What’s the Plural of Ox? Irregular Forms Explained

Written by
Ernest Bio Bogore

Reviewed by
Ibrahim Litinine

Language evolves constantly, carrying with it fragments of historical linguistic patterns that sometimes defy modern conventions. The plural form of "ox" stands as one such linguistic artifact—a reminder of English's complex evolutionary path and its Germanic roots. Understanding these irregular plural patterns offers critical insights into how language formation operates and why certain words retain their distinctive characteristics across centuries.
What Is the Plural of Ox?
The standard plural form of "ox" is "oxen." This irregular plural formation differs from the typical English pattern of adding "-s" or "-es" to form plurals. When referring to multiple ox animals, the correct term is "oxen," not "oxes."
Examples:
- One ox is pulling the cart.
- Three oxen are grazing in the field.
- The farmer owns five oxen.
This irregular plural formation represents one of English's linguistic fossils—preserving an ancient Germanic plural pattern that has largely disappeared from modern usage.
Why Is "Oxen" the Plural of "Ox"?
The "-en" plural ending in "oxen" originates from Old English, where many nouns formed their plurals using this suffix. This grammatical pattern stems from Proto-Germanic languages, specifically the weak noun declension system.
In Old English (approximately 450-1100 CE), many nouns followed this pattern:
- oxa (singular) → oxan (plural)
As English evolved through Middle English into Modern English, most irregular plural forms disappeared through a process called regularization. Most nouns that once used the "-en" suffix eventually adopted the standard "-s" plural pattern. However, "oxen" persisted, resisting this linguistic shift.
Linguistic historians attribute this persistence to several factors:
- The cultural significance of oxen in agricultural societies
- The word's frequent usage in everyday speech during formative periods of English
- Its appearance in important religious and literary texts that helped preserve older forms
This preservation of an archaic form provides valuable insight into how certain words can resist broader linguistic change patterns.
Other Words That End in "-en" in the Plural
While "oxen" stands as the most prominent example of the "-en" plural suffix in modern English, a few other words retain this pattern, though some have become increasingly archaic:
- Child → Children (with an additional phonological change)
- Brother → Brethren (in religious contexts only; otherwise "brothers")
- Sister → Sistren (archaic, now primarily used in specific religious or feminist contexts)
Historically, many more English nouns followed this pattern:
- Eye → Eyen (now "eyes")
- Shoe → Shoen (now "shoes")
- Knee → Kneen (now "knees")
- Bee → Been (now "bees")
- House → Housen (now "houses")
The gradual disappearance of these forms demonstrates how language standardization processes typically favor regular patterns, with only a few exceptional cases surviving.
Old English Plurals: A Brief History
The "-en" suffix represents just one of several plural formation patterns that existed in Old English. Understanding this historical context helps explain why certain words maintain their irregular forms.
Old English featured a complex noun classification system with multiple declension patterns, each with distinct ways of forming plurals:
- Strong masculine nouns: Often used no ending or a vowel change (umlaut)
- stān (stone) → stānas (stones)
- Strong feminine nouns: Typically added -a or -e
- gief (gift) → giefa (gifts)
- Strong neuter nouns: Often used no ending for short stems
- scip (ship) → scip (ships)
- Weak nouns: Added -an (which evolved into -en)
- nama (name) → naman (names)
- oxa (ox) → oxan (oxen)
As English transitioned through the Middle English period (1100-1500 CE), these systems underwent significant simplification. The Norman Conquest introduced French influences, accelerating the breakdown of Old English grammatical systems.
During this transition, the weak declension pattern with the -en ending competed with the emerging dominant -s/-es pattern borrowed from Norman French. While most nouns eventually adopted the -s pattern, a few—including "ox"—retained their historical forms.
Other Irregular Plural Patterns in English
The English language maintains several other irregular plural patterns beyond the "-en" suffix, each preserving different aspects of historical grammatical systems:
Vowel Change (Umlaut)
Some nouns form plurals by changing their internal vowel:
- Man → Men
- Woman → Women
- Foot → Feet
- Tooth → Teeth
- Goose → Geese
- Mouse → Mice
This pattern derives from a phonological process in Proto-Germanic languages called i-mutation or i-umlaut, where a vowel changed when an i or j followed in the next syllable.
Identical Singular and Plural Forms
Some nouns maintain the same form in both singular and plural:
- Sheep → Sheep
- Deer → Deer
- Fish → Fish (though "fishes" can be used when referring to multiple species)
- Moose → Moose
- Aircraft → Aircraft
- Species → Species
These unchanging plurals often derive from Old English neuter nouns that didn't change in the plural or from later borrowings that retained their original plural patterns.
