What is the Past and Past Participle Form of Shoot?

Written by
Ernest Bio Bogore

Reviewed by
Ibrahim Litinine

The English language presents numerous challenges for learners and native speakers alike, particularly when navigating its irregular verb forms. Understanding the past and past participle forms of irregular verbs is crucial for effective communication. The verb "shoot" stands as a perfect example of this complexity, with its unique transformation patterns that don't follow the standard "-ed" ending of regular verbs.
Mastering these irregular forms isn't merely an academic exercise—it's fundamental to expressing yourself accurately in various contexts, from casual conversations to professional writing. Whether you're describing a photography session from yesterday, explaining what happened during a basketball game, or discussing a film production, knowing how to use "shoot" correctly in its past forms enables precise communication.
This comprehensive guide explores the past and past participle forms of "shoot," examining their correct usage through practical examples, identifying common mistakes, and providing effective strategies for remembering these forms. By the end of this article, you'll have gained a thorough understanding of how to use this versatile verb correctly across all its tenses.
The Present, Past, and Past Participle Forms of "Shoot"
Base Form: Shoot
The present form "shoot" functions as the foundation of this irregular verb. It represents actions occurring in the present or habitual activities. For example:
- "I shoot photographs every weekend."
- "They shoot scenes for the movie on Tuesdays."
- "Professional photographers shoot in various lighting conditions."
The verb "shoot" possesses remarkable versatility, appearing in numerous contexts from sports to photography, filmmaking to hunting, and even in metaphorical expressions.
Past Form: Shot
The past simple form of "shoot" is "shot"—not "shooted" as some might incorrectly assume. This form indicates a completed action that occurred at a specific time in the past:
- "I shot a documentary in Alaska last summer."
- "She shot ten baskets during practice yesterday."
- "The director shot that scene in a single take."
This transformation from "shoot" to "shot" exemplifies the irregular nature of English verbs, where the vowel sound changes completely rather than simply adding an "-ed" ending.
Past Participle: Shot
The past participle form of "shoot" is also "shot," making it identical to the simple past form. This pattern is common among some irregular verbs in English. The past participle combines with auxiliary verbs like "have," "has," or "had" to form perfect tenses:
- "I have shot hundreds of photos for this portfolio."
- "He has shot three films in that location."
- "They had shot all the necessary footage before the storm arrived."
The past participle "shot" also serves in passive constructions with forms of "to be":
- "The movie was shot in black and white."
- "These photographs were shot using natural light."
- "The basketball was shot from half-court."
Complete Conjugation of "Shoot"
To fully grasp the verb "shoot," examine its conjugation across all tenses and forms:
Present Tense
- I/we/you/they shoot
- He/she/it shoots
Past Tense
- I/he/she/it/we/you/they shot
Future Tense
- I/he/she/it/we/you/they will shoot
Present Perfect
- I/we/you/they have shot
- He/she/it has shot
Past Perfect
- I/he/she/it/we/you/they had shot
Future Perfect
- I/he/she/it/we/you/they will have shot
Present Continuous
- I am shooting
- He/she/it is shooting
- We/you/they are shooting
Past Continuous
- I/he/she/it was shooting
- We/you/they were shooting
Future Continuous
- I/he/she/it/we/you/they will be shooting
Present Perfect Continuous
- I/we/you/they have been shooting
- He/she/it has been shooting
Past Perfect Continuous
- I/he/she/it/we/you/they had been shooting
Future Perfect Continuous
- I/he/she/it/we/you/they will have been shooting
Practical Examples of "Shoot" in Different Tenses
Understanding how "shoot" functions in various contexts and tenses solidifies your grasp of this irregular verb. Consider these practical applications:
Present Simple
"Professional photographers shoot in RAW format to preserve image data." This sentence describes a habitual action or general truth.
Present Continuous
"The crew is shooting the final episode today." This indicates an action in progress at the present moment.
Past Simple
"The team shot brilliantly during the championship game." This describes a completed action at a specific time in the past.
Past Continuous
"They were shooting the documentary when the earthquake struck." This shows an ongoing action in the past that was interrupted.
Present Perfect
"She has shot over fifty commercials in her career." This connects a past action to the present, emphasizing experience or accomplishment.
Present Perfect Continuous
"The director has been shooting films for three decades." This emphasizes the ongoing nature of an action that began in the past and continues to the present.
Past Perfect
"By the time I arrived, they had already shot the crucial scene." This indicates an action completed before another past action.
Past Perfect Continuous
"The photographer had been shooting for eight hours when his equipment failed." This describes an ongoing action in the past that was in progress before another past event.
Future Simple
"We will shoot the interview next Tuesday." This expresses a planned future action.
Future Continuous
"This time tomorrow, they will be shooting the sunrise scene." This describes an action that will be in progress at a specific time in the future.
Future Perfect
"By next month, we will have shot all the episodes for the season." This indicates an action that will be completed before a specific point in the future.
Future Perfect Continuous
"By December, he will have been shooting wildlife documentaries for twenty-five years." This expresses the duration of an ongoing action up to a future point.
