What is the Meaning of Thee, Thou, and Thy in English?

Written by
Ernest Bio Bogore

Reviewed by
Ibrahim Litinine

In today's rapidly evolving linguistic landscape, we often encounter archaic expressions in classical literature that seem foreign to our modern understanding. Among these linguistic relics, the pronouns "thee," "thou," and "thy" stand as fascinating vestiges of Old English that continue to mystify contemporary readers. This article delves into the historical significance, grammatical functions, and contextual applications of these archaic pronouns, offering valuable insights for language enthusiasts and students alike.
The Historical Context of Thee, Thou, and Thy
Before the standardization of Modern English, pronouns followed a more complex system that distinguished between formal and informal address. "Thee," "thou," and "thy" originated from Old English and Middle English periods, serving as second-person singular pronouns that gradually fell out of common usage by the 18th century.
The historical trajectory of these pronouns reveals much about social dynamics in medieval and Early Modern England. Initially, "thou" was the standard form of address for all individuals, regardless of social standing. However, as social hierarchies became more rigid during the Middle Ages, "you" emerged as the formal variant, while "thou" became reserved for informal situations or addressing social inferiors.
This linguistic evolution mirrored similar developments in other European languages that maintain formal/informal distinctions, such as the French "tu/vous" or the German "du/Sie." However, English eventually abandoned this distinction, with "you" becoming the universal second-person pronoun in both formal and informal contexts.
Grammatical Functions: Understanding the Differences
To truly grasp the meaning and appropriate usage of these pronouns, we must understand their distinct grammatical functions:
- Thou: Functions as the subject form (nominative case) in a sentence, equivalent to modern "you" when used as a subject.
- Thee: Serves as the object form (objective case), used when the pronoun receives the action of a verb or follows a preposition.
- Thy/Thine: Represent possessive forms, with "thy" used before consonants and "thine" before vowels or the letter 'h' - similar to how we use "a" and "an" in modern English.
This systematic grammatical structure follows patterns that once governed all English pronouns, making them less arbitrary than they might initially appear to modern readers.
Illustrative Examples in Context
To illuminate these distinctions, consider these examples that demonstrate the proper usage of each form:
Subject Form (Thou):
- "Thou hast completed thy task admirably." (Modern: You have completed your task admirably.)
- "Whither goest thou this fine morning?" (Modern: Where are you going this fine morning?)
Object Form (Thee):
- "The king has summoned thee to court." (Modern: The king has summoned you to court.)
- "This message was written for thee." (Modern: This message was written for you.)
Possessive Forms (Thy/Thine):
- "Thy wisdom exceeds thy years." (Modern: Your wisdom exceeds your years.)
- "Thine eyes reflect the stars above." (Modern: Your eyes reflect the stars above.)
These examples demonstrate how these pronouns functioned within the grammatical framework of Early Modern English, providing essential context for readers encountering them in historical texts.
Where You'll Encounter These Pronouns Today
Although "thee," "thou," and "thy" have largely disappeared from everyday English usage, they persist in several specific contexts that merit attention:
1. Religious Texts and Settings
The King James Bible, first published in 1611, extensively employs these archaic pronouns, particularly when addressing God. Many traditional prayers, hymns, and religious ceremonies continue to use this form of address, creating a sense of reverence and historical continuity.
2. Literary Works
Shakespeare's plays and sonnets feature these pronouns prominently, using them to indicate relationships between characters and social dynamics. Other literary works from the Early Modern period likewise employ these forms, making familiarity with them essential for students of literature.
3. Historical and Regional Dialects
Interestingly, certain English dialects, particularly in parts of Yorkshire, Lancashire, and among some Quaker communities, preserved these pronoun forms well into the 19th and even 20th centuries. Some rural communities maintained these linguistic features as part of their distinctive regional identity.
4. Contemporary Artistic Expression
Modern poets, novelists, and songwriters occasionally incorporate these archaic pronouns to evoke historical settings, create a sense of formality, or simply add artistic flavor to their work. Fantasy literature, historical fiction, and certain musical genres regularly draw upon this linguistic heritage.