Foreign Plural Patterns
English has borrowed many words along with their plural formation patterns:
Latin Origins:
- Cactus → Cacti (also "cactuses")
- Focus → Foci (also "focuses")
- Terminus → Termini (also "terminuses")
- Curriculum → Curricula (also "curriculums")
- Formula → Formulae (also "formulas")
Greek Origins:
- Crisis → Crises
- Analysis → Analyses
- Basis → Bases
- Hypothesis → Hypotheses
Hebrew Origins:
- Cherub → Cherubim (also "cherubs")
- Seraph → Seraphim (also "seraphs")
These varied patterns illustrate English's nature as a language that readily adopts foreign words while sometimes preserving their original grammatical patterns.
Common Mistakes When Using "Ox" in the Plural
Even native English speakers occasionally make errors when using irregular plural forms like "oxen." Understanding these common mistakes helps avoid confusion:
Incorrect Regularization
The most frequent error involves applying the regular plural pattern:
- ❌ "The farmers used three oxes to plow the field."
- ✓ "The farmers used three oxen to plow the field."
This mistake stems from the natural tendency to apply regular patterns to all nouns, especially with uncommonly used words like "ox."
Confusion with Similar-Sounding Words
"Ox" can sometimes be confused with "ox" as a combining form:
- "Oxford" (a ford or crossing for oxen)
- "Oxbow" (a U-shaped bend in a river, or a collar for oxen)
These compound forms don't take the "-en" plural ending when pluralized:
- "Oxbows" (not "oxbowen")
- "Oxcarts" (not "oxcarten")
Using "Oxen" as Singular
Occasionally, people unfamiliar with the word might mistake "oxen" as the singular form:
- ❌ "Look at that oxen pulling the cart."
- ✓ "Look at that ox pulling the cart."
Confusion with Possessive Forms
The possessive form of "oxen" adds an apostrophe and s:
- ❌ "The oxens' yokes were removed at sundown."
- ✓ "The oxen's yokes were removed at sundown."
The Cultural and Historical Significance of Oxen
The linguistic persistence of "oxen" connects deeply to the cultural and historical importance of these animals. Understanding this context provides insight into why this particular word retained its irregular form.
Oxen—castrated male cattle trained as draft animals—played a crucial role in agricultural societies for millennia. Their strength, endurance, and docility made them invaluable for:
- Agricultural revolution: Oxen pulling plows dramatically increased food production capabilities
- Transportation: Before mechanization, oxen transported heavy goods across vast distances
- Industrial processes: From grinding grain to powering machinery, oxen provided essential energy
This central economic and cultural position ensured the word remained in common usage throughout English's developmental periods, helping preserve its irregular form while similar patterns disappeared elsewhere.
Historical records show that in medieval England, the typical peasant farmer might own one or two oxen—often the most valuable possession a family owned. This widespread practical importance reinforced the word's resistance to regularization.
Oxen in Literature and Language
The cultural significance of oxen appears prominently in literature, idioms, and expressions throughout English's history:
Literary References
Oxen feature prominently in classical and biblical literature:
- In Homer's Odyssey, the slaughter of Helios's sacred oxen brings divine punishment
- The Bible contains numerous references to oxen as sacrificial animals and agricultural necessities
- In medieval literature, the ox often symbolizes patient strength and steady labor
Idiomatic Expressions
Several English expressions derive from oxen:
- "Strong as an ox": Referring to exceptional physical strength
- "Ox-like patience": Describing extraordinary endurance or forbearance
- "To take the ox by the horns": A variant of "take the bull by the horns," meaning to confront a challenge directly
These linguistic artifacts demonstrate how deeply oxen were integrated into English-speaking cultures, helping explain the preservation of the irregular plural form.
Scientific Classification and Terminology Related to Oxen
In scientific and zoological contexts, understanding precise terminology related to oxen helps avoid confusion:
Biological Classification:
- Oxen belong to the family Bovidae
- They are domesticated forms of Bos taurus (domestic cattle)
- Technically, an ox is not a distinct species but rather a trained, castrated male bovine
Related Terminology:
- Bull: An intact (uncastrated) male bovine
- Cow: An adult female bovine that has given birth
- Heifer: A young female bovine that has not yet had a calf
- Steer: A castrated male bovine, typically younger than an ox
- Bullock: In British English, refers to a young bull or steer
- Ox: Specifically a trained, castrated adult male bovine used as a draft animal
The specificity of these terms highlights the importance of oxen in agricultural contexts and explains the preservation of distinct terminology, including the irregular plural form.
The Plural of Ox in Different English Dialects
While "oxen" remains the standard plural form across all major English dialects, some regional variations exist in usage and pronunciation:
British English
In traditional British rural dialects, particularly in regions with historical agricultural emphasis:
- The pronunciation sometimes emphasizes the second syllable: /ˈɒk.sən/
- Some dialectal forms like "oxens" existed historically but are now considered non-standard
American English
In American English:
- The pronunciation typically places equal stress on both syllables: /ˈɑk.sən/
- The word "oxen" appears less frequently in everyday American speech due to earlier mechanization of agriculture
Australian and New Zealand English
In these dialects:
- The pronunciation follows broadly British patterns
- Historical usage was significant during colonial settlement periods when oxen were essential for agricultural development
African and Asian English Varieties
In regions where ox-drawn plows remain in use:
- The term "oxen" often maintains active, everyday usage
- Some localized dialects have developed specialized vocabulary around oxen and their management
These variations reflect both the historical development of English and the differing cultural relationships with these animals across English-speaking regions.