Common Uses and Contexts for "Shoot"
The verb "shoot" appears in numerous contexts, each with slightly different connotations. Understanding these varied applications enhances your ability to use the verb appropriately.
Photography
"The photographer shoots primarily with natural light." "She shot an impressive portfolio during her travels." "They have shot cover images for several major magazines."
Filmmaking
"The director shoots most scenes in sequence." "They shot the entire film in just three weeks." "These scenes were shot using drone cameras."
Sports
"He shoots from beyond the three-point line with remarkable accuracy." "She shot the winning goal in overtime." "The team has shot with 60% accuracy this season."
Hunting
"They don't shoot endangered species." "The hunter shot a deer during the permitted season." "No animals have been shot in this protected area."
Metaphorical Uses
"Don't shoot the messenger." "She shot him a warning glance." "The company has shot to the top of the industry."
Common Mistakes with Past Forms of "Shoot"
Even native English speakers occasionally make errors with irregular verbs like "shoot." Recognizing these common mistakes helps avoid them in your own communication.
Using "Shooted" Instead of "Shot"
Incorrect: "He shooted the ball into the basket." Correct: "He shot the ball into the basket."
The error stems from applying regular verb patterns to an irregular verb. Remember that "shoot" follows an irregular pattern and does not take the standard "-ed" ending.
Confusing "Shoot" and "Shot" in Complex Sentences
Incorrect: "After she has shoot the scene, we'll review the footage." Correct: "After she has shot the scene, we'll review the footage."
In perfect tenses, always use the past participle "shot" after auxiliary verbs like "have," "has," or "had."
Misusing Forms in Passive Voice
Incorrect: "The film was shoot in Iceland." Correct: "The film was shot in Iceland."
In passive constructions, use the past participle "shot" after forms of "to be."
Incorrect Pronunciation
Some English learners mispronounce "shot," conflating it with words like "shoot" or "shut." The correct pronunciation of "shot" is /ʃɒt/ (UK) or /ʃɑːt/ (US), with a short vowel sound.
Phrasal Verbs with "Shoot"
The verb "shoot" combines with prepositions and adverbs to create phrasal verbs with distinct meanings. Mastering these expressions enhances your English fluency.
Shoot for
Meaning: To aim for or attempt to achieve something "We're shooting for completion by December." "She shoots for perfection in her work."
Shoot up
Meaning: To grow quickly or rise suddenly "Prices have shot up since last year." "The startup's valuation shot up after securing major funding."
Shoot down
Meaning: To reject or criticize severely; literally, to cause to fall by shooting "The committee shot down his proposal without discussion." "Her confidence was shot down by the harsh criticism."
Shoot off
Meaning: To leave quickly; to send or fire off "He shot off an angry email to customer service." "They shot off before the party ended."
Shoot back
Meaning: To reply quickly or sharply "When questioned, she shot back a witty response." "He shot back with a counterargument."
Idiomatic Expressions with "Shot"
The past form "shot" appears in numerous idiomatic expressions, adding color and nuance to English communication.
Give it a shot
Meaning: To try something "I've never played tennis before, but I'll give it a shot."
Shot in the dark
Meaning: A guess or attempt with little information "The detective's theory was a shot in the dark that turned out to be correct."
Call the shots
Meaning: To be in charge or make the decisions "In this department, the senior manager calls the shots."
Long shot
Meaning: Something unlikely to succeed "Winning the competition was a long shot, but she entered anyway."
Shot in the arm
Meaning: Something that provides encouragement or stimulus "The new investment gave the company a much-needed shot in the arm."
Big shot
Meaning: An important or influential person "He became a big shot in the film industry after his movie won an award."
Distinction: Shot vs. Shoot in Context
Understanding the difference between "shot" and "shoot" in various contexts prevents confusion and enhances precision in communication.
Temporal Difference
"Shoot" refers to present or future actions, while "shot" indicates past actions.
Present: "I shoot portraits every Tuesday." Past: "I shot portraits last Tuesday."
Nominal vs. Verbal Uses
As a noun, "shot" refers to the act or result of shooting: "That was a perfect shot." (referring to a photograph or a sports attempt)
As a verb, "shoot" (present) and "shot" (past) describe the action: "I'll shoot a new portrait tomorrow." "I shot a new portrait yesterday."
In Compound Structures
"I like to shoot in natural light." "I have shot in natural light for years."
The distinction highlights the temporal relationship between actions and maintaining tense consistency in complex sentences.
Learning Strategies for Mastering "Shoot" Forms
Irregular verbs like "shoot" require specific learning approaches. These strategies help cement the correct forms in your memory.
Pattern Recognition
"Shoot" follows a pattern similar to other irregular verbs that change vowel sounds, such as:
- Shoot → Shot (like Meet → Met)
- This pattern recognition helps you predict forms of similar verbs.
Contextual Practice
Create or study sentences that use "shoot" in various tenses and contexts. Repeated exposure reinforces correct usage:
- "I shoot photos on weekends."
- "I shot some amazing landscapes yesterday."