Modern Equivalents and Translation Guide
For clarity, here's a comprehensive guide to translating between archaic and modern pronouns:
- Thou: Used as a subject - equivalent to modern "you" when used as a subject
- Thee: Used as an object - equivalent to modern "you" when used as an object
- Thy: Possessive form used before consonants - equivalent to modern "your"
- Thine: Possessive form used before vowels or 'h' - equivalent to modern "your" or "yours"
- Ye: Used as a plural subject - equivalent to modern plural "you"
This equivalence framework helps readers navigate historical texts with greater confidence and precision.
The Sociolinguistic Dimension: Formality and Intimacy
Beyond mere grammatical differences, these pronouns carried significant social implications in their historical context. "Thou" often indicated familiarity, intimacy, or sometimes condescension, while "you" signaled respect, distance, or formality.
Shakespeare masterfully exploited this distinction to reveal character relationships. In his plays, shifts between "thou" and "you" often mark crucial developments in relationships or power dynamics between characters. For instance, a character might address another as "you" in public but switch to the more intimate "thou" in private settings.
This nuanced sociolinguistic dimension adds layers of meaning that modern English, with its single second-person pronoun, cannot readily convey without additional context.
Grammatical Rules for Verb Conjugation
Another complexity of these archaic pronouns involves verb conjugation. When using "thou," verbs typically take a distinctive ending, usually -est or -st:
- Thou walkest (You walk)
- Thou speakest (You speak)
- Thou dost (You do)
- Thou hast (You have)
For irregular verbs:
- Thou art (You are)
- Thou wilt (You will)
- Thou canst (You can)
These conjugation patterns must be mastered to construct grammatically correct sentences using these archaic forms.
Practical Applications for Language Learners
Understanding these archaic pronouns offers several practical benefits for language learners:
- Enhanced Comprehension of Classical Literature: Familiarity with these pronouns unlocks deeper appreciation of works by Shakespeare, Milton, and other canonical authors.
- Historical Linguistic Perspective: These pronouns provide insight into how English has evolved over centuries, illustrating broader patterns of language change.
- Creative Writing Applications: For those interested in historical fiction, fantasy writing, or poetry, mastering these forms enables more authentic and nuanced expression.
- Comparative Linguistic Understanding: The thou/you distinction helps English speakers better understand similar distinctions in other languages like French, Spanish, or German.
Common Misconceptions and Errors
Several misconceptions about these archaic pronouns persist in popular understanding:
- The Formality Misconception: Many incorrectly assume that "thee" and "thou" were always formal or reverent forms, when historically they were actually the informal, familiar forms.
- Inconsistent Usage: Even within historical texts, usage wasn't always consistent, reflecting the transitional nature of language during the Early Modern period.
- Pronunciation Confusion: Modern readers often mispronounce these terms, not realizing that "thee" rhymed with "see," and "thou" with "now."
- Overuse of "Thine": Many incorrectly use "thine" before all words, not just those beginning with vowels or 'h'.
Addressing these misconceptions helps modern readers approach historical texts with greater accuracy and confidence.
Test Your Understanding: Practice Exercises
To solidify your grasp of these archaic pronouns, try completing these sentences with the correct form:
- _____ must complete the task before sunset. (Subject form)
- The knight presented the sword to _____. (Object form)
- _____ courage inspires all who know thee. (Possessive form)
- I shall remember _____ always. (Object form)
- _____ opinion matters greatly to the council. (Possessive form)
Answers: 1. Thou, 2. thee, 3. Thy, 4. thee, 5. Thy
The Enduring Relevance of Archaic Pronouns
Though seemingly obsolete, these pronouns continue to enrich our linguistic landscape in meaningful ways:
- Cultural Preservation: They maintain connections to our literary and cultural heritage.
- Linguistic Diversity: They remind us of the historical richness and evolution of English.
- Expressive Potential: They offer stylistic options for creative and artistic expression that modern pronouns cannot provide.
- Educational Value: They serve as valuable tools for teaching language history and grammatical concepts.
Learn Any Language with Kylian AI
Private language lessons are expensive. Paying between 15 and 50 euros per lesson isn’t realistic for most people—especially when dozens of sessions are needed to see real progress.