Teaching and Learning the Plural of "Ox"
For language educators and learners, the irregular plural "oxen" presents both challenges and opportunities:
Pedagogical Approaches
Effective strategies for teaching this irregular form include:
- Historical context: Explaining the origin helps students understand rather than merely memorize
- Pattern recognition: Grouping "oxen" with other irregular plurals creates cognitive frameworks
- Mnemonic devices: Creating memorable phrases or stories around "oxen"
- Frequency reinforcement: Incorporating the word in various contexts to build familiarity
For English Language Learners
Common challenges for non-native speakers include:
- Overgeneralization of regular plural patterns
- Confusion with other irregular plural types
- Difficulty recognizing when to use the irregular form in spontaneous speech
Focused practice with irregular plurals like "oxen" helps develop broader understanding of English's complex morphological system.
The Evolution of Plural Forms in English: A Broader Perspective
The case of "oxen" illuminates broader patterns in English's grammatical evolution:
Regularization Processes
Languages typically demonstrate a tendency toward regularization—simplifying irregular patterns over time. This process occurs through:
- Analogy: Extending common patterns to irregular forms
- Efficiency: Reducing cognitive load by minimizing exceptions
- Language contact: Borrowing simpler patterns from other languages
Yet some irregular forms resist regularization due to:
- Frequency: Commonly used words maintain irregular patterns longer
- Early acquisition: Words learned early in childhood better preserve irregularities
- Cultural significance: Terms with special importance resist change
The Balance Between Regularity and Irregularity
English grammar represents a balance between:
- Regular patterns that facilitate learning and communication
- Irregular forms that preserve historical information and create distinctive expressions
This balance reflects the dual nature of language as both a practical communication system and a cultural repository.
Digital Age Implications: Autocorrect and Spell Check Challenges
In modern digital communication, spell-checking and autocorrect systems sometimes struggle with irregular plurals like "oxen":
- Some automated systems may flag "oxen" as an error and suggest "oxes"
- Natural language processing systems require specific programming to recognize irregular forms
- Search engines must account for users entering incorrect forms like "oxes"
These technological challenges remind us that understanding linguistic exceptions remains important even in an age of digital communication aids.
The Future of "Oxen" in English
Will "oxen" maintain its irregular plural indefinitely? Linguistic trends suggest:
Factors Supporting Preservation
- Standardization: Modern educational systems and reference materials consistently teach "oxen"
- Literary presence: The term appears in classic literature that remains widely read
- Distinctiveness: The unusual form makes "oxen" a recognizable example of linguistic history
Factors That Might Lead to Change
- Reduced relevance: As oxen become less common in modern agriculture, the word appears less frequently
- Simplification tendency: Natural language evolution often favors regularization
- Global English: Non-native speakers might exert pressure toward regularization
Linguistic evidence suggests that highly irregular but commonly known forms like "oxen" tend to persist longer than more obscure irregularities, making it likely that "oxen" will remain the standard plural for the foreseeable future.
Learn Any Language with Kylian AI
Private language lessons are expensive. Paying between 15 and 50 euros per lesson isn’t realistic for most people—especially when dozens of sessions are needed to see real progress.
