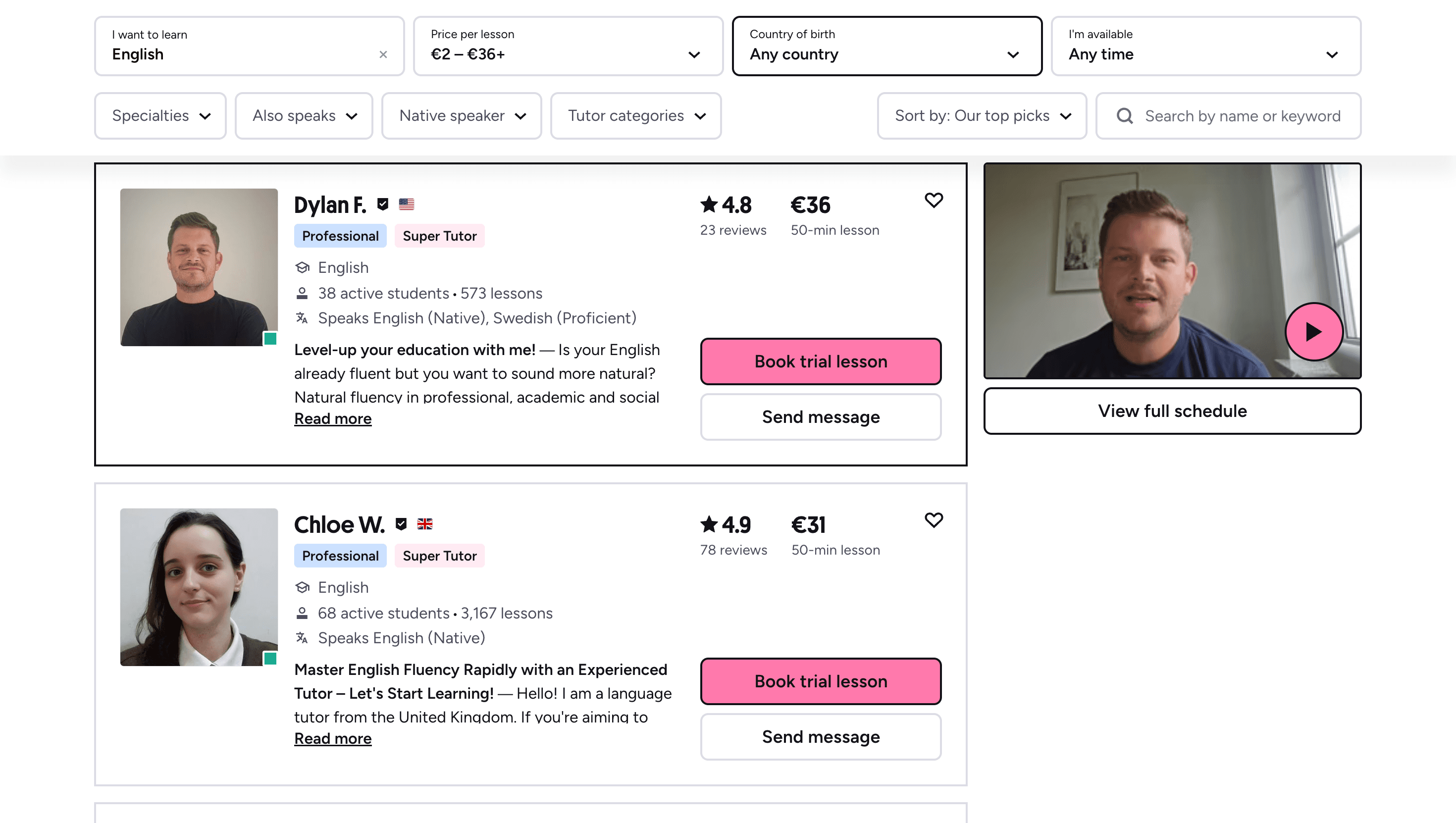
Spanish vs Italian: Decisive Guide for Language Enthusiasts

Written by
Ernest Bio Bogore

Reviewed by
Ibrahim Litinine

Choosing your next language learning journey requires careful consideration. When contemplating Romance languages, Spanish and Italian often emerge as top contenders. Both offer rich cultural heritage, practical applications, and accessible learning curves for English speakers. This guide dissects the critical differences and similarities to help you make an informed decision aligned with your personal goals.
The Core Comparison: Spanish and Italian at a Glance
Both Spanish and Italian trace their lineage to Latin, creating natural parallels between them. Understanding their shared foundations and distinct evolutions provides context for your language selection process.