- "I have shot with this camera for years."
Mnemonic Devices
Create memory aids that connect the present and past forms: "When I shoot today, remember that yesterday I shot."
Voice Recording Practice
Record yourself using "shoot" and "shot" in different sentences, then listen back to reinforce both pronunciation and usage.
Immersive Learning
Watch films, documentaries, or tutorials about photography or sports where these terms appear frequently in context.
"Shoot" in Different English Variants
While the basic conjugation of "shoot" remains consistent across English variants, subtle differences exist in usage patterns and idiomatic expressions.
American English
In American English, "shoot" frequently appears in sports contexts, especially basketball: "He shoots from downtown!" (basketball commentary) "She shot 85% from the free-throw line this season."
The expression "shoot the breeze" (casual conversation) is more common in American usage.
British English
British English speakers might use "shoot" in contexts like: "They're shooting a documentary for the BBC." "He shot a glorious goal from outside the penalty area."
The expression "shoot from the hip" (speak candidly without careful consideration) appears in both variants but with slightly different connotations.
Australian English
Australian English incorporates distinctive phrases with "shoot": "Let's shoot through" (let's leave quickly)
Canadian English
Canadian usage generally aligns with American patterns but sometimes incorporates British expressions, creating a unique blend.
Historical Evolution of "Shoot" Forms
The verb "shoot" has ancient roots in Germanic languages, and its irregular pattern reflects historical sound changes.
Old English Origins
