What Are the 3 Dots Called? Complete Guide to Ellipsis

Written by
Ernest Bio Bogore

Reviewed by
Ibrahim Litinine

Three consecutive dots appearing in text represent one of the most misunderstood yet powerful punctuation marks in written English. These dots—formally called an ellipsis—serve critical functions that extend far beyond simple omission. Understanding their proper application distinguishes professional writing from amateur attempts.
What Is an Ellipsis?
An ellipsis consists of three periods (…) functioning as a single punctuation unit. This mark serves three primary purposes: indicating omitted material, representing pauses in dialogue, and signaling incomplete thoughts. The term derives from the Greek word "elleipsis," meaning "omission" or "falling short."
The ellipsis operates differently from other punctuation marks because it explicitly acknowledges what isn't present rather than defining what is. This unique characteristic makes it invaluable for writers who need to maintain meaning while condensing content or creating specific emotional effects.
Primary Functions of the Ellipsis
Indicating Omitted Text
The ellipsis serves as editorial shorthand when quoting sources. Rather than reproducing entire passages, writers can extract relevant portions while maintaining contextual integrity. This function proves essential in academic writing, journalism, and legal documentation.
Consider how the ellipsis transforms lengthy quotations into focused excerpts. Original text that spans multiple sentences or paragraphs can be condensed to highlight specific arguments without losing meaning. The ellipsis signals to readers that material has been removed, maintaining transparency about editorial choices.
Representing Speech Patterns
Natural conversation includes hesitations, interruptions, and trailing thoughts. The ellipsis captures these vocal patterns in written form, creating authentic dialogue that mirrors actual speech. This application appears frequently in fiction, interviews, and dramatic writing.
The ellipsis distinguishes between different types of pauses. Unlike dashes, which suggest sudden breaks or interruptions, ellipses indicate gradual fading or uncertainty. This subtle distinction affects how readers interpret character emotions and intentions.
Signaling Incomplete Thoughts
Writers use ellipses to suggest that thoughts extend beyond what's explicitly stated. This technique creates engagement by allowing readers to complete ideas mentally. The ellipsis becomes a tool for implication rather than direct statement.
This function proves particularly effective in persuasive writing, where suggesting consequences or possibilities can be more powerful than stating them directly. The ellipsis invites readers to participate in the thought process rather than passively consuming information.
Practical Applications and Examples
Academic and Professional Writing
Academic contexts require precise quotation practices. The ellipsis enables scholars to extract relevant portions from lengthy sources while maintaining scholarly integrity. Research papers, dissertations, and professional reports rely on this function to support arguments efficiently.
When incorporating ellipses in academic work, writers must ensure that omitted material doesn't alter the original meaning. The ellipsis should preserve the author's intent while serving the new context's needs.
Creative Writing and Literature
Fiction writers employ ellipses to create realistic dialogue and internal monologues. Characters who hesitate, search for words, or leave thoughts unfinished become more authentic through strategic ellipsis use. This punctuation mark helps writers show rather than tell character emotions.
Consider how ellipses can indicate various emotional states: nervousness when a character can't complete sentences, contemplation when thoughts drift, or dramatic tension when revelations remain unspoken. The ellipsis becomes a tool for character development rather than mere punctuation.
Digital Communication
Modern communication platforms have transformed ellipsis usage. Text messages, emails, and social media posts frequently employ ellipses to convey tone and emotion. However, this casual usage sometimes conflicts with formal writing standards.
The ellipsis in digital contexts can suggest passive-aggressiveness, uncertainty, or dramatic effect. Understanding these connotations helps writers choose appropriate punctuation for their intended audience and purpose.
Technical Rules and Formatting
Spacing and Typography
Standard formatting requires no spaces between the three dots of an ellipsis. However, spacing rules vary depending on style guides and publication standards. Associated Press style differs from Modern Language Association guidelines, reflecting different editorial priorities.