Spanish stands as the second most widely spoken native language globally, with over 460 million native speakers across 21 countries spanning Europe, Latin America, and Africa. Its reach extends significantly into the United States, where Spanish proficiency increasingly offers professional advantages.
Italian, while more geographically concentrated, boasts approximately 85 million speakers worldwide. It serves as the official language of Italy, San Marino, and partially of Vatican City, with substantial communities in Switzerland, Croatia, Slovenia, and worldwide Italian diaspora.
Linguistic Similarities: The Connecting Threads
The shared Latin heritage of Spanish and Italian manifests in several significant ways that can ease the transition between learning either language:
Grammatical Foundation
Both languages incorporate gendered nouns, a concept unfamiliar to English speakers but consistent between the two Romance languages. Every noun falls into either masculine or feminine categories, affecting articles, adjectives, and pronouns. For instance:
- "The book" appears as "il libro" (masculine) in Italian and "el libro" (masculine) in Spanish
- "The house" translates to "la casa" (feminine) in both languages
Article Systems
Spanish and Italian employ similar definite and indefinite article systems that correspond to noun gender and number:
- Italian uses "il," "lo," "la" for definite articles and "un," "uno," "una" for indefinite articles
- Spanish employs "el," "la" for definite and "un," "una" for indefinite articles
These parallel structures create a transferable knowledge base, beneficial for learners tackling both languages sequentially or simultaneously.
Lexical Overlap
An extensive vocabulary foundation overlaps between these languages. Many words appear nearly identical or require only minor adjustments in spelling or pronunciation:
- Amore (Italian) / Amor (Spanish) - Love
- Città (Italian) / Ciudad (Spanish) - City
- Università (Italian) / Universidad (Spanish) - University
- Biblioteca (Italian) / Biblioteca (Spanish) - Library
This shared lexicon accelerates the learning process, particularly for those who have already studied one of these languages before approaching the other.
Crucial Differences: Where the Languages Diverge
Despite their commonalities, Italian and Spanish diverge in several fundamental ways that impact both learning trajectory and practical usage:
Pronunciation Distinctions
Pronunciation represents perhaps the most immediately noticeable difference between these languages:
Italian features a melodic quality with clear, distinct vowel sounds and the characteristic rolling "r." The language maintains consistent pronunciation rules with minimal exceptions, making reading relatively straightforward once fundamentals are mastered.
Spanish pronunciation varies more significantly across regions but generally features the distinctive "ñ" sound and the Castilian "th" sound for "c" and "z" (in Spain). Many Spanish dialects feature faster speech patterns and more consonant blending than standard Italian.
Grammatical Nuances
While sharing broad grammatical frameworks, these languages differ in several structural elements:
Spanish employs two distinct verbs for "to be" - "ser" and "estar" - each with specific contextual applications. While Italian also has "essere" and "stare," their usage patterns differ substantially from their Spanish counterparts.
Sentence structure often follows subject-verb-object patterns in Spanish, whereas Italian frequently employs subject-object-verb constructions, particularly in complex sentences.
False Friends: The Linguistic Traps
Perhaps the most challenging aspect for learners studying both languages are "false friends" - words that appear similar but carry different meanings:
- "Burro" means butter in Italian but donkey in Spanish
- "Imbarazzata" means embarrassed in Italian while "embarazada" means pregnant in Spanish
- "Salire" in Italian means to rise or go up, while "salir" in Spanish means to leave or exit
- "Caldo" means hot in Italian but broth in Spanish
These linguistic traps require careful attention and present one of the more challenging aspects for learners attempting to master both languages simultaneously.
Cultural Dimensions: Beyond Linguistics
Language selection extends beyond grammar and vocabulary to embrace cultural considerations that might align with personal interests and aspirations.
Italian: The Cultural Legacy
Italian offers unparalleled access to art history, Renaissance thought, and architectural marvels. Speaking Italian transforms visits to Florence, Rome, and Venice, allowing direct engagement with cultural landmarks in their original context.
Italian cuisine vocabulary permeates global gastronomy, with terms like "al dente," "cappuccino," and "prosciutto" entering international lexicons. For culinary enthusiasts, Italian provides the authentic language of food preparation and appreciation.
The Italian musical tradition has shaped global musical terminology, with directions like "allegro," "pianissimo," and "forte" becoming universal standards. Opera appreciation deepens significantly when experienced in its original Italian language, particularly works by Verdi, Puccini, and Rossini.
Spanish: Global Reach and Diversity
Spanish unlocks diverse cultural experiences across multiple continents, from the architectural wonders of Barcelona to the ancient Inca ruins of Machu Picchu.
Literary treasures from authors like Gabriel García Márquez, Isabel Allende, and Miguel de Cervantes become accessible in their original form, preserving the nuances lost in translation.