In Old English, the verb was "scēotan," with past tense "scēat" and past participle "scoten." The modern forms evolved through gradual sound changes and simplification.
Middle English Transition
By Middle English, the forms had evolved to "sheten" (infinitive), "shot" (past), and "shoten" (past participle). The modern pattern was taking shape.
Modern Standardization
The Great Vowel Shift (14th-18th centuries) influenced the pronunciation, while standardization of written English eventually established the current forms.
This historical perspective explains why "shoot" doesn't follow the regular "-ed" pattern—it carries the imprint of ancient language patterns.
Enhanced Memory Techniques for Irregular Verbs Like "Shoot"
Beyond basic strategies, these advanced techniques can solidify your mastery of "shoot" and similar irregular verbs.
Visualization
Create mental images that connect the meaning to the form. Visualize a camera "shooting" (present) and then see the completed photograph as having been "shot" (past).
Story-Chain Method
Create a narrative that uses multiple forms: "Every day I shoot wildlife photos. Yesterday, I shot a picture of a rare bird. Over my career, I have shot thousands of nature images."
The narrative context helps cement the proper forms in sequence.
Sensory Association
Associate the pronunciation of "shot" with the sharp click sound of a camera shutter, creating a sensory link to reinforce memory.
Spaced Repetition
Instead of cramming, review the verb forms at increasing intervals over time—first daily, then weekly, then monthly—to strengthen long-term retention.
Peer Teaching
Explain the forms and usage of "shoot" to someone else. Teaching others solidifies your own understanding and highlights any areas of uncertainty.
Learn Any Language with Kylian AI
