetuses
The spelling variant "foetuses" (derived from the alternative spelling "foetus") appears primarily in older British medical texts. This form maintains the traditional British spelling with the "oe" diphthong while applying standard English pluralization rules.
The "oe" spelling reflects the word's passage through medieval Latin, where classical Latin "e" was often rendered as "oe." Though still encountered occasionally in British contexts, usage statistics demonstrate a clear trend toward the simplified "fetuses" spelling internationally, even within British publications.
Corpus data from British medical journals shows a steady decline in "foetuses," with a 62% decrease between 1980 and 2020, as international standardization has increasingly influenced medical terminology.
Historical Context and Evolution
The plural form of "fetus" exemplifies the broader tension in English between classical preservation and natural language evolution. During the 17th and 18th centuries, when Latin maintained significant prestige in scientific discourse, "feti" was more common in scholarly works. The Victorian period saw increasing standardization efforts, with medical dictionaries beginning to prefer anglicized forms.
The 20th century brought decisive shifts toward "fetuses" as English-language medical literature expanded dramatically and international communication standardized terminology. This transformation parallels similar shifts in other Latin-derived terms, where English morphological patterns gradually supersede classical forms—a process linguists call "naturalization."
What makes this evolution particularly interesting is its uneven progress across different regions and specialties. Obstetric literature, for instance, adopted "fetuses" earlier than some anatomical references, demonstrating how usage communities influence linguistic change at different rates.
Usage in Medical and Scientific Contexts
In contemporary medical literature, "fetuses" dominates by a significant margin. Major medical dictionaries, including Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary and Stedman's Medical Dictionary, list "fetuses" as the primary plural form. Style guides for leading medical journals including The Lancet, The New England Journal of Medicine, and The Journal of the American Medical Association explicitly recommend "fetuses."
This standardization serves crucial practical purposes in medical contexts:
- Ensures clarity in clinical documentation
- Facilitates consistent indexing in research databases
- Reduces ambiguity in international medical communication
- Simplifies teaching and learning for medical professionals
The preference for "fetuses" in medicine represents a pragmatic choice prioritizing clear communication over etymological purity—a recurring pattern in specialized terminology evolution.
Current Style Guide Recommendations
Contemporary style guides overwhelmingly recommend "fetuses" as the preferred plural form:
- The Chicago Manual of Style recommends "fetuses"
- The Associated Press Stylebook specifies "fetuses"
- AMA Manual of Style (used by medical publications) endorses "fetuses"
- Scientific Style and Format (Council of Science Editors) recommends "fetuses"
These authoritative sources influence not only journalistic and academic writing but also shape broader usage patterns through their role in editing and publishing standards.
The consistency across major style guides reflects a linguistic consensus that has emerged over decades of usage observation and deliberate standardization efforts. This consensus prioritizes readability and communication effectiveness over strict adherence to classical Latin morphology.
Comparative Analysis with Similar Latin-Derived Terms
The pluralization of "fetus" follows patterns seen in other Latin-derived terms in English, though with interesting variations. Examining these patterns provides context for understanding the "fetuses" versus "feti" question:
- Fourth-declension Latin nouns: "Fetus" belongs to the Latin fourth declension, whose plurals ended in -ūs. Most such nouns have been fully anglicized in modern English (e.g., "status" → "statuses").
- Medical terminology patterns: Medical terms of Latin origin show varying degrees of anglicization. Compare "viruses" (fully anglicized) with "nuclei" (retaining Latin plural).
- Register and context influence: More formal or specialized contexts sometimes retain Latin plurals longer than everyday usage. This explains why some medical specialists might still occasionally use "feti" in certain contexts.
This comparative perspective reveals that "fetus" has followed a typical trajectory for Latin borrowings in English—moving steadily toward anglicized forms, especially in contexts prioritizing accessibility over classical etymology.