Musical genres including flamenco, salsa, tango, and reggaeton connect through Spanish, offering rhythmic and lyrical understanding across diverse cultural expressions.
Practical Considerations: Learning Curve and Resources
When evaluating which language to pursue, practical factors often influence the final decision:
Learning Accessibility
Spanish generally offers a slightly gentler introduction for English speakers, particularly regarding pronunciation and spelling consistency. Many linguists consider Spanish among the most straightforward foreign languages for English speakers to acquire.
Italian pronunciation presents fewer exceptions than Spanish, with a more direct correlation between spelling and sound. However, some grammatical elements, particularly verb conjugations, can present greater complexity in Italian.
Resource Availability
Spanish learning resources abound globally, with extensive textbooks, digital applications, and immersion opportunities widely available. Spanish language media has expanded dramatically with streaming services offering content from various Spanish-speaking regions.
Italian resources, while not as ubiquitous as Spanish, remain readily accessible through traditional and digital channels. Several language learning platforms have expanded their Italian offerings substantially in recent years, though Spanish typically maintains broader representation.
Professional Applications
Spanish proficiency provides significant advantages in multiple professional sectors, particularly in North America where demographic shifts continue to increase demand for bilingual professionals in healthcare, education, business, and legal fields.
Italian specialization offers distinct advantages in fine arts, fashion, culinary arts, architecture, and design industries. Tourism and hospitality sectors in regions with significant Italian tourism also value Italian language skills.
Making Your Decision: Strategic Considerations
The optimal language choice ultimately depends on personal factors that vary significantly between learners:
Geographic Relevance
Consider your current location and travel aspirations. Spanish offers practical applications across more countries and regions, while Italian provides depth within a more concentrated geographic area.
For those in North America, Spanish often provides immediate practical applications within local communities. European residents might find more balanced utility between the languages depending on their proximity to Italy or Spain.
Career Trajectory
Evaluate your professional field and future aspirations. Industries like international business, diplomatic services, and tourism increasingly value Spanish proficiency. Fields like art history, classical music, and high-end culinary arts often prioritize Italian language skills.
The technology sector has seen increased demand for Spanish skills as Latin American tech ecosystems develop rapidly, while Italian may offer advantages in design-focused technology fields.
Personal Passion
Perhaps most importantly, consider which language inspires greater personal enthusiasm. Sustained language learning requires consistent motivation, and cultural affinity often provides the strongest foundation for language acquisition success.
Those drawn to operatic music, Renaissance art, and Italian cinema may find greater intrinsic motivation with Italian. Enthusiasts of Latin American literature, Spanish architecture, or Latin dance forms might naturally gravitate toward Spanish.
Beyond the Binary: The Multilingual Advantage
While this guide frames the decision as a choice between alternatives, many language enthusiasts ultimately pursue both languages sequentially or even simultaneously.
Starting with Spanish often provides a slightly gentler introduction to Romance language structures, creating a foundation that facilitates later Italian acquisition. Conversely, beginning with Italian can establish strong pronunciation habits applicable to subsequent Spanish learning.
Whichever language you choose initially, the knowledge gained transfers substantially to other Romance languages, creating momentum for potential multilingual development including French, Portuguese, Romanian, and Catalan.
Immersion Strategies: Accelerating Acquisition
Regardless of which language you select, certain strategies accelerate acquisition and maintain engagement throughout the learning process:
Digital Immersion
Create a digital environment supporting your target language. Change smartphone settings, follow social media accounts from native speakers, and explore podcasts and YouTube channels in your chosen language.
Streaming services now offer extensive content libraries in both Spanish and Italian, providing entertainment that simultaneously develops listening comprehension and cultural understanding.
Language Exchange
Find conversation partners through language exchange applications that connect you with native speakers interested in your native language. These exchanges provide authentic communication practice beyond classroom contexts.
For Spanish learners, the large number of speakers worldwide makes finding exchange partners relatively straightforward. Italian learners may need to search more specifically but can still find ample exchange opportunities online.
Cultural Engagement
Integrate cultural elements that maintain motivation throughout the language learning process:
- Spanish learners might explore salsa dancing, Latin American cooking, or Spanish cinema
- Italian enthusiasts could investigate opera, Italian cuisine, or Renaissance art history
These cultural connections provide contextual reinforcement that enhances vocabulary retention and cultural nuance understanding.
The Mutual Intelligibility Factor
An intriguing aspect of Spanish and Italian is their degree of mutual intelligibility – the extent to which speakers of one language can understand the other without formal study.