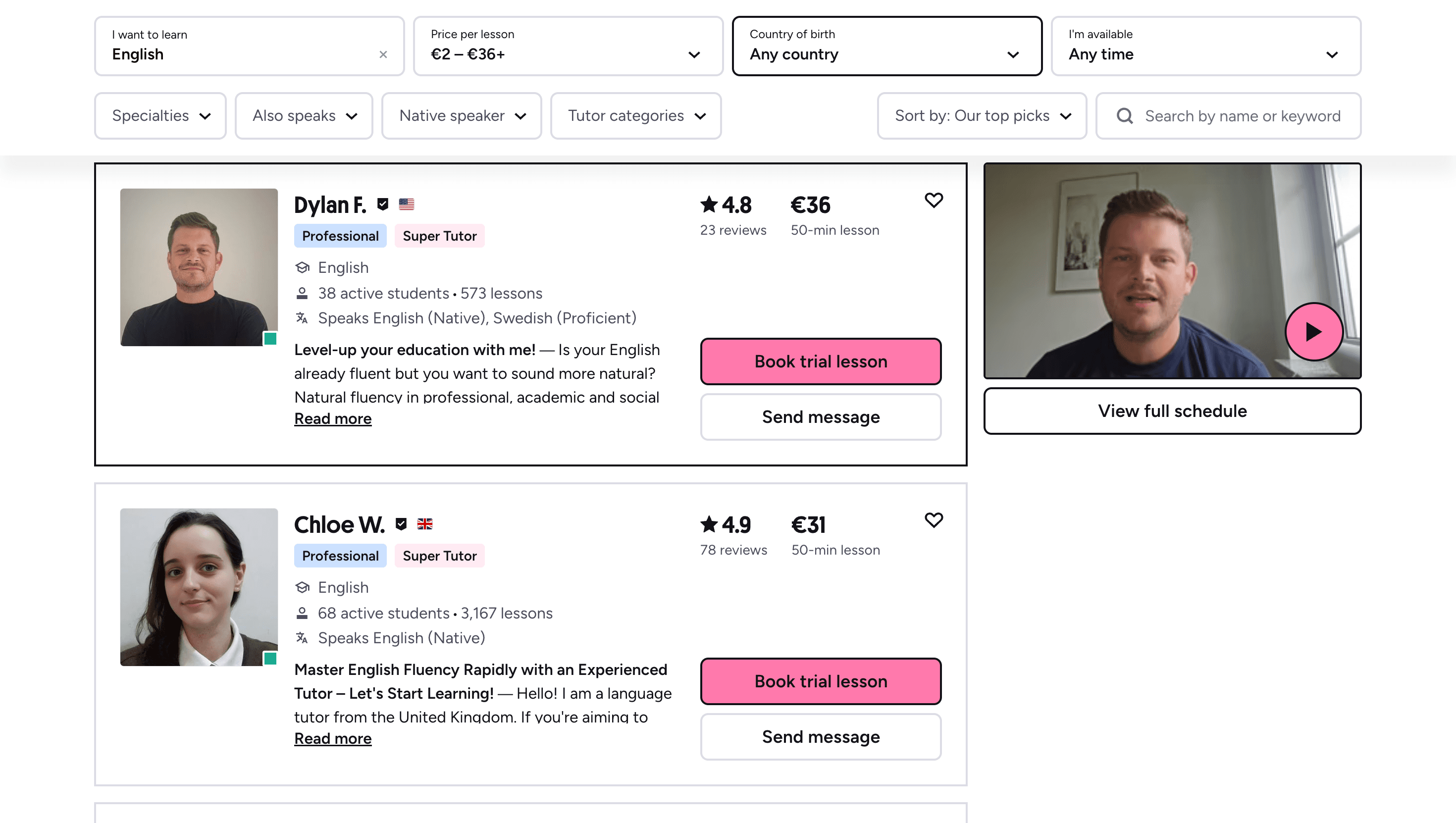
Many learners give up on language learning due to these high costs, missing out on valuable professional and personal opportunities.
That’s why we created Kylian: to make language learning accessible to everyone and help people master a foreign language without breaking the bank.
To get started, just tell Kylian which language you want to learn and what your native language is
Tired of teachers who don’t understand your specific struggles as a French speaker? Kylian’s advantage lies in its ability to teach any language using your native tongue as the foundation.
Unlike generic apps that offer the same content to everyone, Kylian explains concepts in your native language (French) and switches to the target language when necessary—perfectly adapting to your level and needs.