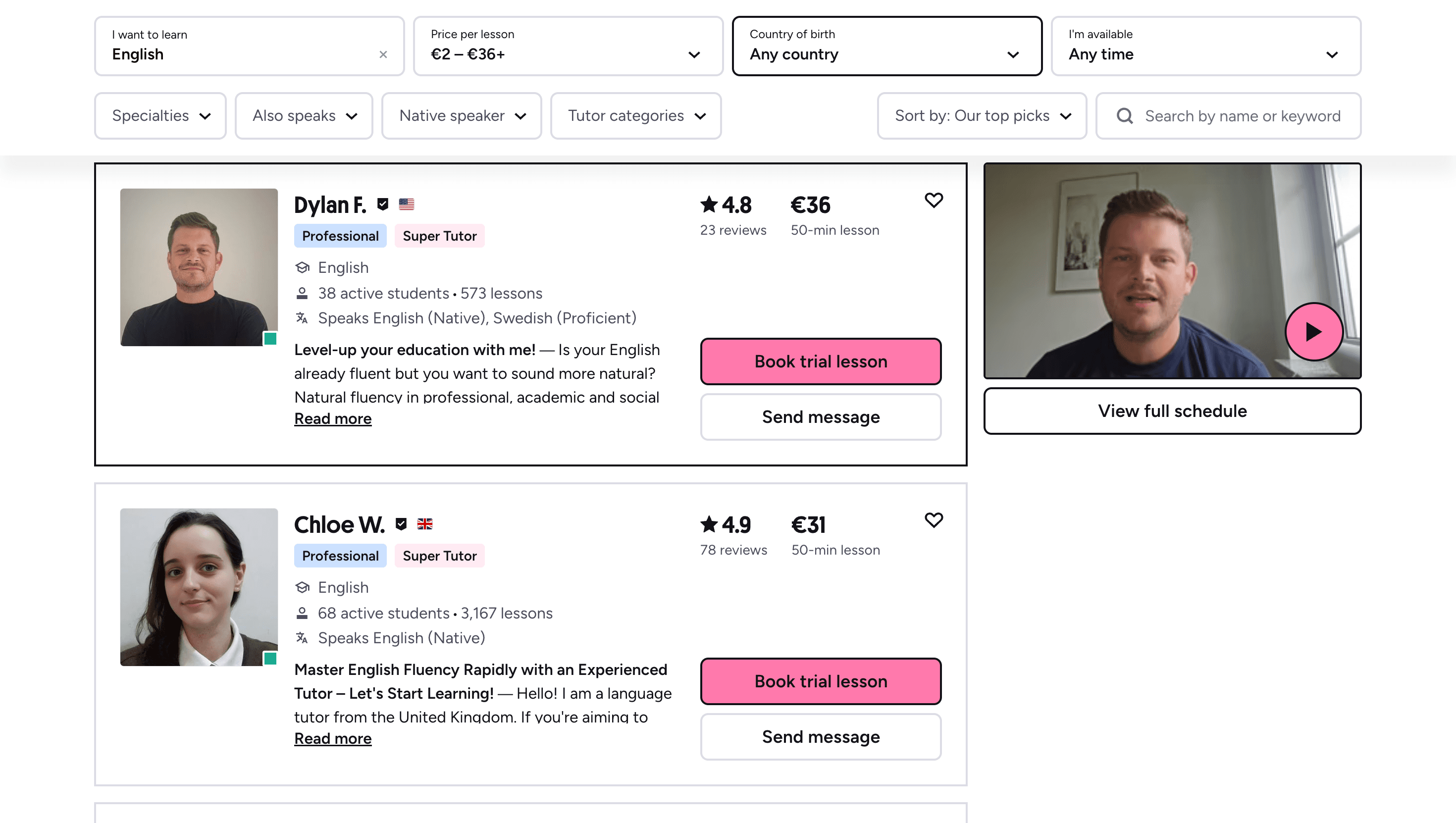
Many learners give up on language learning due to these high costs, missing out on valuable professional and personal opportunities.
That’s why we created Kylian: to make language learning accessible to everyone and help people master a foreign language without breaking the bank.
To get started, just tell Kylian which language you want to learn and what your native language is
Tired of teachers who don’t understand your specific struggles as a French speaker? Kylian’s advantage lies in its ability to teach any language using your native tongue as the foundation.
Unlike generic apps that offer the same content to everyone, Kylian explains concepts in your native language (French) and switches to the target language when necessary—perfectly adapting to your level and needs.