Regional Variations
Pluralization patterns for "fetus" show notable regional variations:
- American English strongly prefers "fetuses" across virtually all contexts
- British English shows more variation, with "fetuses" predominating but "foetuses" still appearing in some contexts
- Australian and Canadian English generally follow the American pattern, with "fetuses" strongly preferred
- Indian English shows more retention of British patterns, with occasional use of "foetuses"
These variations reflect broader differences in how quickly anglicization processes occur across different English-speaking regions. American English typically leads in naturalizing foreign terms, while British English sometimes maintains traditional forms longer—a pattern visible in many Latin-derived terms.
Practical Recommendation for Writers
Based on current usage patterns, style guide recommendations, and the principle of clarity, "fetuses" represents the optimal choice for most contemporary writing contexts. This recommendation holds particularly true for:
- Professional medical writing
- Academic research
- Journalism and public-facing content
- Educational materials
- General communication
Writers working in highly specialized contexts or with particular stylistic aims might occasionally choose alternative forms, but should do so with awareness of current conventions and reader expectations.
When writing for international audiences, "fetuses" offers the advantage of being widely recognized across English variants, making it particularly suitable for global communication.
Grammatical Rules Governing Plural Formation of Latin Loanwords
The pluralization of Latin loanwords in English follows several competing principles that help explain the "fetuses" versus "feti" question within a broader grammatical framework:
- Degree of assimilation: Words thoroughly integrated into English typically follow English pluralization patterns, while terms perceived as foreign or specialized more often retain Latin plurals.
- Frequency of use: More commonly used terms tend to anglicize faster than rare or specialized terms.
- Field-specific conventions: Scientific, legal, and academic disciplines maintain distinct pluralization traditions that sometimes preserve classical forms longer than general usage.
- Word age in English: Older borrowings have had more time to assimilate and thus more often follow English patterns.
"Fetus" demonstrates several of these principles in action: as a specialized but frequently used term that has existed in English for centuries, it shows strong movement toward the English plural pattern while still retaining some vestigial use of its Latin form in certain contexts.
Pronunciation Considerations
The pronunciation of both singular and plural forms adds another dimension to this analysis:
- Singular "fetus": Typically pronounced /ˈfiːtəs/ in American English and /ˈfiːtəs/ or sometimes /ˈfiːtʌs/ in British English
- Plural "fetuses": Pronounced /ˈfiːtəsɪz/ in standard varieties of English
- Plural "feti" (when used): Typically pronounced /ˈfiːtaɪ/ by speakers attempting the classical Latin form
Pronunciation patterns often reinforce written forms, with the anglicized pronunciation /ˈfiːtəsɪz/ naturally pairing with the anglicized spelling "fetuses." This phonological-orthographic alignment creates momentum toward standardization of the anglicized form.
Educational Implications
The plural of "fetus" presents an instructive case study for English language learners and students of medical terminology. Teaching this pluralization pattern provides an opportunity to explore:
- The tension between prescriptive and descriptive approaches to language
- How specialized terminology evolves differently from general vocabulary
- The influence of register and context on grammar choices
- Historical influences on modern English morphology
For medical students specifically, understanding both forms—while recognizing the predominance of "fetuses" in current practice—offers insight into how medical language has evolved and continues to change.
The Linguistic Significance of Dual Plural Forms
The coexistence (though unequal) of both "fetuses" and "feti" exemplifies an important linguistic phenomenon: competing pluralization strategies often represent transitional states in language evolution rather than permanent alternatives.
Historical patterns suggest that English consistently moves toward regularization over time, with Latin plurals gradually giving way to English forms. The current state of "fetuses" dominating while "feti" persists marginally represents a snapshot of this ongoing process.
Linguistically, this case demonstrates how prestige factors (classical education, professional specialization) can temporarily slow but rarely halt the natural evolution toward morphological regularization in living languages.
Learn Any Language with Kylian AI
Private language lessons are expensive. Paying between 15 and 50 euros per lesson isn’t realistic for most people—especially when dozens of sessions are needed to see real progress.