Native Spanish speakers typically understand approximately 50-60% of spoken Italian without prior exposure, while Italian speakers comprehend a similar percentage of Spanish. This partial intelligibility creates interesting dynamics for learners:
Those who master one language often develop passive comprehension of the other more rapidly than with unrelated languages. This phenomenon creates a practical advantage for eventually learning both languages compared to selecting, for instance, Spanish and German.
The mutual intelligibility also explains why learners sometimes confuse elements between these languages, particularly when studying them concurrently.
Regional Variations: The Dialect Dimension
Both Spanish and Italian feature significant regional variations that merit consideration when selecting which version of the language to prioritize:
Spanish Variations
Spanish dialects vary considerably between Spain and Latin America, with further variations between Latin American countries. Major distinctions include:
- Castilian Spanish (Spain) features the distinctive "th" sound for "c" and "z"
- Latin American Spanish typically pronounces these letters with an "s" sound
- Vocabulary differences emerge across regions, with terms like "driving" appearing as "conducir" in Spain but "manejar" in Mexico
Italian Variations
Italian standard language derives from the Tuscan dialect, but regional variations persist throughout Italy:
- Northern Italian dialects show greater Germanic influence
- Southern Italian features more Greek and Arabic influences
- Sicilian contains elements making it occasionally considered a separate language entirely
For learners, these variations typically present limited initial concerns, as standard versions remain widely understood across regions. However, awareness of major regional differences prevents confusion during travel or when consuming media from different regions.
Technology and Language Learning: Modern Advantages
Contemporary language learners benefit from technological advances that simplify the acquisition process for both Italian and Spanish:
Language applications provide gamified practice that maintains motivation through immediate feedback and progress tracking. These platforms typically offer equally robust curriculum paths for both Spanish and Italian.
Translation technologies, while not substitutes for language proficiency, provide invaluable support during the learning process. These tools assist with comprehension while learners build independent skills.
Virtual reality applications have begun incorporating language learning experiences that simulate immersion environments without international travel, creating new possibilities for experiential learning.
Final Verdict: Making Your Selection
Having explored the multifaceted considerations surrounding Spanish and Italian, the decision ultimately remains personal. Consider these closing insights:
Choose Spanish if:
- You value language with maximum global application
- Your professional ambitions align with Spanish-speaking markets
- You anticipate extensive travel throughout Latin America
- You appreciate diverse cultural expressions across multiple continents
Choose Italian if:
- You have specific interest in Italian art, music, cuisine, or history
- Your professional path intersects with design, fashion, or classical arts
- You anticipate extended time in Italy or with Italian communities
- You feel particularly drawn to Italian phonetics and expressiveness
Whichever language you select, approach the journey with cultural curiosity and practical consistency. Both paths offer rewarding linguistic experiences that transform how you perceive and interact with the world around you.
Remember that language acquisition represents a continuous journey rather than a destination. The process offers valuable cognitive benefits regardless of which language you ultimately select – enhanced memory, improved decision-making, and expanded cultural perspective.
Choose confidently, learn joyfully, and recognize that either selection opens doors to new cultural dimensions and communication possibilities previously inaccessible in your linguistic repertoire.
Learn Any Language with Kylian AI
Private language lessons are expensive. Paying between 15 and 50 euros per lesson isn’t realistic for most people—especially when dozens of sessions are needed to see real progress.
Many learners give up on language learning due to these high costs, missing out on valuable professional and personal opportunities.
That’s why we created Kylian: to make language learning accessible to everyone and help people master a foreign language without breaking the bank.