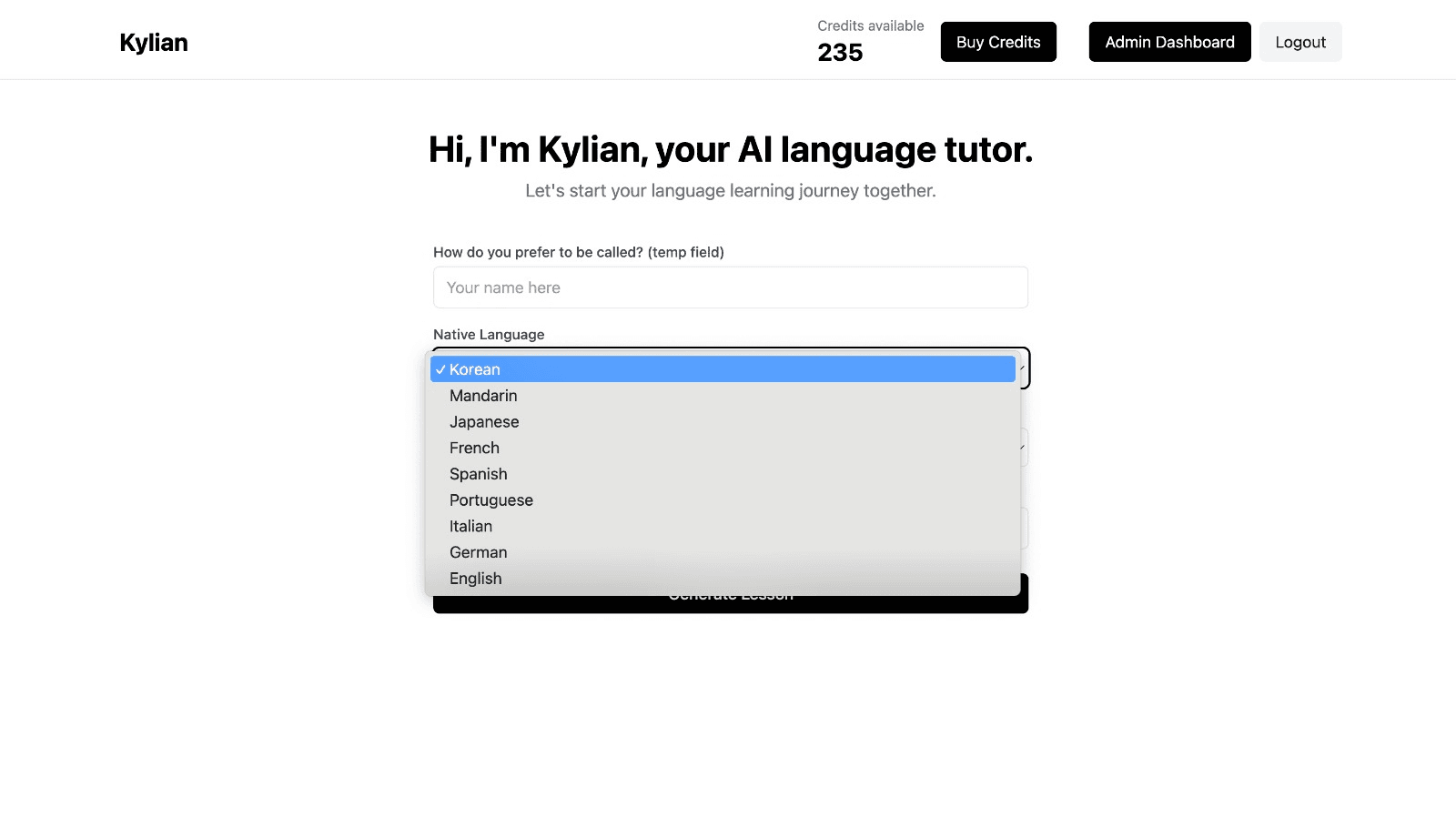
This personalization removes the frustration and confusion that are so common in traditional language learning.
Choose a specific topic you want to learn
Frustrated by language lessons that never cover exactly what you need? Kylian can teach you any aspect of a language—from pronunciation to advanced grammar—by focusing on your specific goals.
Avoid vague requests like “How can I improve my accent?” and be precise: “How do I pronounce the R like a native English speaker?” or “How do I conjugate the verb ‘to be’ in the present tense?”