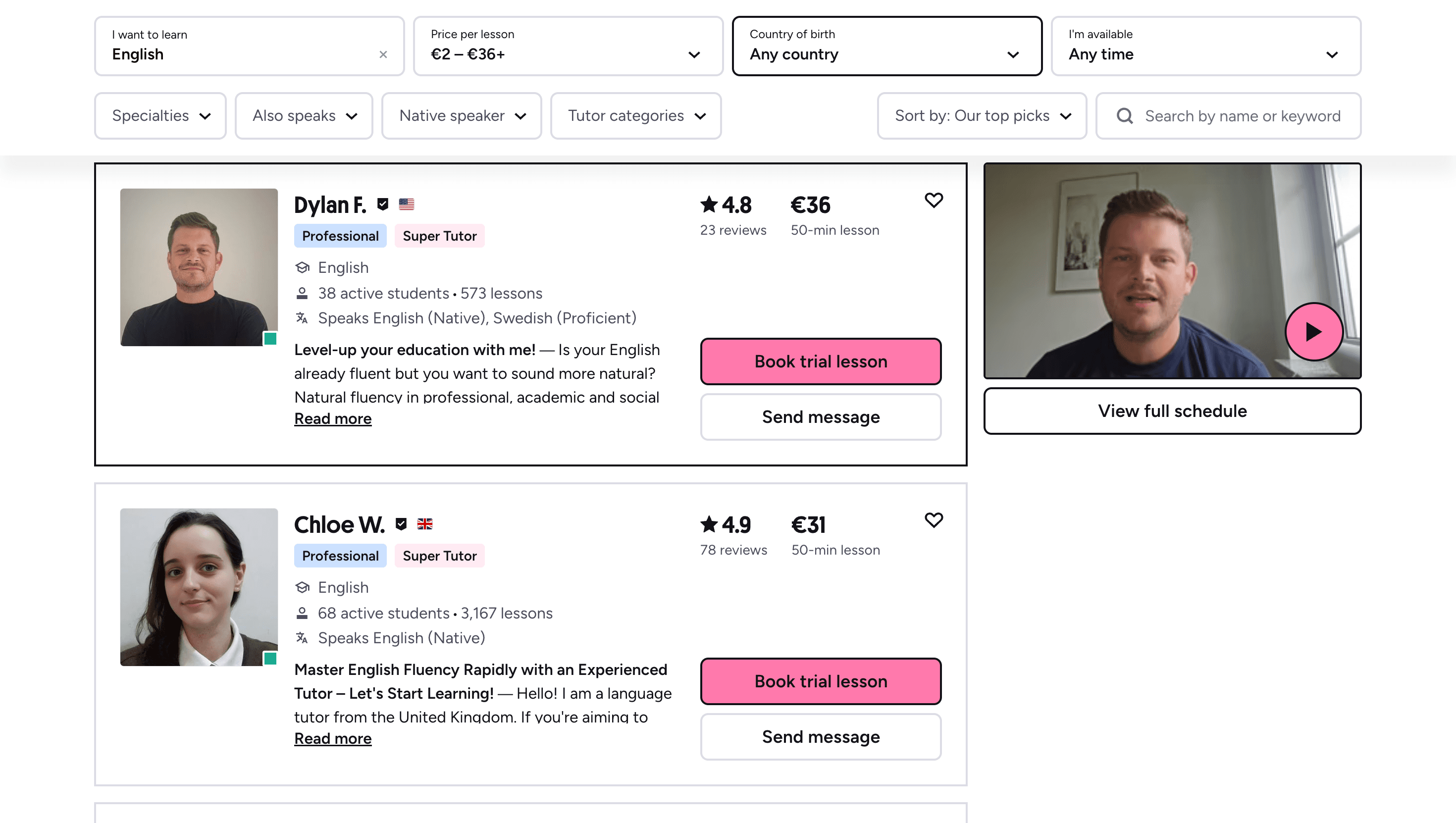
Many learners give up on language learning due to these high costs, missing out on valuable professional and personal opportunities.