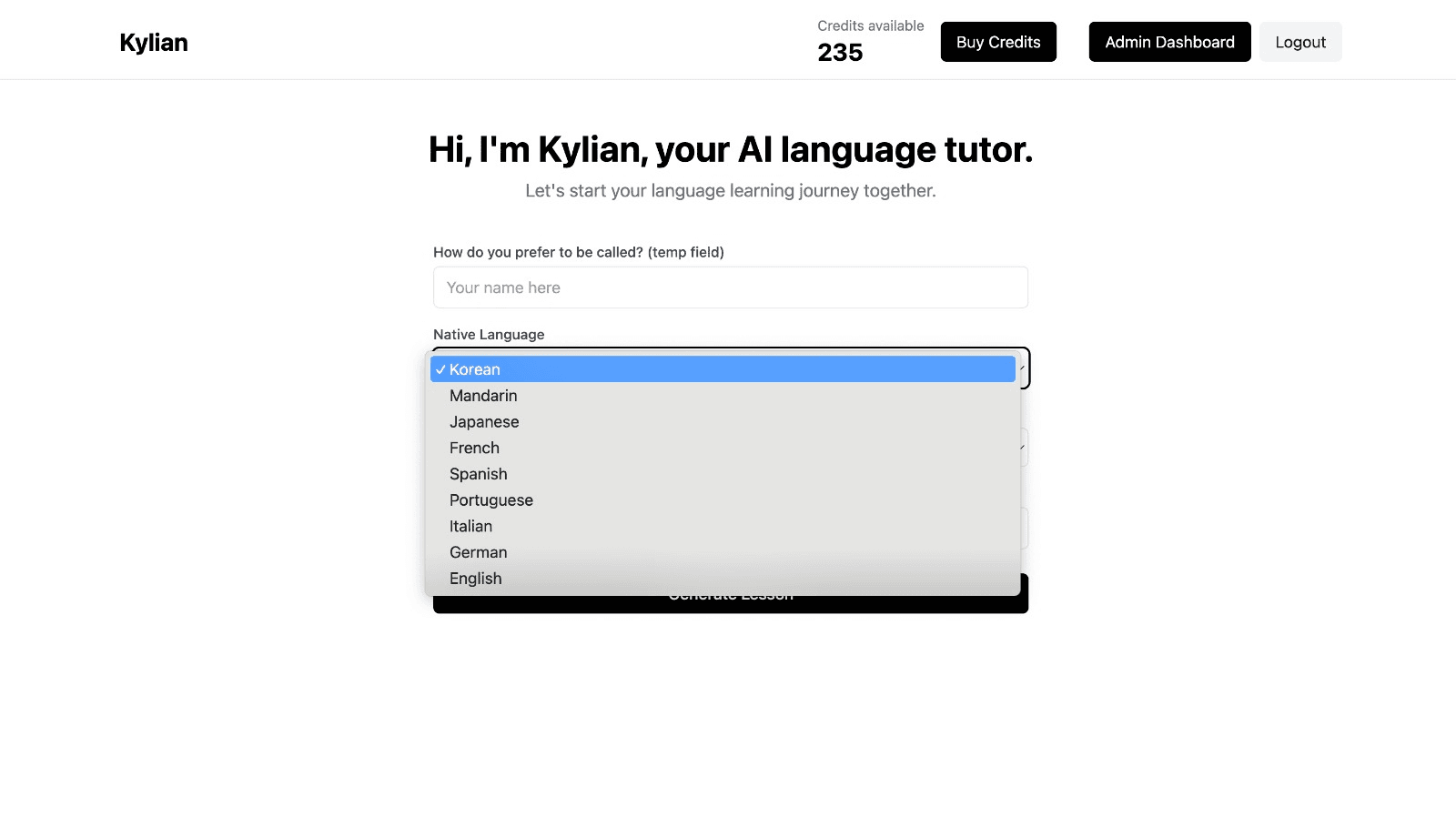
To get started, just tell Kylian which language you want to learn and what your native language is
Tired of teachers who don’t understand your specific struggles as a French speaker? Kylian’s advantage lies in its ability to teach any language using your native tongue as the foundation.
Unlike generic apps that offer the same content to everyone, Kylian explains concepts in your native language (French) and switches to the target language when necessary—perfectly adapting to your level and needs.
This personalization removes the frustration and confusion that are so common in traditional language learning.
Choose a specific topic you want to learn
Frustrated by language lessons that never cover exactly what you need? Kylian can teach you any aspect of a language—from pronunciation to advanced grammar—by focusing on your specific goals.
Avoid vague requests like “How can I improve my accent?” and be precise: “How do I pronounce the R like a native English speaker?” or “How do I conjugate the verb ‘to be’ in the present tense?”