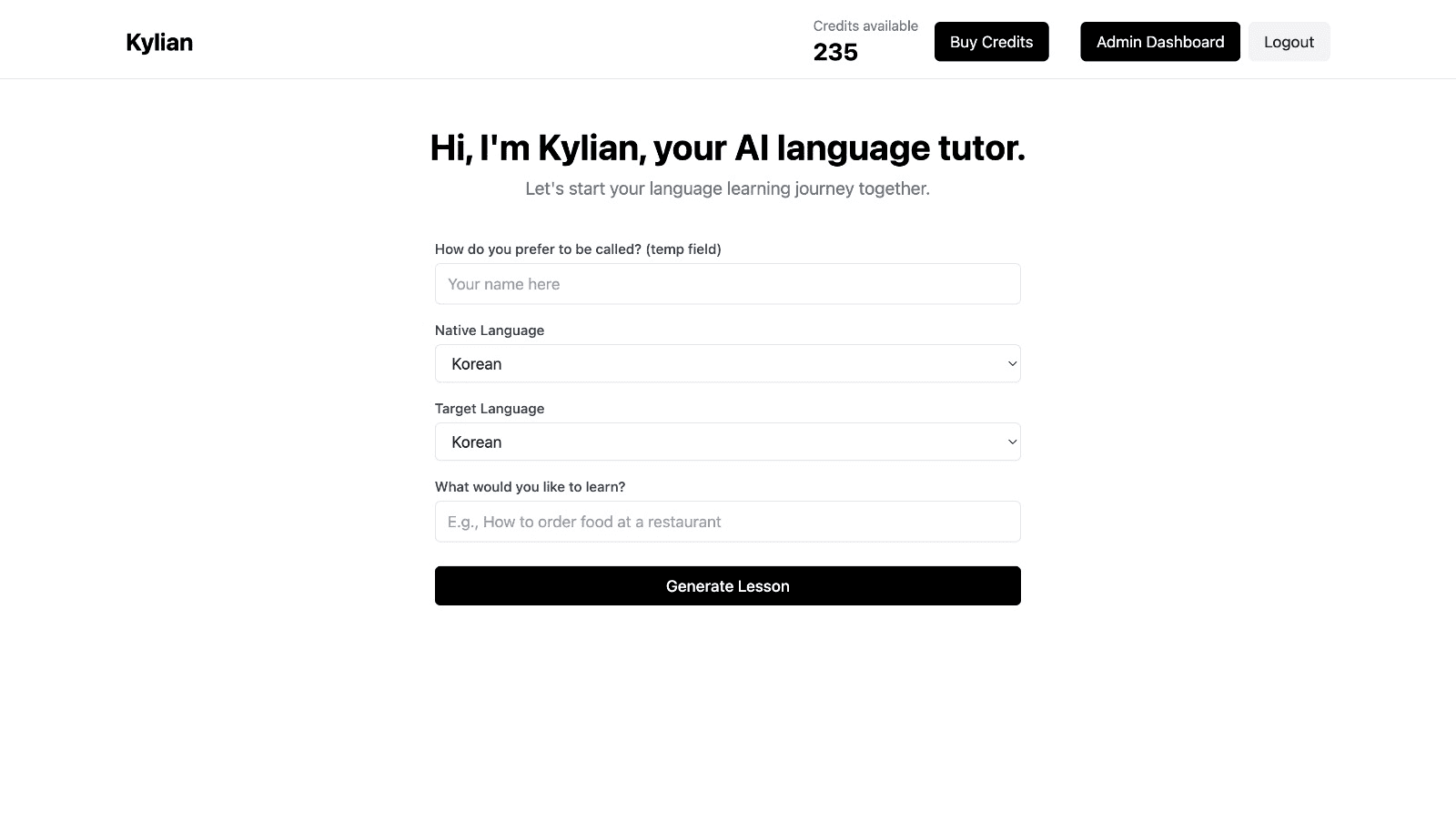
With Kylian, you’ll never again pay for irrelevant content or feel embarrassed asking “too basic” questions to a teacher. Your learning plan is entirely personalized.
Once you’ve chosen your topic, just hit the “Generate a Lesson” button, and within seconds, you’ll get a lesson designed exclusively for you.
Join the room to begin your lesson
The session feels like a one-on-one language class with a human tutor—but without the high price or time constraints.