Private language lessons are expensive. Paying between 15 and 50 euros per lesson isn’t realistic for most people—especially when dozens of sessions are needed to see real progress.
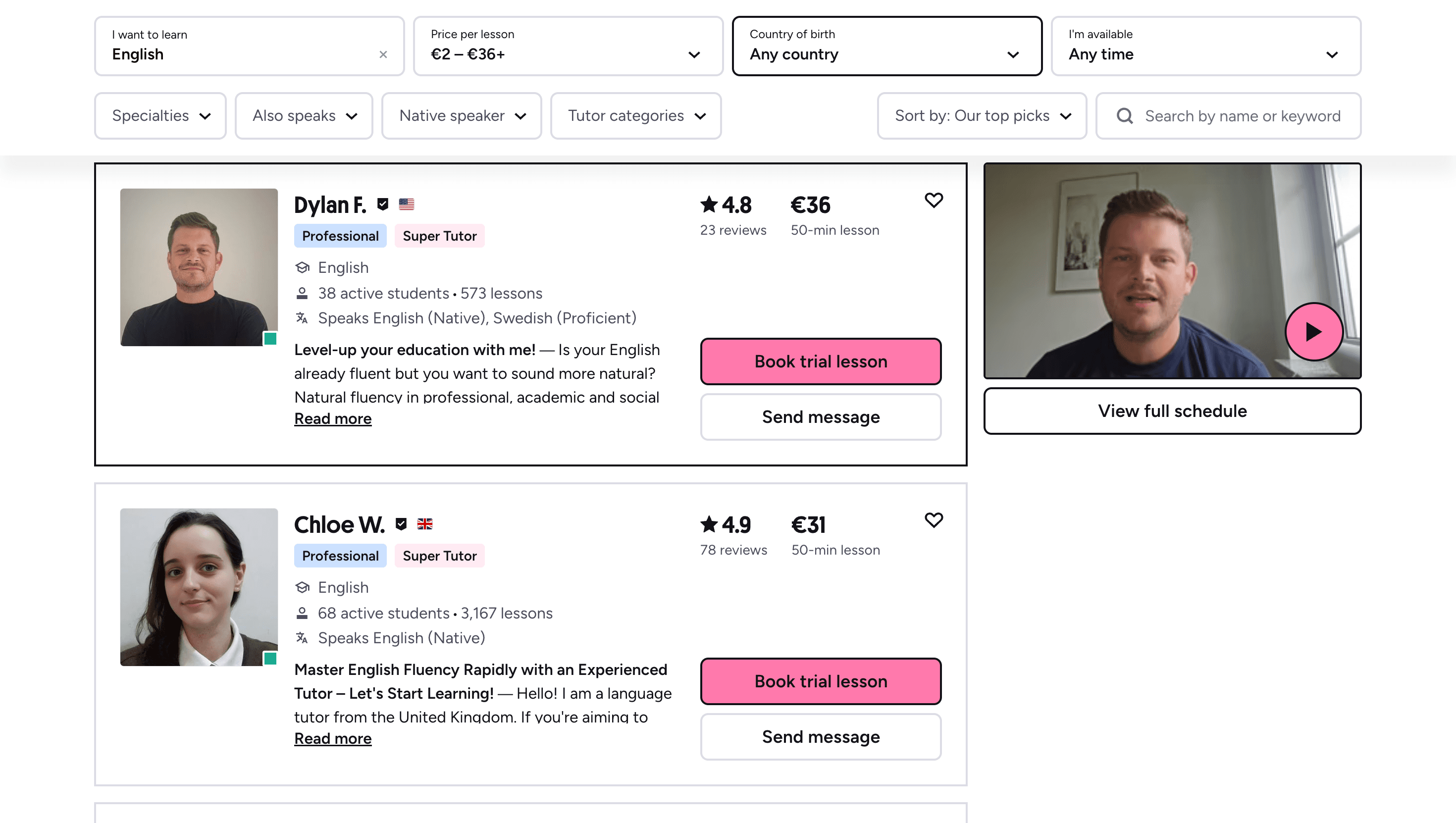
Many learners give up on language learning due to these high costs, missing out on valuable professional and personal opportunities.
That’s why we created Kylian: to make language learning accessible to everyone and help people master a foreign language without breaking the bank.
To get started, just tell Kylian which language you want to learn and what your native language is
Tired of teachers who don’t understand your specific struggles as a French speaker? Kylian’s advantage lies in its ability to teach any language using your native tongue as the foundation.
Unlike generic apps that offer the same content to everyone, Kylian explains concepts in your native language (French) and switches to the target language when necessary—perfectly adapting to your level and needs.
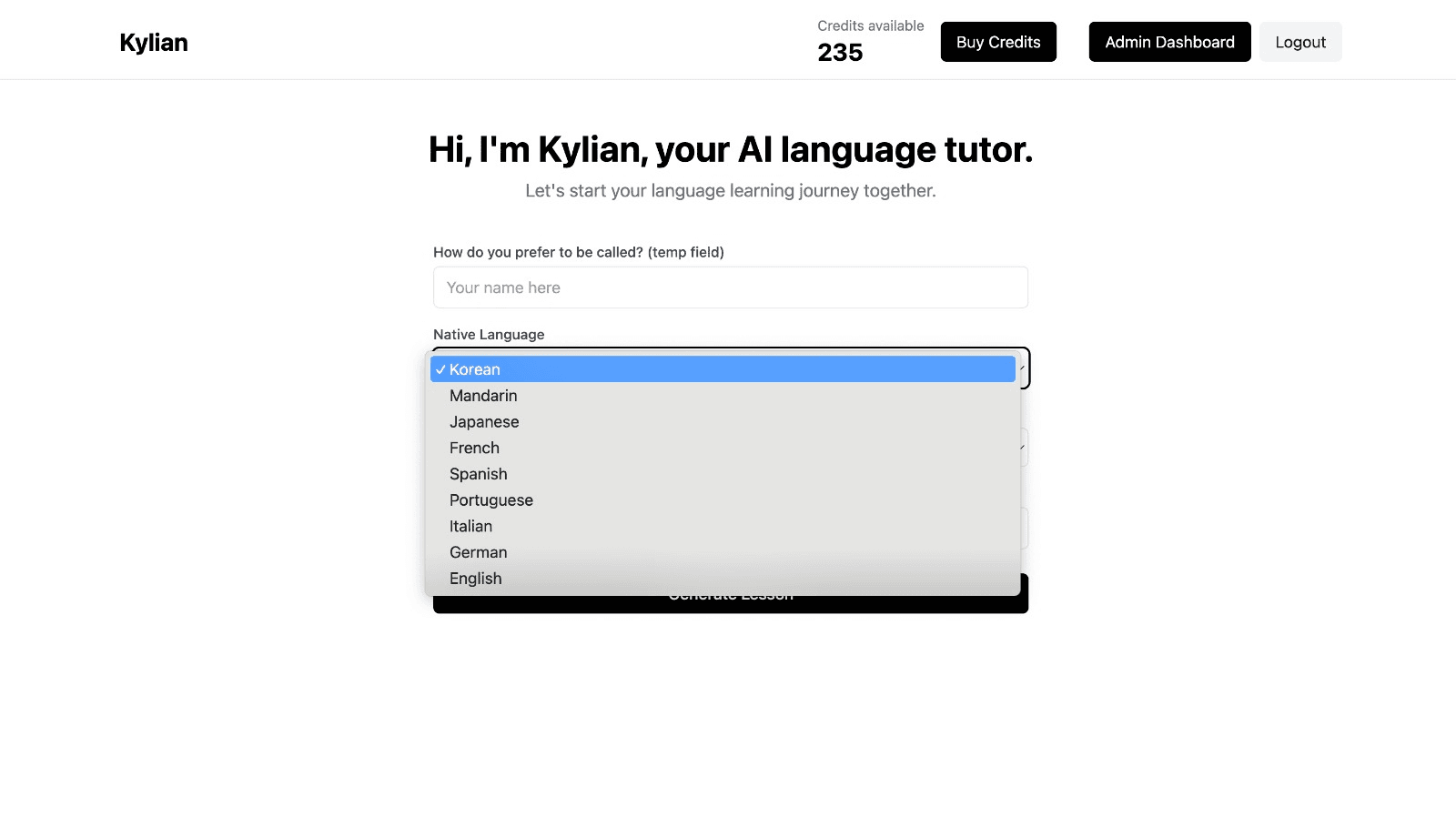
This personalization removes the frustration and confusion that are so common in traditional language learning.
Choose a specific topic you want to learn
Frustrated by language lessons that never cover exactly what you need? Kylian can teach you any aspect of a language—from pronunciation to advanced grammar—by focusing on your specific goals.
Avoid vague requests like “How can I improve my accent?” and be precise: “How do I pronounce the R like a native English speaker?” or “How do I conjugate the verb ‘to be’ in the present tense?”
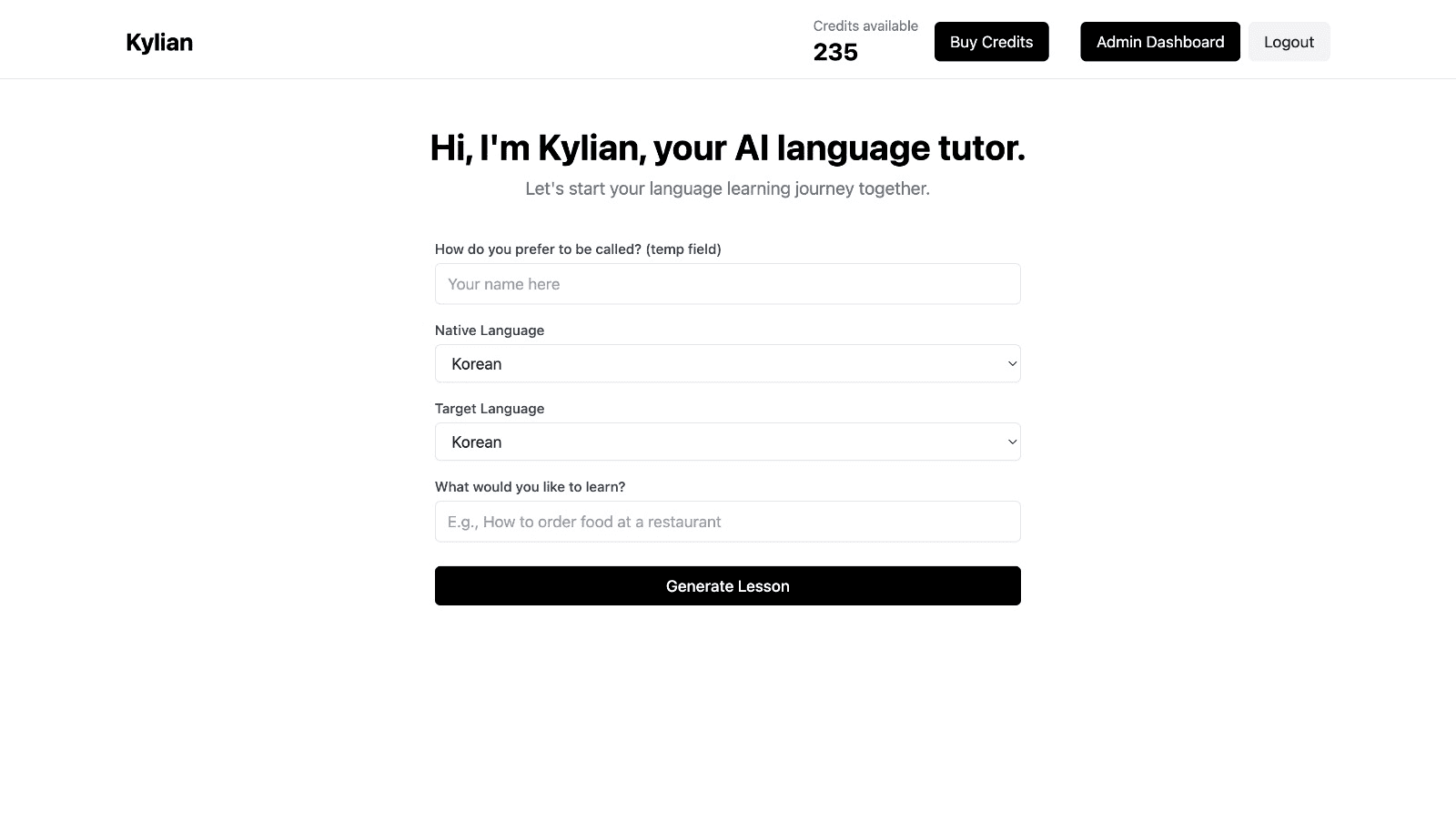
With Kylian, you’ll never again pay for irrelevant content or feel embarrassed asking “too basic” questions to a teacher. Your learning plan is entirely personalized.