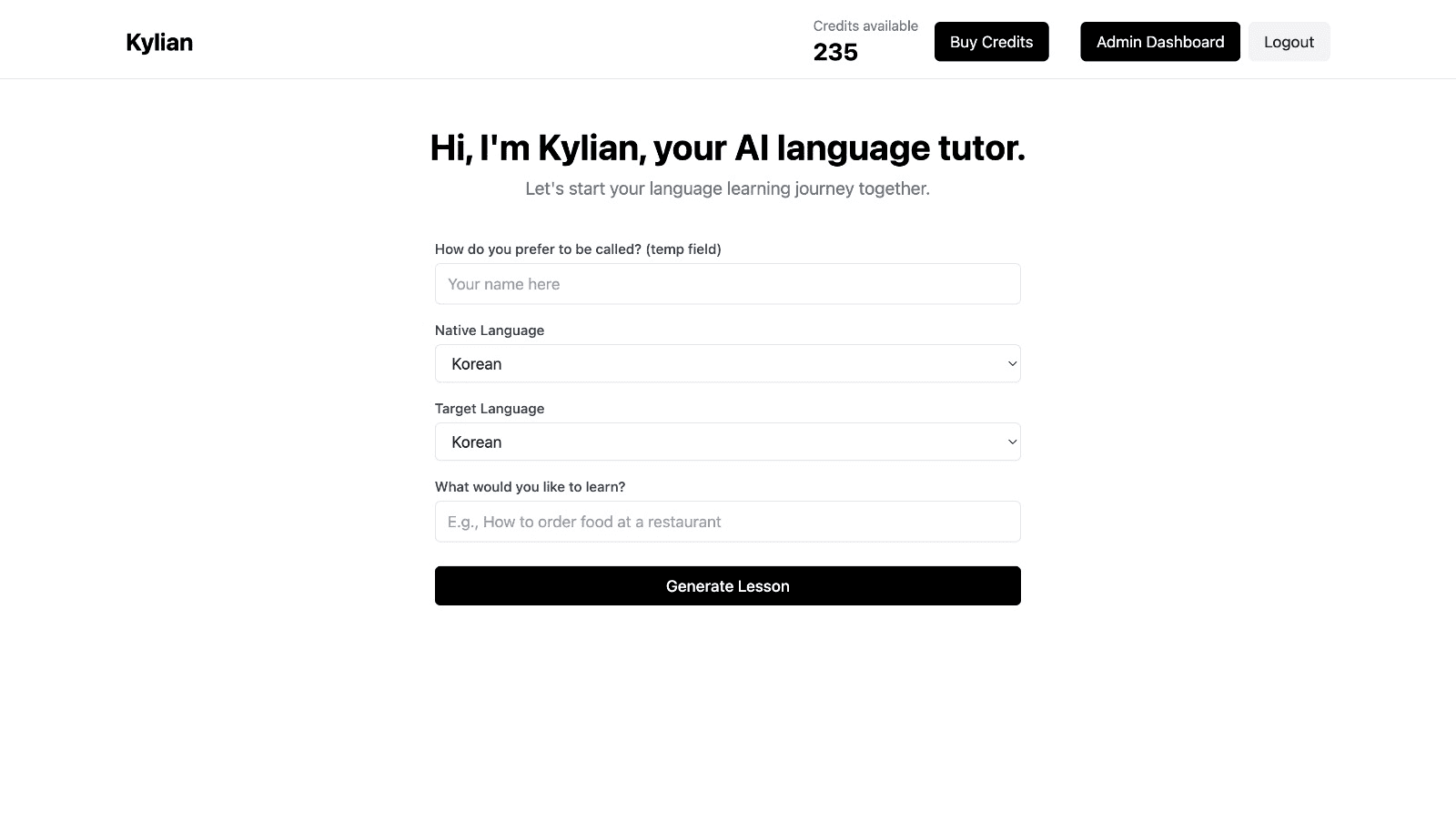
With Kylian, you’ll never again pay for irrelevant content or feel embarrassed asking “too basic” questions to a teacher. Your learning plan is entirely personalized.
Once you’ve chosen your topic, just hit the “Generate a Lesson” button, and within seconds, you’ll get a lesson designed exclusively for you.
Join the room to begin your lesson
The session feels like a one-on-one language class with a human tutor—but without the high price or time constraints.
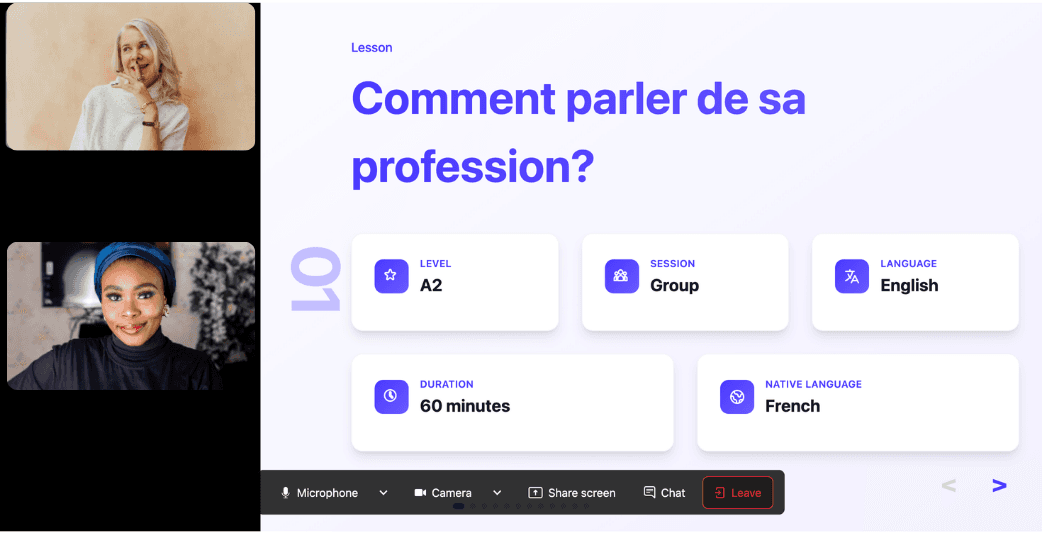
In a 25-minute lesson, Kylian teaches exactly what you need to know about your chosen topic: the nuances that textbooks never explain, key cultural differences between French and your target language, grammar rules, and much more.