When an ellipsis appears at the end of a sentence, writers must decide whether to include a fourth period. This decision depends on whether the ellipsis represents omitted material or an incomplete thought. The distinction affects both appearance and meaning.
Integration with Other Punctuation
Ellipses interact with surrounding punctuation in specific ways. Commas, semicolons, and quotation marks require careful positioning relative to ellipses. These relationships affect both visual appearance and grammatical correctness.
The ellipsis can precede or follow other punctuation marks, but each combination serves different purposes. Understanding these relationships prevents confusion and maintains professional writing standards.
Common Mistakes and Misconceptions
Overuse in Formal Writing
Beginning writers often overuse ellipses, creating text that appears hesitant or unprofessional. Excessive ellipses suggest uncertainty about content rather than deliberate stylistic choice. This overuse particularly damages business writing and academic work.
Professional writing requires confidence and clarity. While ellipses serve legitimate purposes, they shouldn't become default punctuation for uncertain writers. Each ellipsis should serve a specific function rather than filling space or creating false drama.
Misunderstanding Emotional Connotations
Different audiences interpret ellipses differently. What seems dramatic to one reader might appear passive-aggressive to another. Writers must consider their audience's expectations and communication norms when employing ellipses.
Generational differences particularly affect ellipsis interpretation. Younger readers might view ellipses as normal punctuation, while older audiences might perceive them as suggesting negative emotions or uncertainty.
Incorrect Formatting
Many writers create ellipses using multiple periods with spaces between them. This formatting creates visual inconsistency and suggests unfamiliarity with proper punctuation standards. Professional writing requires attention to these details.
Word processing software often provides ellipsis characters (…) that appear as single units rather than three separate periods. Using these characters ensures consistent formatting and professional appearance.
Alternative Terms and Regional Variations
Technical Terminology
While "ellipsis" represents the standard term, various contexts employ alternative descriptions. Editorial work might reference "omission marks" or "suspension points." These variations reflect specialized usage rather than general communication.
Technical writing sometimes uses "continuation dots" or "truncation marks" to describe similar functions. These terms emphasize the ellipsis's role in indicating incomplete information rather than its punctuation status.
International Usage Patterns
English-speaking countries generally follow similar ellipsis conventions, but subtle differences exist. British English sometimes employs different spacing rules than American English. Canadian and Australian usage tends to follow British patterns with some American influences.
European languages that use ellipses might employ different spacing conventions. French typography, for example, includes spaces before ellipses. These variations matter for international communication and translation work.
The Psychology of Ellipses
Reader Engagement
Ellipses create psychological effects that extend beyond their grammatical functions. Readers unconsciously respond to the implied incompleteness, often filling gaps with their own thoughts or expectations. This participation creates stronger engagement than complete statements.
The ellipsis functions as a cognitive prompt, encouraging readers to continue thinking beyond the visible text. This effect proves particularly valuable in persuasive writing, where reader participation strengthens argument effectiveness.
Emotional Impact
Different ellipsis applications create distinct emotional responses. Ellipses suggesting hesitation evoke different feelings than those indicating omitted text. Writers who understand these psychological effects can manipulate reader emotions more effectively.
The timing and placement of ellipses within sentences affects their emotional impact. Ellipses at sentence beginnings create different effects than those at endings. These subtle variations require careful consideration during the writing process.
Digital Age Considerations
Platform-Specific Usage
Social media platforms have developed their own ellipsis conventions. Twitter's character limits encourage ellipsis use for brevity, while professional platforms like LinkedIn require more formal approaches. Understanding platform expectations prevents communication failures.
Mobile device keyboards often include ellipsis shortcuts, making this punctuation more accessible than traditional typing methods. This accessibility has increased ellipsis usage across all writing forms, not always appropriately.
Evolution of Meaning
Digital communication has expanded ellipsis meanings beyond traditional grammar rules. Texting culture uses ellipses to indicate typing pauses, thinking time, or dramatic effect. These new applications sometimes conflict with formal writing standards.