Once you’ve chosen your topic, just hit the “Generate a Lesson” button, and within seconds, you’ll get a lesson designed exclusively for you.
Join the room to begin your lesson
The session feels like a one-on-one language class with a human tutor—but without the high price or time constraints.
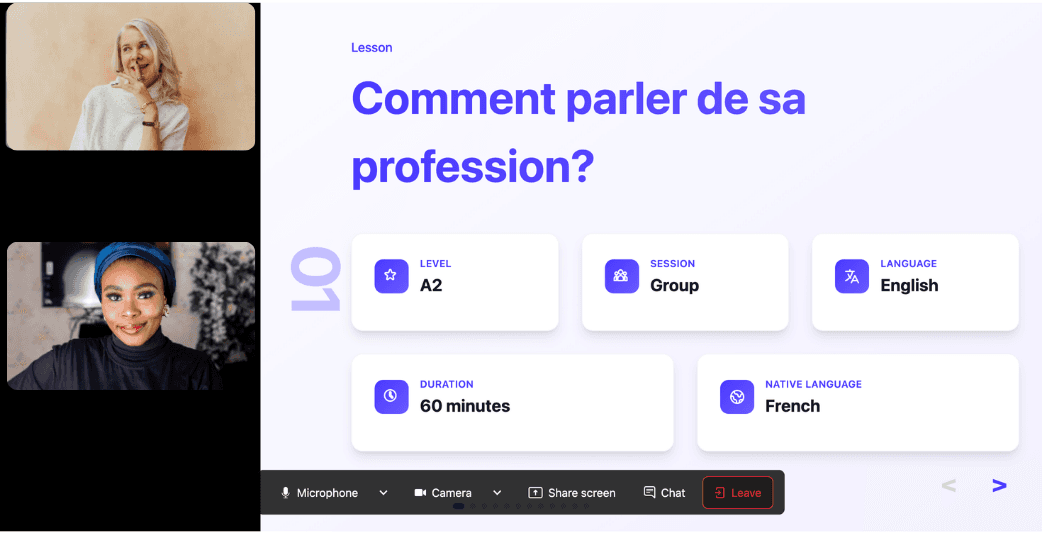
In a 25-minute lesson, Kylian teaches exactly what you need to know about your chosen topic: the nuances that textbooks never explain, key cultural differences between French and your target language, grammar rules, and much more.
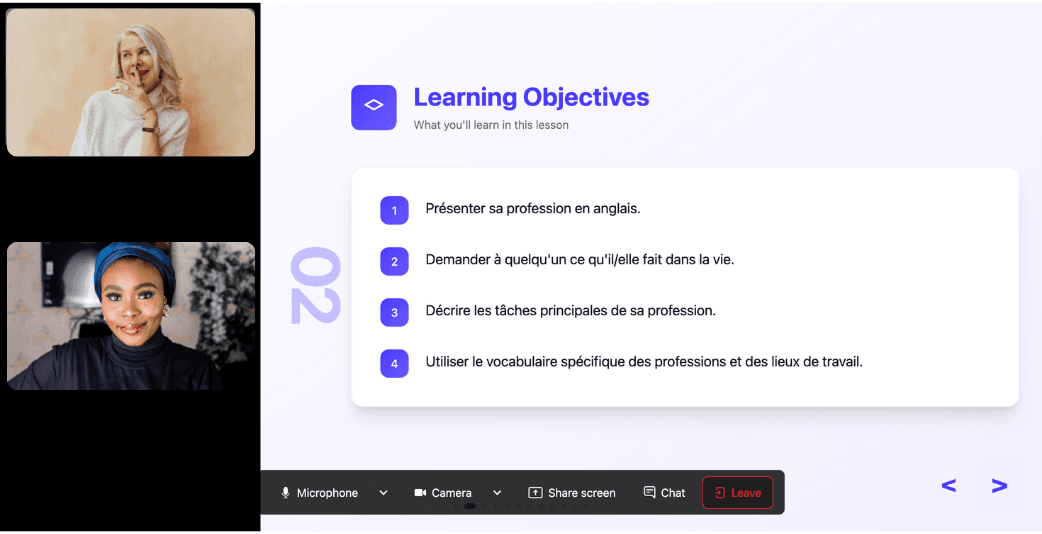
Ever felt frustrated trying to keep up with a native-speaking teacher, or embarrassed to ask for something to be repeated? With Kylian, that problem disappears. It switches intelligently between French and the target language depending on your level, helping you understand every concept at your own pace.