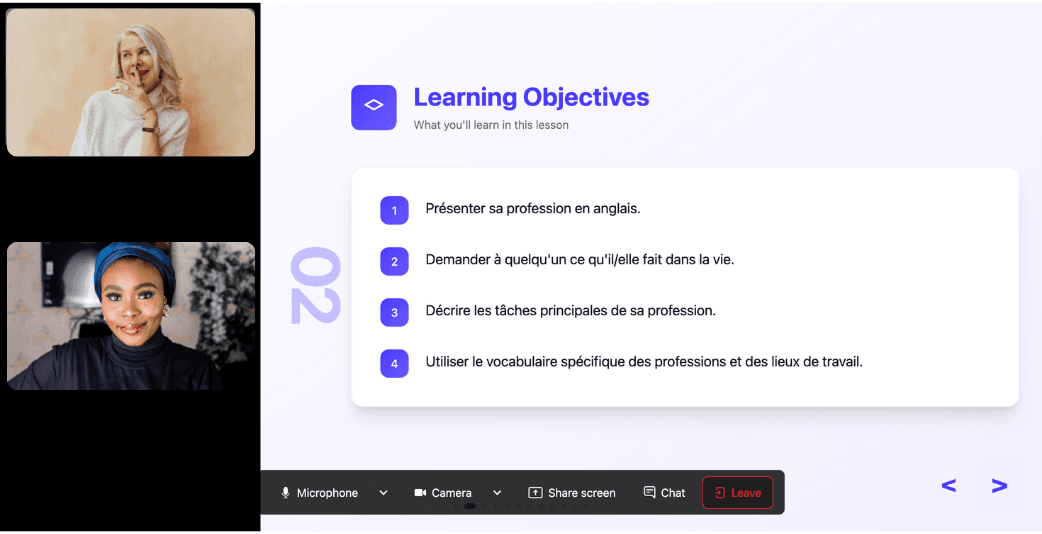
Ever felt frustrated trying to keep up with a native-speaking teacher, or embarrassed to ask for something to be repeated? With Kylian, that problem disappears. It switches intelligently between French and the target language depending on your level, helping you understand every concept at your own pace.
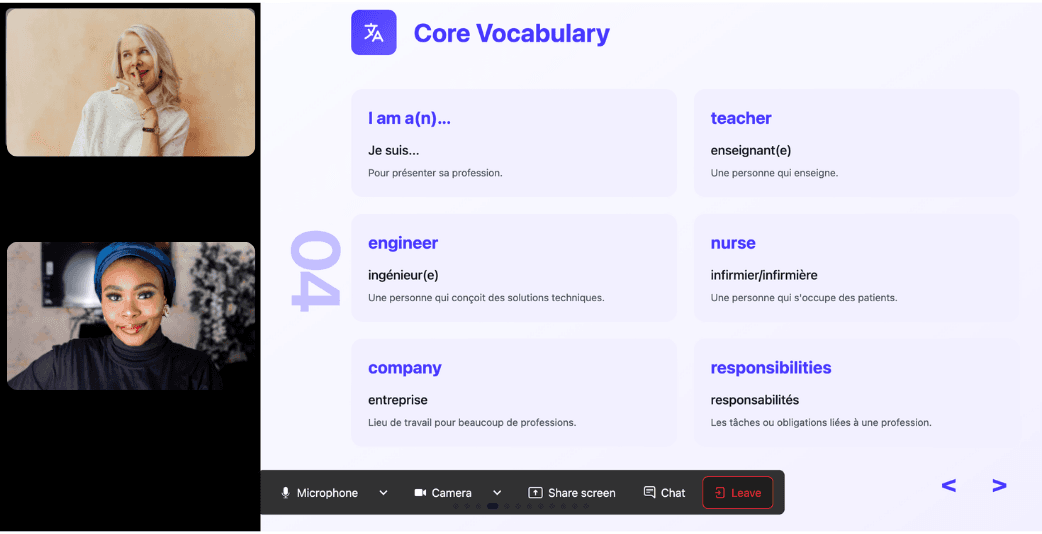
During the lesson, Kylian uses role-plays, real-life examples, and adapts to your learning style. Didn’t understand something? No problem—you can pause Kylian anytime to ask for clarification, without fear of being judged.