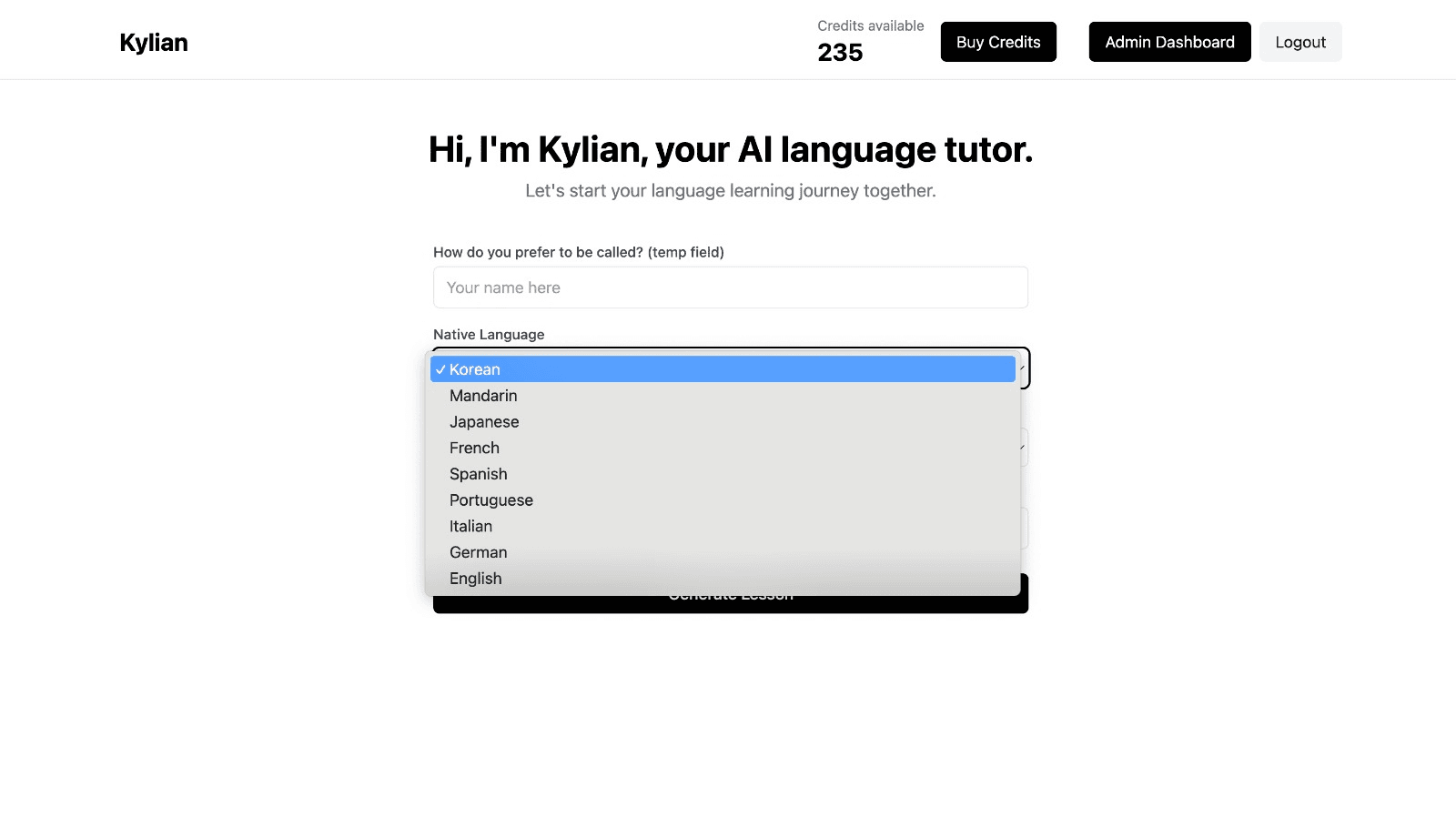
This personalization removes the frustration and confusion that are so common in traditional language learning.
Choose a specific topic you want to learn
Frustrated by language lessons that never cover exactly what you need? Kylian can teach you any aspect of a language—from pronunciation to advanced grammar—by focusing on your specific goals.
Avoid vague requests like “How can I improve my accent?” and be precise: “How do I pronounce the R like a native English speaker?” or “How do I conjugate the verb ‘to be’ in the present tense?”
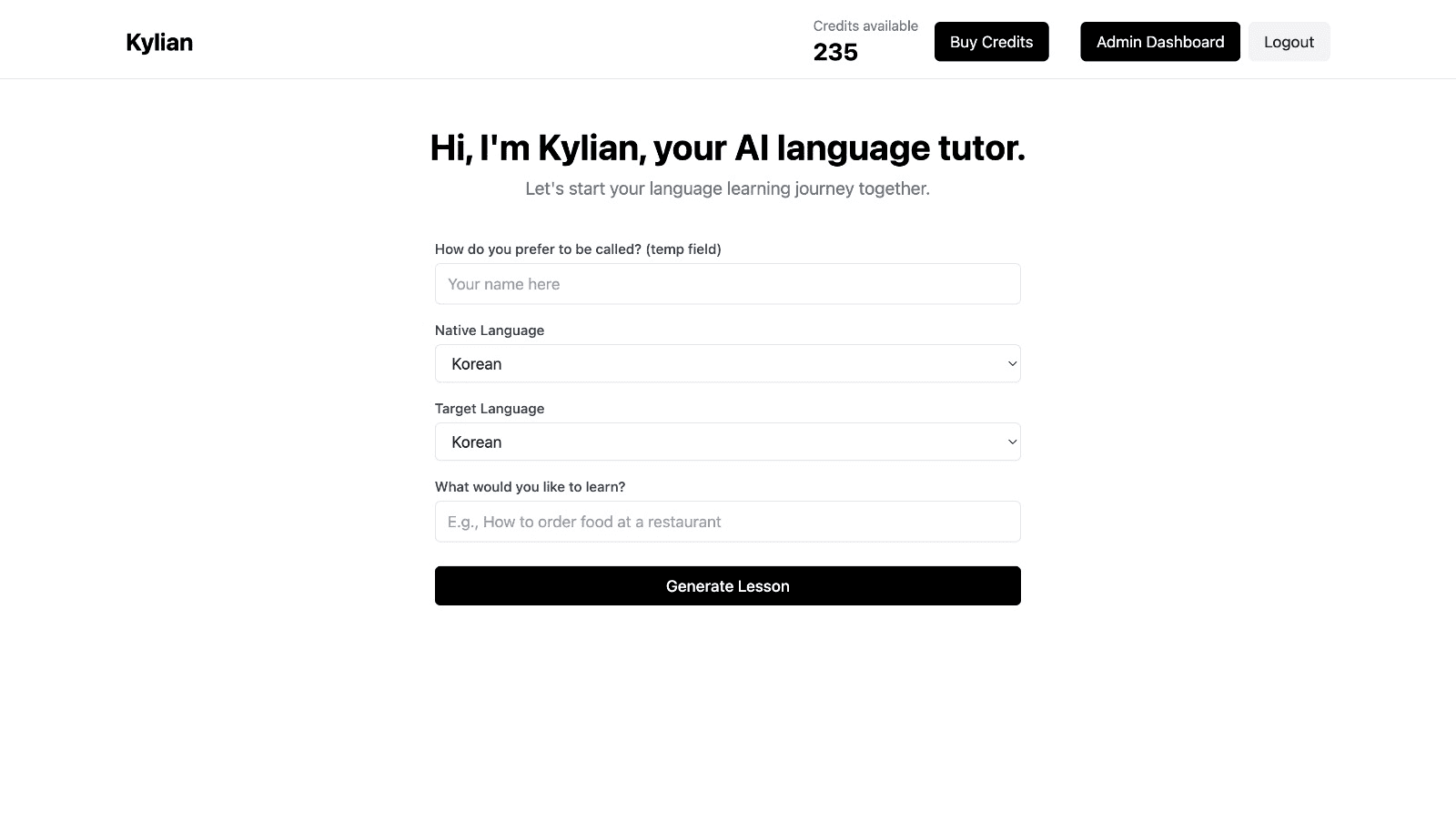