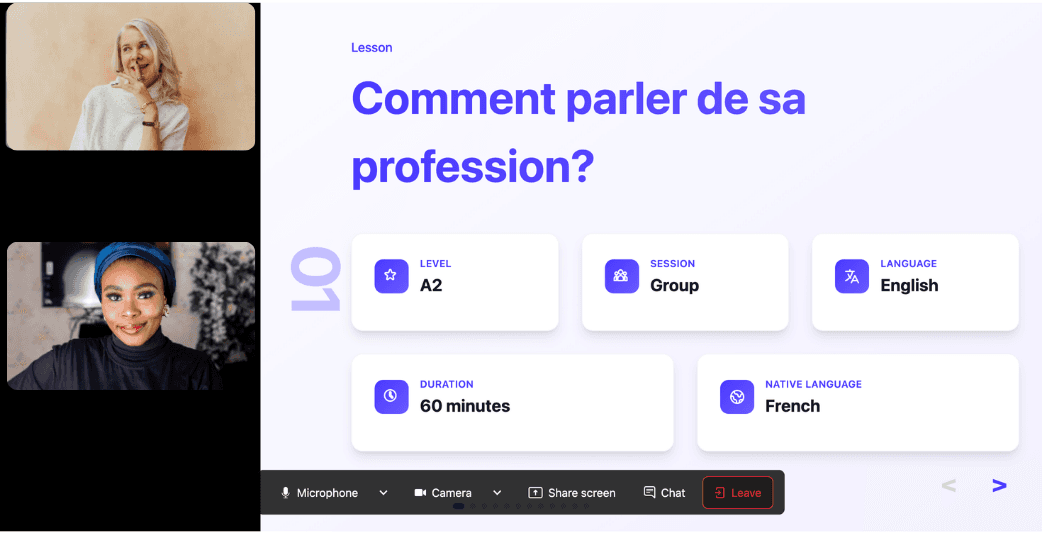
In a 25-minute lesson, Kylian teaches exactly what you need to know about your chosen topic: the nuances that textbooks never explain, key cultural differences between French and your target language, grammar rules, and much more.
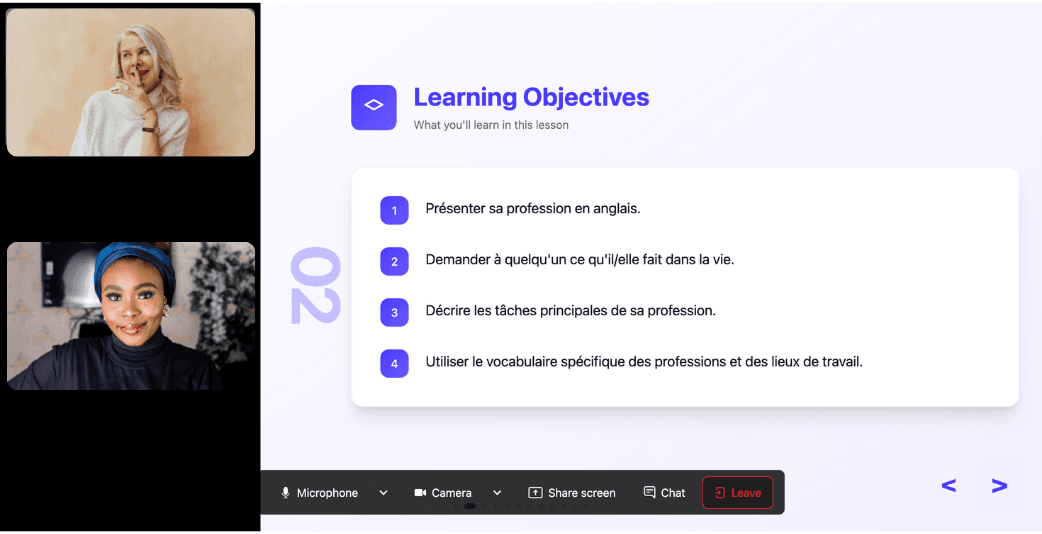
Ever felt frustrated trying to keep up with a native-speaking teacher, or embarrassed to ask for something to be repeated? With Kylian, that problem disappears. It switches intelligently between French and the target language depending on your level, helping you understand every concept at your own pace.