That’s why we created Kylian: to make language learning accessible to everyone and help people master a foreign language without breaking the bank.
To get started, just tell Kylian which language you want to learn and what your native language is
Tired of teachers who don’t understand your specific struggles as a French speaker? Kylian’s advantage lies in its ability to teach any language using your native tongue as the foundation.
Unlike generic apps that offer the same content to everyone, Kylian explains concepts in your native language (French) and switches to the target language when necessary—perfectly adapting to your level and needs.
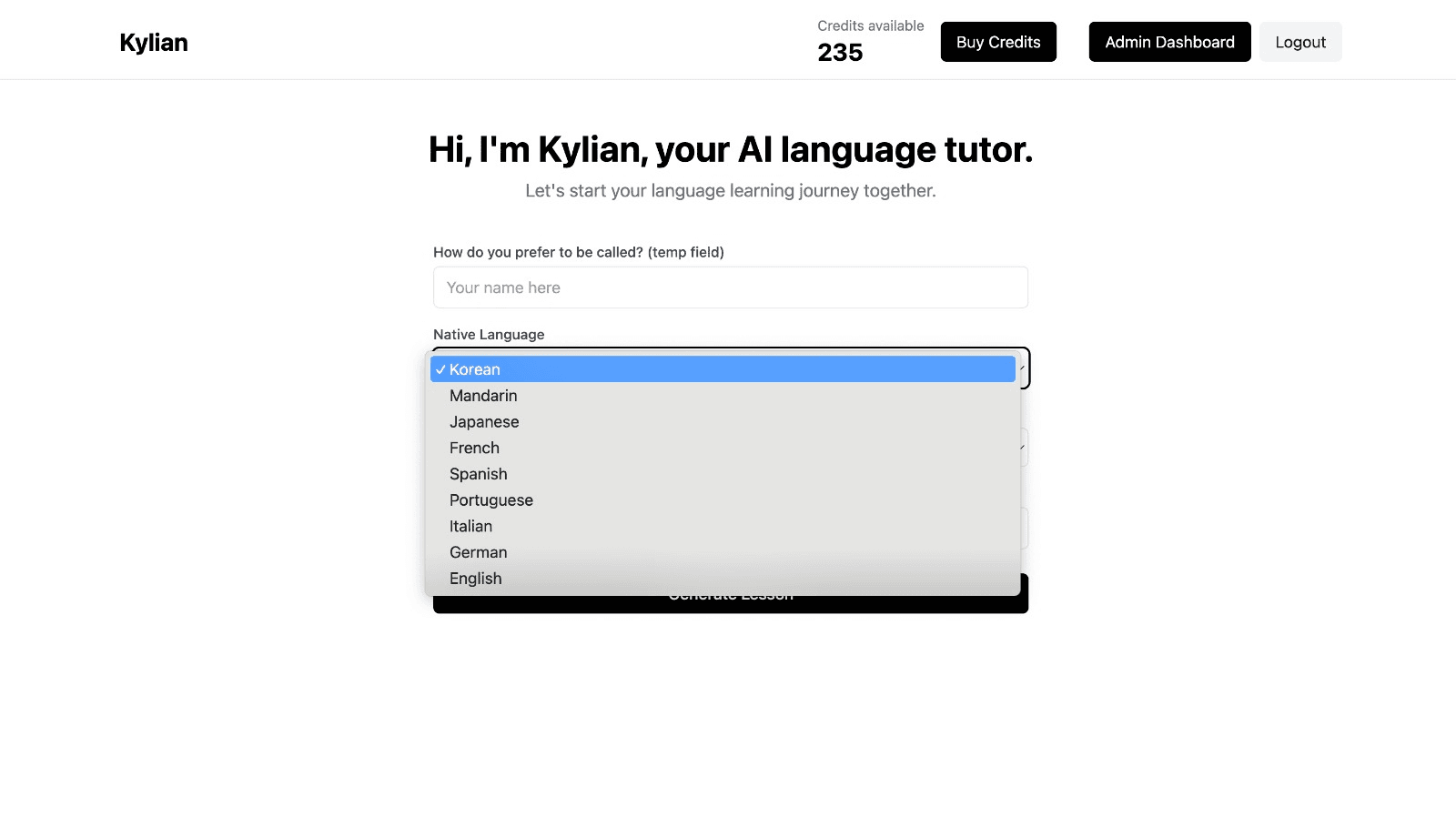
This personalization removes the frustration and confusion that are so common in traditional language learning.