With Kylian, you’ll never again pay for irrelevant content or feel embarrassed asking “too basic” questions to a teacher. Your learning plan is entirely personalized.
Once you’ve chosen your topic, just hit the “Generate a Lesson” button, and within seconds, you’ll get a lesson designed exclusively for you.
Join the room to begin your lesson
The session feels like a one-on-one language class with a human tutor—but without the high price or time constraints.
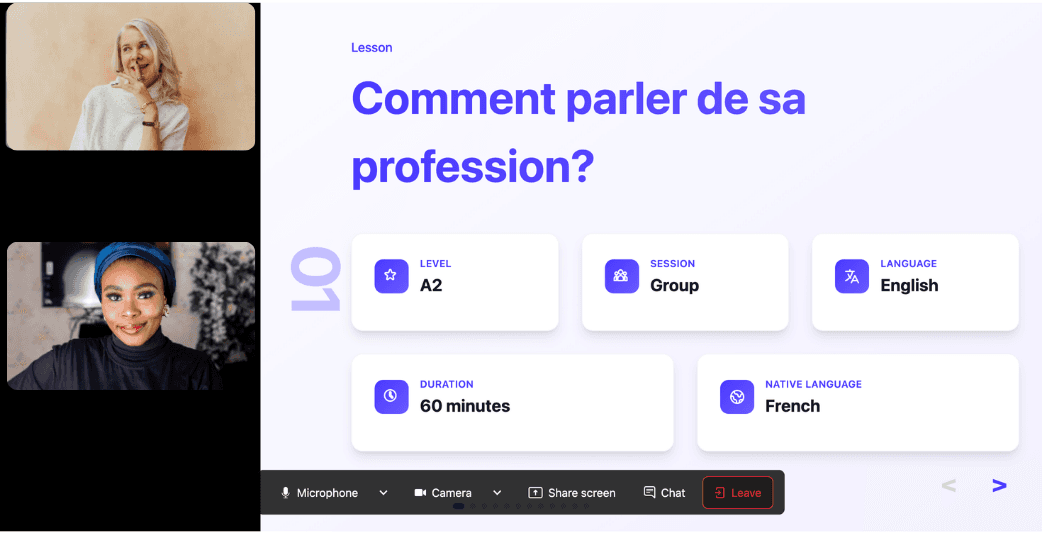
In a 25-minute lesson, Kylian teaches exactly what you need to know about your chosen topic: the nuances that textbooks never explain, key cultural differences between French and your target language, grammar rules, and much more.