The ellipsis has evolved from purely grammatical tool to emotional expression mechanism. This evolution reflects broader changes in written communication as digital platforms replace traditional correspondence.
Best Practices for Effective Ellipsis Use
Context-Appropriate Application
Successful ellipsis use requires understanding context and audience expectations. Academic writing demands different approaches than creative fiction or casual communication. Writers must match their ellipsis usage to their specific communication goals.
Consider the document's purpose, audience sophistication, and communication medium when deciding whether to employ ellipses. Each context creates different expectations and interpretive frameworks.
Strategic Placement
Effective ellipsis placement enhances meaning rather than creating confusion. The punctuation should serve the sentence's purpose while maintaining clarity. Random or excessive ellipsis use diminishes rather than strengthens communication effectiveness.
Writers should evaluate each potential ellipsis location for its contribution to overall meaning. If the ellipsis doesn't add value or clarity, standard punctuation probably serves better.
Learn Any Language with Kylian AI
Private language lessons are expensive. Paying between 15 and 50 euros per lesson isn’t realistic for most people—especially when dozens of sessions are needed to see real progress.
Many learners give up on language learning due to these high costs, missing out on valuable professional and personal opportunities.
That’s why we created Kylian: to make language learning accessible to everyone and help people master a foreign language without breaking the bank.
To get started, just tell Kylian which language you want to learn and what your native language is
Tired of teachers who don’t understand your specific struggles as a French speaker? Kylian’s advantage lies in its ability to teach any language using your native tongue as the foundation.
Unlike generic apps that offer the same content to everyone, Kylian explains concepts in your native language (French) and switches to the target language when necessary—perfectly adapting to your level and needs.
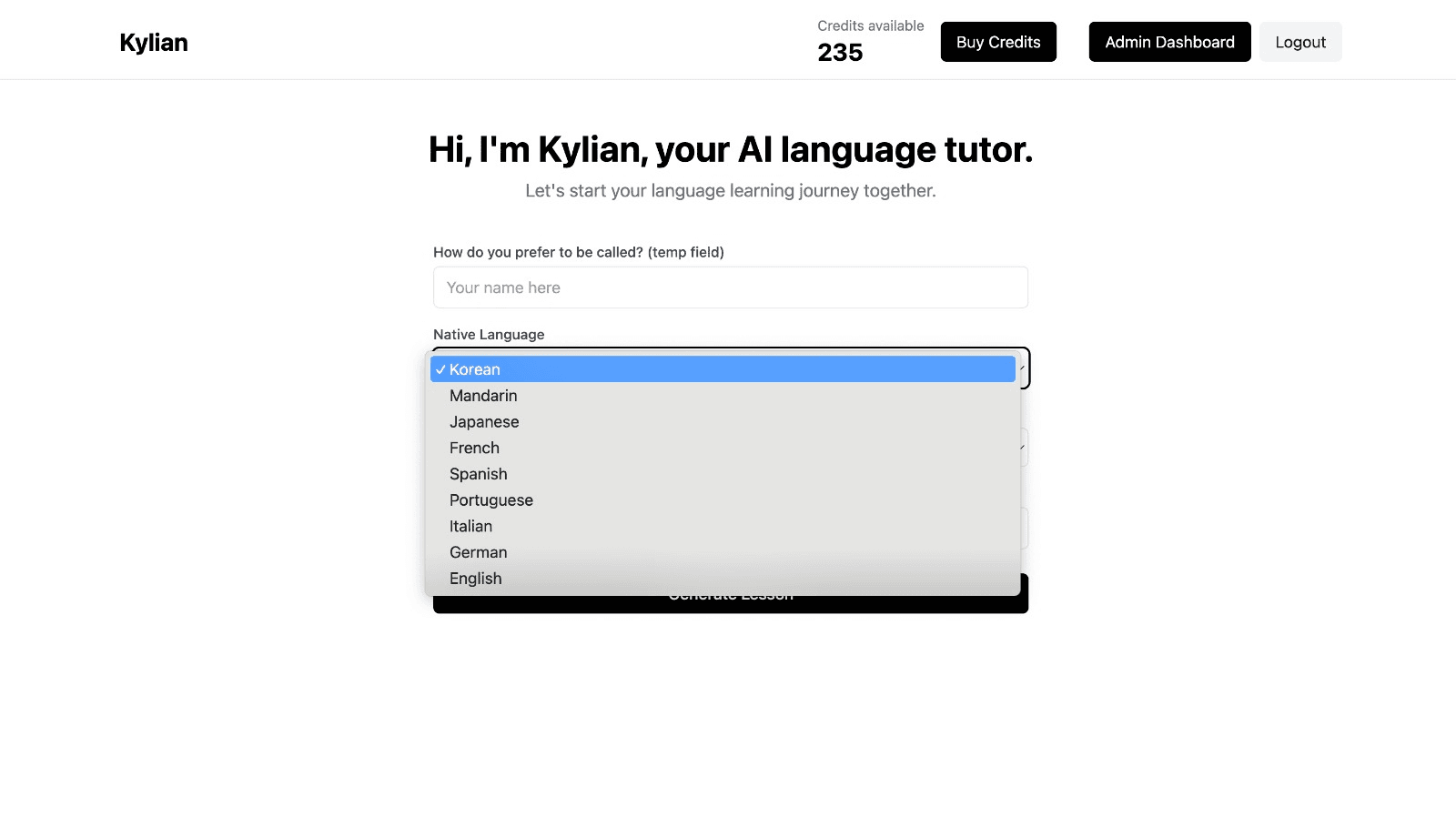
This personalization removes the frustration and confusion that are so common in traditional language learning.