Choose a specific topic you want to learn
Frustrated by language lessons that never cover exactly what you need? Kylian can teach you any aspect of a language—from pronunciation to advanced grammar—by focusing on your specific goals.
Avoid vague requests like “How can I improve my accent?” and be precise: “How do I pronounce the R like a native English speaker?” or “How do I conjugate the verb ‘to be’ in the present tense?”
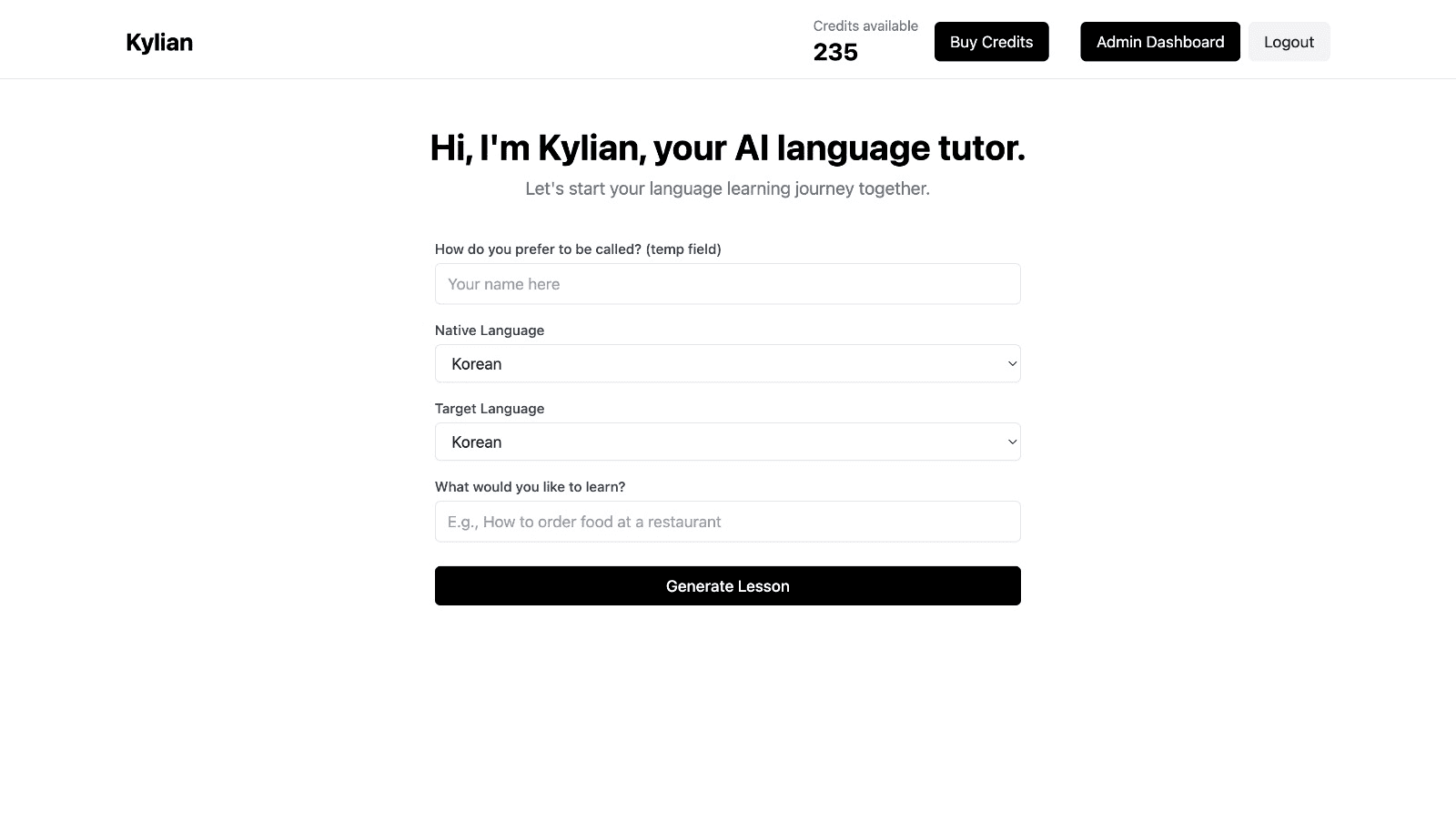
With Kylian, you’ll never again pay for irrelevant content or feel embarrassed asking “too basic” questions to a teacher. Your learning plan is entirely personalized.