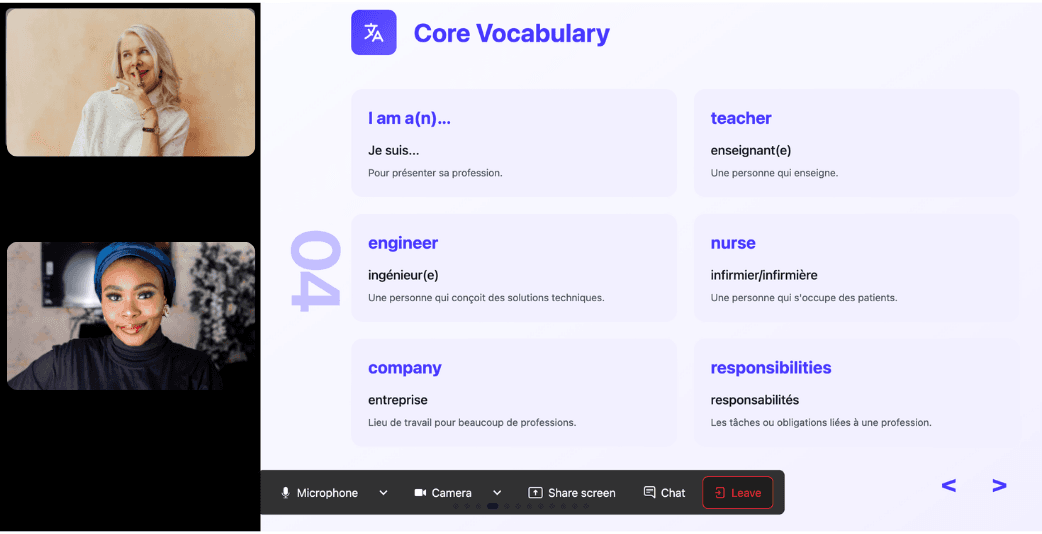
During the lesson, Kylian uses role-plays, real-life examples, and adapts to your learning style. Didn’t understand something? No problem—you can pause Kylian anytime to ask for clarification, without fear of being judged.
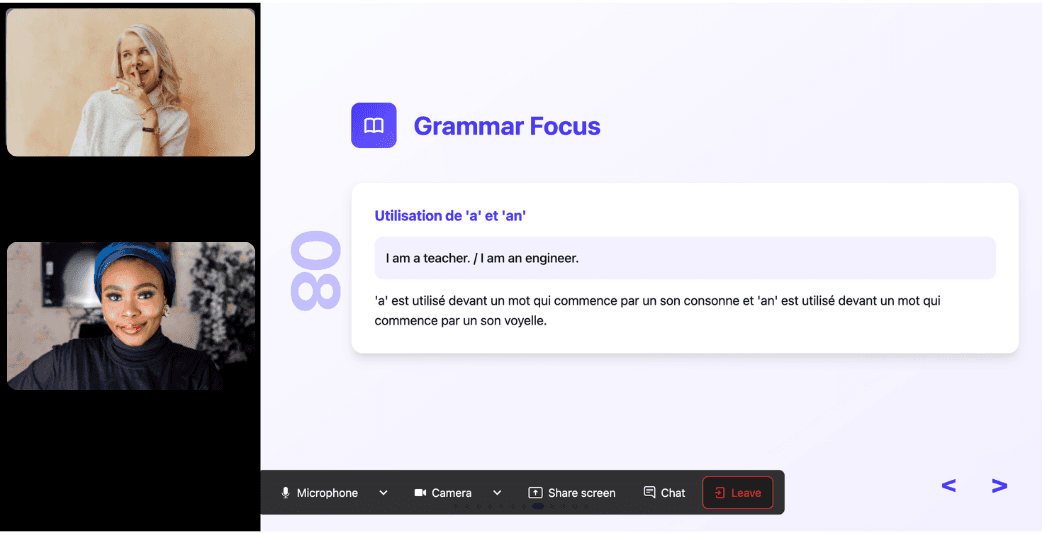
Ask all the questions you want, repeat sections if needed, and customize your learning experience in ways traditional teachers and generic apps simply can’t match.