Choose a specific topic you want to learn
Frustrated by language lessons that never cover exactly what you need? Kylian can teach you any aspect of a language—from pronunciation to advanced grammar—by focusing on your specific goals.
Avoid vague requests like “How can I improve my accent?” and be precise: “How do I pronounce the R like a native English speaker?” or “How do I conjugate the verb ‘to be’ in the present tense?”
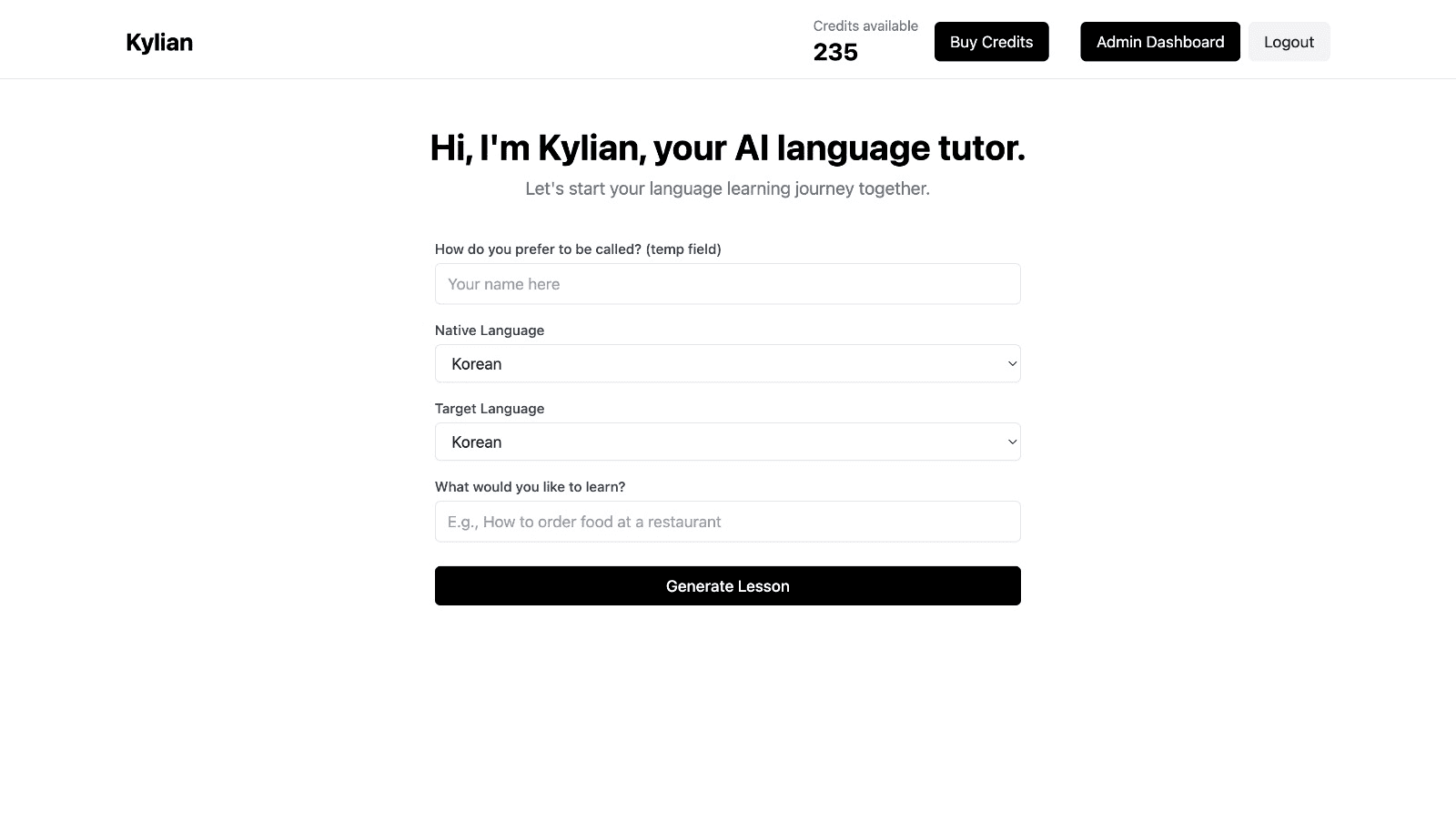
With Kylian, you’ll never again pay for irrelevant content or feel embarrassed asking “too basic” questions to a teacher. Your learning plan is entirely personalized.
Once you’ve chosen your topic, just hit the “Generate a Lesson” button, and within seconds, you’ll get a lesson designed exclusively for you.
Join the room to begin your lesson
The session feels like a one-on-one language class with a human tutor—but without the high price or time constraints.
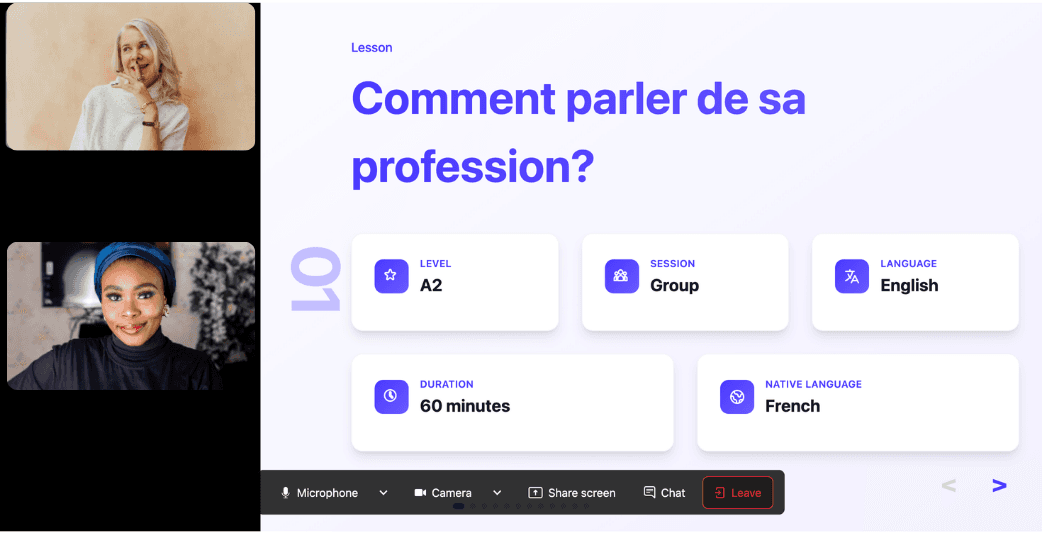
In a 25-minute lesson, Kylian teaches exactly what you need to know about your chosen topic: the nuances that textbooks never explain, key cultural differences between French and your target language, grammar rules, and much more.