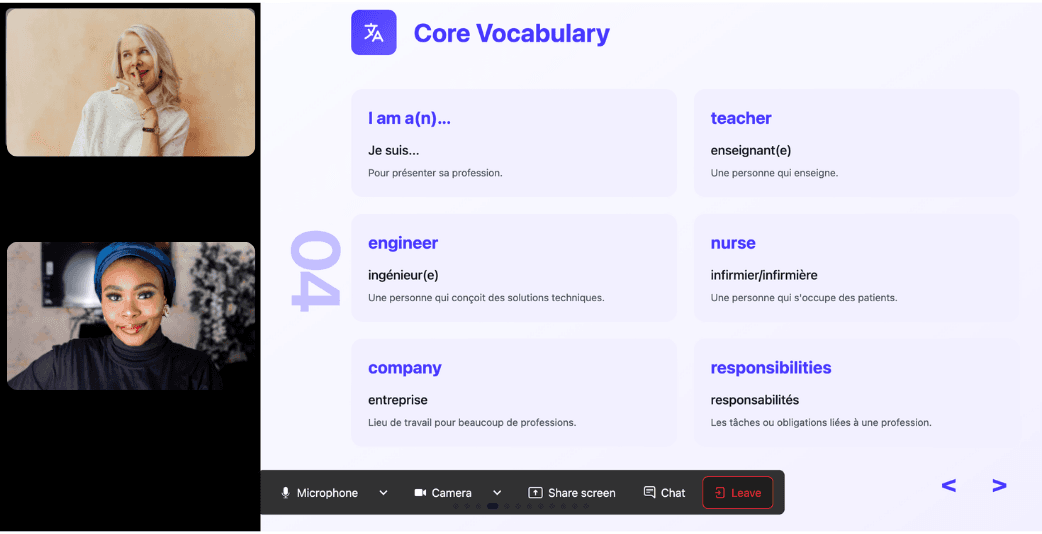
During the lesson, Kylian uses role-plays, real-life examples, and adapts to your learning style. Didn’t understand something? No problem—you can pause Kylian anytime to ask for clarification, without fear of being judged.
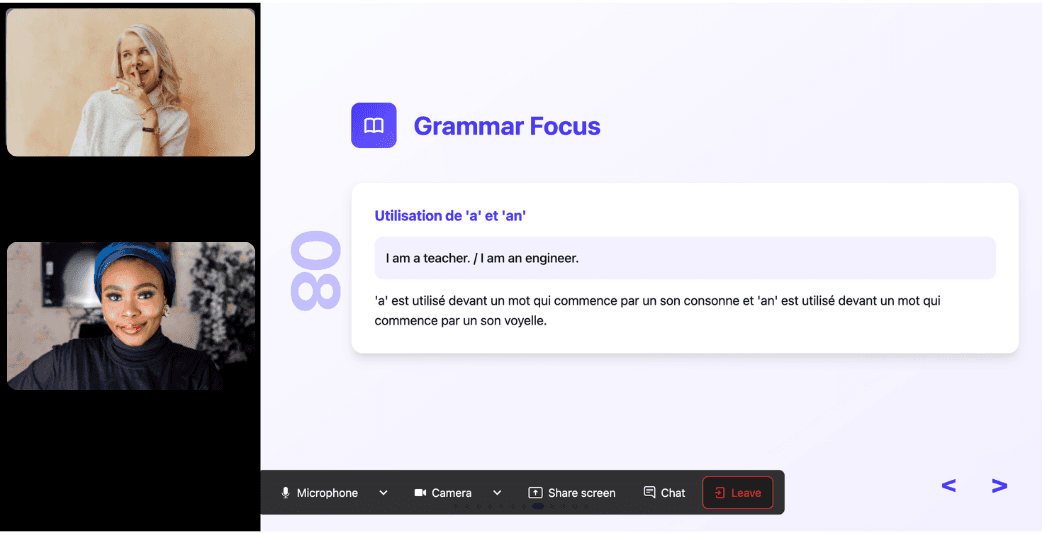
Ask all the questions you want, repeat sections if needed, and customize your learning experience in ways traditional teachers and generic apps simply can’t match.