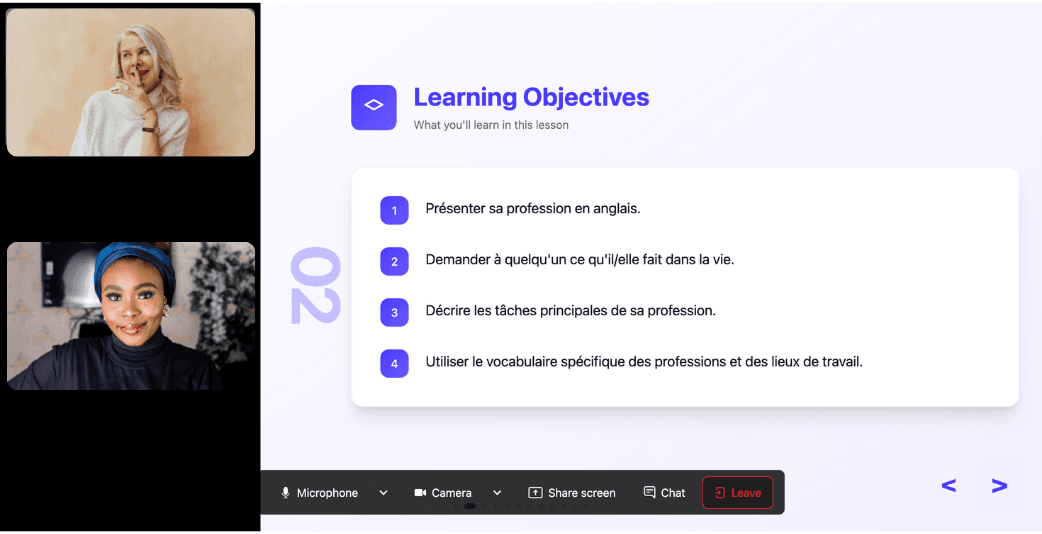
Ever felt frustrated trying to keep up with a native-speaking teacher, or embarrassed to ask for something to be repeated? With Kylian, that problem disappears. It switches intelligently between French and the target language depending on your level, helping you understand every concept at your own pace.
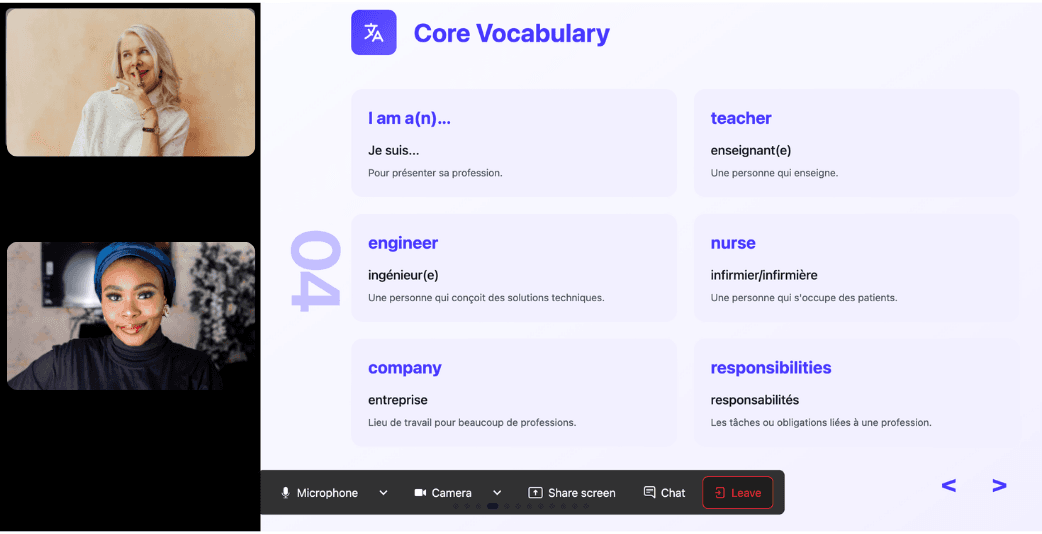
During the lesson, Kylian uses role-plays, real-life examples, and adapts to your learning style. Didn’t understand something? No problem—you can pause Kylian anytime to ask for clarification, without fear of being judged.
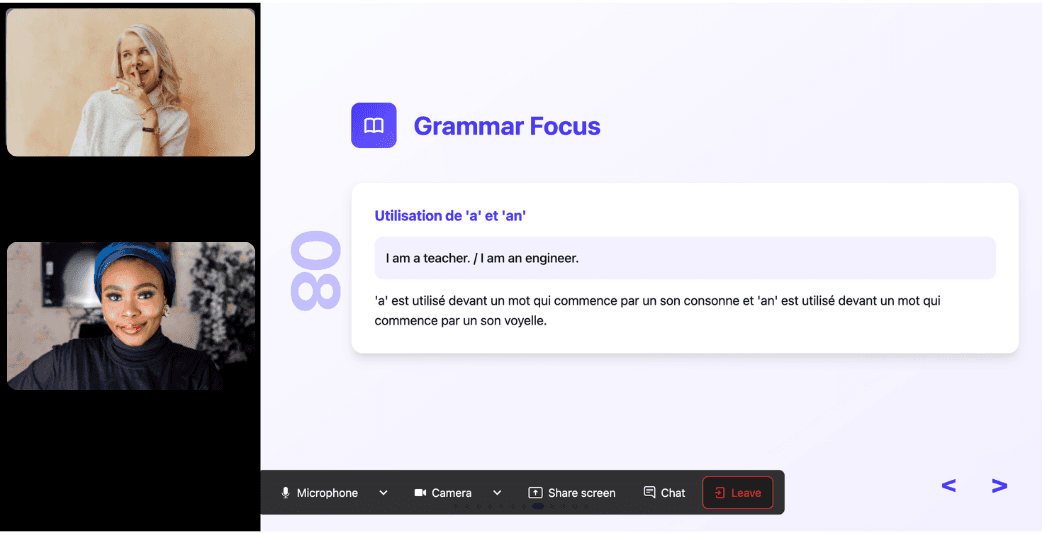
Ask all the questions you want, repeat sections if needed, and customize your learning experience in ways traditional teachers and generic apps simply can’t match.