Ever felt frustrated trying to keep up with a native-speaking teacher, or embarrassed to ask for something to be repeated? With Kylian, that problem disappears. It switches intelligently between French and the target language depending on your level, helping you understand every concept at your own pace.
During the lesson, Kylian uses role-plays, real-life examples, and adapts to your learning style. Didn’t understand something? No problem—you can pause Kylian anytime to ask for clarification, without fear of being judged.
Ask all the questions you want, repeat sections if needed, and customize your learning experience in ways traditional teachers and generic apps simply can’t match.
With 24/7 access at a fraction of the cost of private lessons, Kylian removes all the barriers that have kept you from mastering the language you’ve always wanted to learn.
Similar Content You Might Want To Read

Direct and Indirect Speech: Rules for Clear Communication
Mastering the difference between direct and indirect speech represents a crucial milestone for anyone seeking proficiency in English grammar. These two speech forms govern how we report conversations and statements, dramatically influencing meaning, tone, and impact. Understanding when and how to convert between them enables more sophisticated writing and speaking abilities while preventing misrepresentation of others' words.

Applications For vs. In : Core Differences (English)
The prepositions "for" and "in" may appear interchangeable when discussing applications in relation to English, but they create substantially different meanings that reflect distinct conceptual relationships. This comprehensive analysis examines the semantic, grammatical, and practical distinctions between "applications FOR English" and "applications IN English," providing language learners and educators with precise understanding of these prepositions in context.

Learning Professional English: Phone Communication Skills
Phone conversations remain a critical professional skill, despite our increasing reliance on text-based communication. For non-native English speakers, these calls can be particularly challenging without the visual cues of face-to-face interaction. This comprehensive guide provides practical strategies to enhance your professional phone communication in English.

60 English Verbs for Beginners: Building Your Foundation
Learning English requires a strategic approach. When faced with thousands of words to memorize, knowing which ones to prioritize makes all the difference in your progress. Verbs—the action words that drive your sentences—form the backbone of effective communication. Master the right ones first, and you'll achieve conversational ability much faster.

Better Ways to Say "I Like" and "I Don't Like" in English
Do you find yourself repeatedly using the same phrases to express your preferences? The ability to articulate what you enjoy or dislike with precision and variety not only enriches your conversations but also demonstrates language proficiency. This article explores alternative expressions to the common "I like" and "I don't like" statements, providing you with a diverse vocabulary arsenal to communicate your preferences more effectively.

What Does Self-Contradiction Mean & How To Stay Clear?
Communication demands precision. When we express ideas that clash with our previous statements—knowingly or unknowingly—we contradict ourselves. This inconsistency undermines our credibility and confuses our audience. But what exactly constitutes contradiction in language, and why does recognizing it matter so critically for effective communication? Contradictions permeate daily conversations, professional communications, and public discourse. They appear in casual discussions ("I never eat junk food," said while eating chips), academic papers with inconsistent arguments, and political statements that reverse previous positions. These logical fractures disrupt trust and clarity—the foundation of meaningful exchange. This comprehensive analysis delves into the nature of contradictions—their definition, types, causes, detection methods, and avoidance strategies. Understanding contradiction transcends mere linguistic competence; it represents a fundamental aspect of critical thinking and effective expression in English.