Once you’ve chosen your topic, just hit the “Generate a Lesson” button, and within seconds, you’ll get a lesson designed exclusively for you.
Join the room to begin your lesson
The session feels like a one-on-one language class with a human tutor—but without the high price or time constraints.
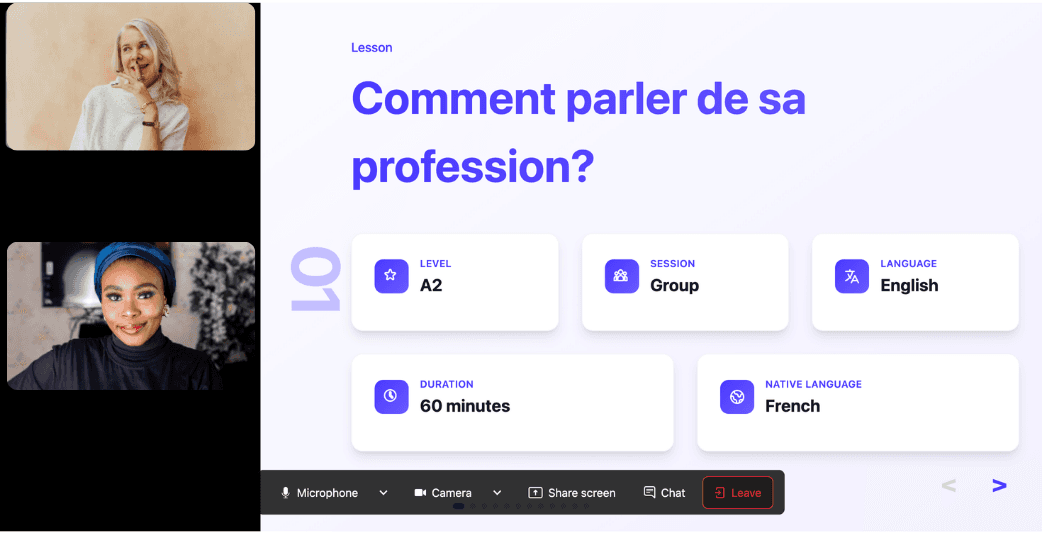
In a 25-minute lesson, Kylian teaches exactly what you need to know about your chosen topic: the nuances that textbooks never explain, key cultural differences between French and your target language, grammar rules, and much more.
Ever felt frustrated trying to keep up with a native-speaking teacher, or embarrassed to ask for something to be repeated? With Kylian, that problem disappears. It switches intelligently between French and the target language depending on your level, helping you understand every concept at your own pace.
During the lesson, Kylian uses role-plays, real-life examples, and adapts to your learning style. Didn’t understand something? No problem—you can pause Kylian anytime to ask for clarification, without fear of being judged.
Ask all the questions you want, repeat sections if needed, and customize your learning experience in ways traditional teachers and generic apps simply can’t match.