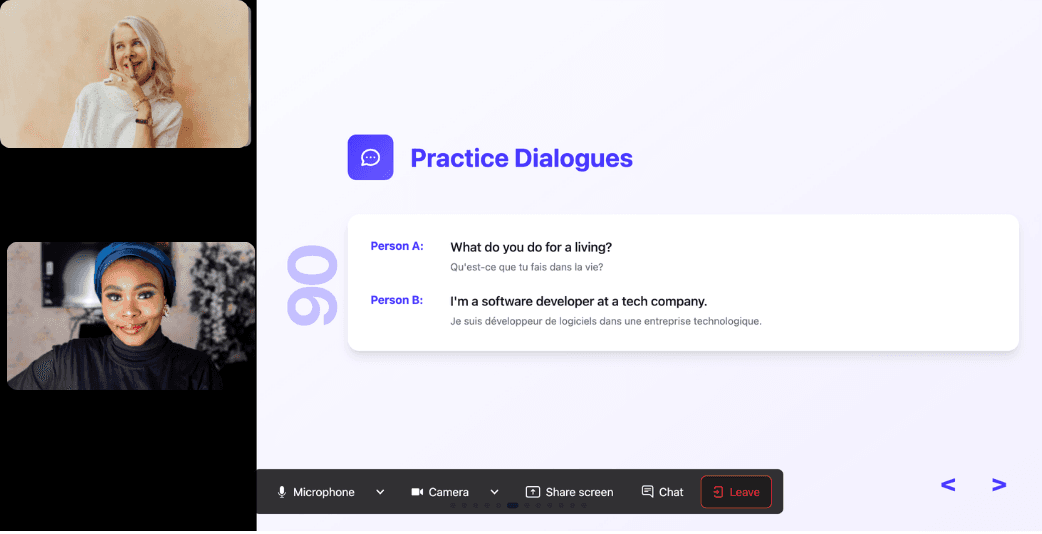
With 24/7 access at a fraction of the cost of private lessons, Kylian removes all the barriers that have kept you from mastering the language you’ve always wanted to learn.
Similar Content You Might Want To Read

English Diphthongs: Examples and Pronunciation Guide
Are you finding English pronunciation challenging because of those blended vowel sounds? Many language learners struggle with diphthongs—these complex vowel combinations that native speakers articulate effortlessly. Mastering these sounds is crucial for achieving fluency and natural-sounding speech in English. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore what diphthongs are, analyze all eight diphthong sounds in English with practical examples, and provide evidence-based strategies to help you pronounce them correctly. By the end, you'll have the knowledge and tools to approach these challenging sounds with confidence.

Common English Suffixes: The Word-Building Guide
In the complex architecture of the English language, suffixes serve as critical building blocks that transform basic words into sophisticated expressions. By mastering these word endings, you can exponentially expand your vocabulary without memorizing thousands of separate terms. This guide explores the most common English suffixes, their functions, and practical strategies to incorporate them into your linguistic toolkit.

5 English Struggles for Spanish Speakers & Fixes
Learning English presents unique challenges for Spanish speakers, yet thousands have successfully achieved fluency by addressing specific linguistic hurdles. Understanding these challenges is the first step toward mastering English effectively.

7 Must-Know English Idioms About Memory
Memory forms the backbone of language acquisition. As English learners navigate the complex landscape of grammar rules, vocabulary, and idiomatic expressions, they often experience moments when previously learned information suddenly becomes inaccessible. This phenomenon—where knowledge seems to vanish precisely when needed most—affects countless language learners worldwide. Does this experience resonate with you? Learning English demands significant cognitive resources. You must internalize countless grammatical structures, memorize vocabulary, and understand cultural contexts. The process requires not just rote memorization but also practical application to cement these linguistic elements in your long-term memory. When discussing memory challenges or celebrating recall successes in English, having specific idiomatic expressions at your disposal enhances both fluency and authenticity in conversation. This article examines seven fundamental English idioms about memory, providing clear explanations and practical examples to incorporate into your everyday English usage.

English Prepositions: Types, Usage & Common Mistakes
Mastering English prepositions is essential for fluent communication, yet these small words often cause significant confusion for language learners. Why? Because prepositions form the connective tissue of English sentences, showing relationships between words in ways that don't always follow predictable patterns. This comprehensive guide will help you understand, learn, and correctly use the wide variety of English prepositions.

30 Must-Know English Proverbs for Language Learners
Mastering proverbs is a fundamental aspect of advanced language acquisition. These concise expressions of wisdom not only enrich your vocabulary but provide invaluable cultural insights that textbooks often fail to capture. For English language learners, understanding the most common proverbs is crucial for achieving authentic communication.