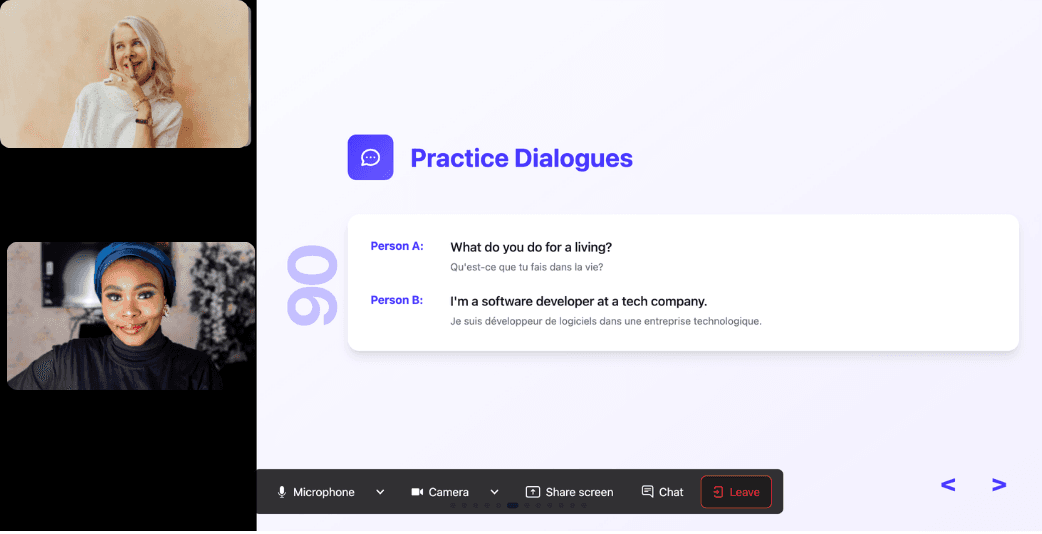
With 24/7 access at a fraction of the cost of private lessons, Kylian removes all the barriers that have kept you from mastering the language you’ve always wanted to learn.
Similar Content You Might Want To Read

Mastering English Homophones: Words That Sound Alike
When someone mentions a "bear market" while holding "bare necessities," they're leveraging a linguistic feature that often causes confusion but adds richness to English: homophones. These words that sound identical but carry entirely different meanings represent a fascinating aspect of language acquisition that merits deeper exploration. Understanding homophones isn't merely academic—it's practical. They illuminate the complexity of English while enabling more precise communication in both written and spoken contexts. By distinguishing between words like "write" and "right," you develop linguistic precision that prevents misunderstandings and enhances your language mastery. This comprehensive guide examines what homophones are, how they differ from similar linguistic phenomena, and why they matter in language acquisition. You'll discover over 100 common homophones with concise definitions and develop strategies for mastering these frequently confused terms.

Present Tense in English: Usage, Rules & Examples
When beginning your English language journey, mastering the present tense forms the foundation of your communication skills. The present tense allows you to express current actions, general facts, and recurring situations - making it essential for everyday conversations. While past and future tenses introduce additional complexity, the present tense offers a straightforward entry point into English grammar. Once you understand how to use it properly, you'll be able to discuss your daily routines, interests, and observations with confidence. Even if you already possess some English proficiency, deepening your knowledge of present tense mechanics can significantly enhance your language accuracy. This comprehensive guide explores everything you need to know about the present tense in English.

12 English Pronunciation Exercises to Perfect Your Speech
English pronunciation presents significant challenges for language learners. The inconsistent phonetic patterns, numerous exceptions to rules, and subtle sound distinctions can make achieving clear articulation difficult. However, with structured practice and effective tools, learners can make remarkable progress. This guide explores ten proven pronunciation exercises and printable resources designed to help English language learners develop clearer, more natural-sounding speech. Each approach targets specific pronunciation challenges while making the learning process engaging and measurable.

Tool Names in English: 30+ Essential Household Tools
In today's increasingly globalized world, mastering technical vocabulary becomes as critical as understanding everyday conversation. This is particularly true when it comes to household tools—objects we might not use daily but are indispensable when needed. For English language learners and native speakers alike, knowing the correct terminology for these implements is valuable knowledge. This comprehensive guide examines over 30 common household tool names in English, categorized by type and function to help you easily identify these important items whether you're shopping at a hardware store, working on a DIY project, or simply trying to communicate with a handyman.

Animal Sounds in English: How Animals Communicate
The animal kingdom resonates with a rich tapestry of sounds—from the subtle buzzing of insects to the thunderous roars of large predators. These sounds aren't merely acoustic phenomena; they're sophisticated communication tools that serve critical functions within and across species. This comprehensive guide explores the diverse range of animal sounds, their significance in both the natural world and human culture, and the specific English terminology used to describe them.

Common Business Abbreviations in English: Useful Guide
In today's fast-paced business environment, efficiency isn't just appreciated—it's expected. One subtle yet powerful way professionals streamline communication is through abbreviations. These shorthand expressions save time and space while conveying complex ideas with remarkable precision. However, encountering unfamiliar business abbreviations can create unnecessary confusion and misunderstanding. For non-native English speakers and professionals new to specific industries, this challenge can be particularly daunting. This comprehensive guide unpacks the most essential business abbreviations in English, providing clarity and context for each. Beyond mere definitions, we'll examine when and how to use these abbreviations effectively, ensuring your business communication remains both efficient and unambiguous.