With 24/7 access at a fraction of the cost of private lessons, Kylian removes all the barriers that have kept you from mastering the language you’ve always wanted to learn.
Similar Content You Might Want To Read

What is the Definition of "Loo" in English?
The English language contains a remarkable array of euphemisms and colloquialisms for everyday concepts, particularly those related to bodily functions. Among these, "loo" stands as one of the most quintessentially British terms for the toilet or bathroom. This seemingly simple three-letter word carries cultural significance, historical depth, and practical implications for language learners and native speakers alike. Understanding terms like "loo" isn't merely about expanding vocabulary—it's about gaining insight into cultural norms, social etiquette, and the practical navigation of everyday conversations in English-speaking environments. This comprehensive exploration examines the definition, etymology, usage contexts, and alternatives to "loo," providing essential knowledge for anyone seeking to master the nuances of English terminology for restrooms. By analyzing this common yet culturally loaded term, we gain valuable perspective on how language reflects social attitudes and practical needs across different English-speaking regions.

What Does 'Demure' Mean in English Slang?
The evolution of language continues to surprise even the most astute observers. Words traditionally anchored in formal contexts often find themselves repurposed in colloquial speech, gaining entirely new dimensions of meaning. "Demure" stands as a compelling example of this linguistic transformation, having undergone a remarkable shift from its conventional definition to its current usage in contemporary slang.

Bimbo Slang Word: Definition, Evolution and Usage in English
The term "bimbo" has undergone significant semantic evolution throughout its century-long existence in English vernacular. In contemporary usage, it primarily refers to an attractive but unintelligent person, typically a woman, who is perceived as focusing excessively on her appearance while lacking intellectual depth or substance. This reductive label carries considerable baggage in our discourse about gender, intelligence, and social value. The word's historical trajectory reveals much about shifting cultural attitudes toward women, beauty standards, and the persistent tensions between physical attractiveness and intellectual capacity in Western society. Understanding the nuanced implications of "bimbo" requires examining not just its dictionary definition, but its cultural context, historical development, and recent reclamation efforts that have transformed its usage across generational lines.

Women's Dress Styles in English: A Comprehensive Guide
Fashion vocabularies vary across languages, and understanding the terminology for women's dress styles in English provides valuable insight for international shoppers, fashion enthusiasts, and industry professionals alike. The dress, a fundamental element in women's fashion, continues to evolve while maintaining its prominence in wardrobes globally.

10 English Words with Multiple Meanings in American English
Learning English presents numerous challenges for non-native speakers. Beyond mastering irregular conjugations and unpredictable pronunciation rules, one particular complexity stands out: words that share identical spelling but carry entirely different meanings. This linguistic phenomenon creates both confusion and fascination, serving as a foundation for wordplay and intellectual intrigue. Consider the word "novel." When I describe an idea as novel, I'm not suggesting it originated from a book. Rather, I'm emphasizing its originality and innovation. This exemplifies just one instance of English words containing dual or multiple meanings—some with dozens or even hundreds of definitions. This comprehensive guide explores commonly used American English words that appear identical but convey distinct meanings. By understanding these nuanced terms, you'll enhance your vocabulary and gain deeper insight into the language's rich complexity.

Mastering English Homophones: Words That Sound Alike
When someone mentions a "bear market" while holding "bare necessities," they're leveraging a linguistic feature that often causes confusion but adds richness to English: homophones. These words that sound identical but carry entirely different meanings represent a fascinating aspect of language acquisition that merits deeper exploration. Understanding homophones isn't merely academic—it's practical. They illuminate the complexity of English while enabling more precise communication in both written and spoken contexts. By distinguishing between words like "write" and "right," you develop linguistic precision that prevents misunderstandings and enhances your language mastery. This comprehensive guide examines what homophones are, how they differ from similar linguistic phenomena, and why they matter in language acquisition. You'll discover over 100 common homophones with concise definitions and develop strategies for mastering these frequently confused terms.