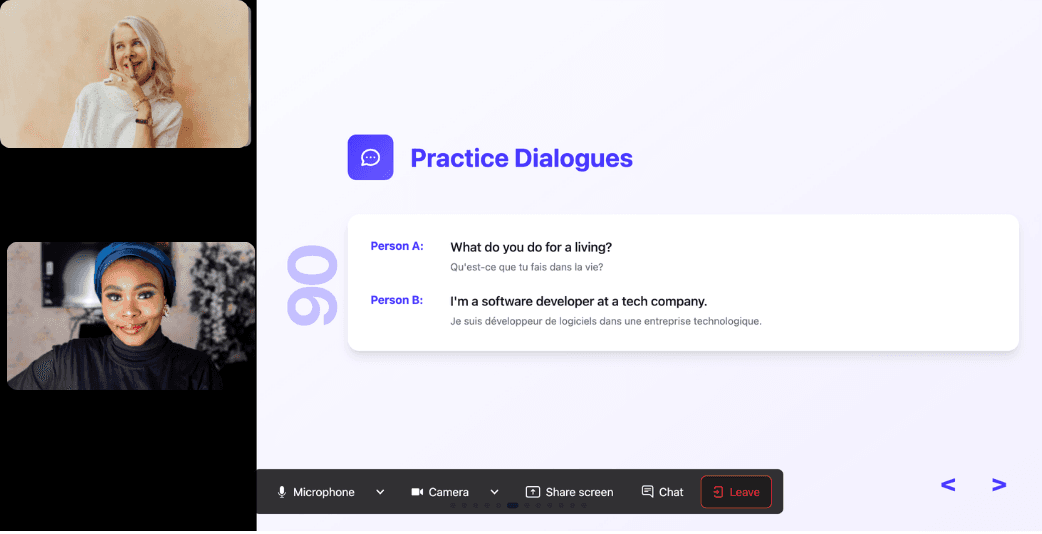
With 24/7 access at a fraction of the cost of private lessons, Kylian removes all the barriers that have kept you from mastering the language you’ve always wanted to learn.
Similar Content You Might Want To Read

9 Different Ways to Say Congratulations in French
There's something profoundly human about celebrating achievements. When we witness someone's success, our instinct is to acknowledge it—to participate in their moment of triumph. This shared experience transcends cultural boundaries, though the expressions we use vary widely across languages. French, with its melodic cadence and rich cultural heritage, offers a particularly elegant array of congratulatory expressions. These phrases do more than convey basic sentiments; they reflect the nuances of French culture and social interactions. This guide explores multiple ways to express congratulations in French, equipping you with the vocabulary to celebrate authentically in any context—from professional achievements to personal milestones, formal occasions to casual encounters.

Months of the Year in Spanish: The Essential Guide
Learning how to say and write dates in Spanish is fundamental for anyone studying the language. This comprehensive guide covers everything from pronunciation to cultural significance of the months in Spanish. We'll explore proper grammar, historical origins, and provide practical tips to help you master this essential vocabulary.

English Prepositions: Types, Usage & Common Mistakes
Mastering English prepositions is essential for fluent communication, yet these small words often cause significant confusion for language learners. Why? Because prepositions form the connective tissue of English sentences, showing relationships between words in ways that don't always follow predictable patterns. This comprehensive guide will help you understand, learn, and correctly use the wide variety of English prepositions.

100 Most Common French Words: Your Path to Fluency
Learning a new language opens doors to new cultures, perspectives, and opportunities. French, with its melodic cadence and global presence, stands as one of the most valuable languages to master. But where should you begin? Research consistently shows that focusing on high-frequency vocabulary delivers the most efficient path to conversational ability.

Master Spanish Verb Conjugations: The Practical Guide
Learning Spanish opens doors to communicating with over 460 million native speakers worldwide. Yet, many learners face a significant challenge: mastering Spanish verb conjugations. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about Spanish conjugations—from basic principles to practical applications.

Reflexive Verbs in Spanish: A Comprehensive Guide
Learning a language requires mastering its core grammatical structures. Among these, reflexive verbs in Spanish represent a fundamental concept that dramatically enhances fluency and authenticity in conversation. This comprehensive guide offers clear explanations, actionable strategies, and contextual examples to help you incorporate reflexive verbs naturally into your Spanish communication. Let's explore this crucial element of Spanish grammar to elevate your language proficiency.