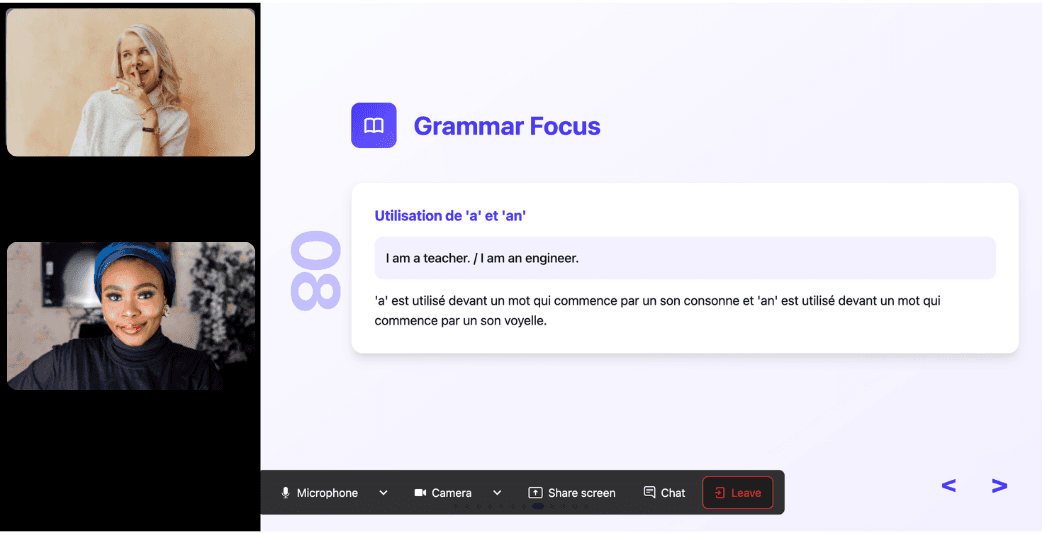
Ask all the questions you want, repeat sections if needed, and customize your learning experience in ways traditional teachers and generic apps simply can’t match.
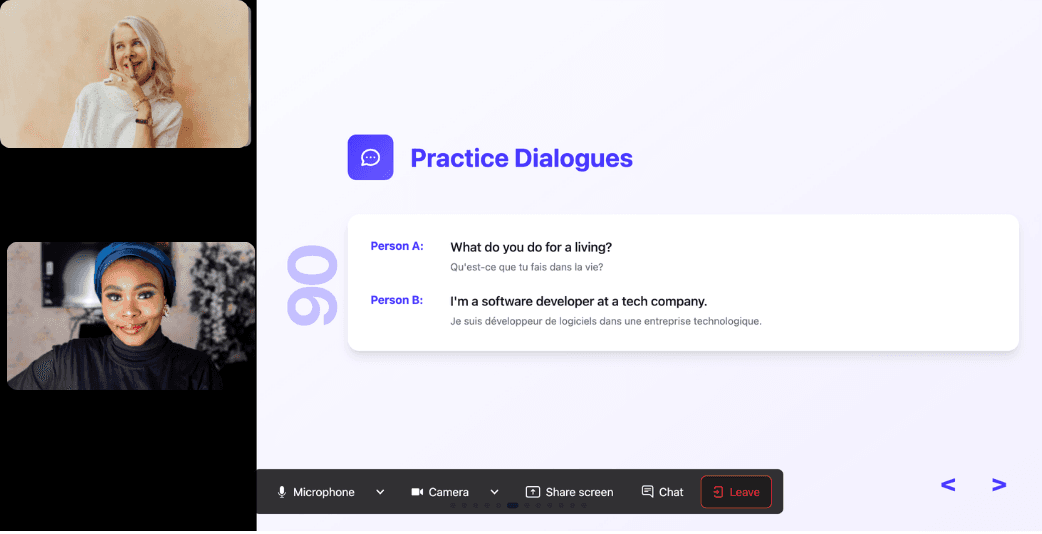
With 24/7 access at a fraction of the cost of private lessons, Kylian removes all the barriers that have kept you from mastering the language you’ve always wanted to learn.
Similar Content You Might Want To Read

14 Main Steps for Moving to Japan: Expat Guide
Relocating to Japan represents a transformative opportunity that combines professional advancement with cultural immersion. This comprehensive guide examines the critical steps required to successfully transition to this dynamic East Asian nation, addressing everything from financial planning to cultural integration.

What Percent of 80 is 60? Basic Math in English
Percentages appear everywhere in our daily lives—from discounts at stores to interest rates on loans, from test scores to statistical analyses. Understanding how to calculate them correctly isn't just an academic exercise; it's a practical skill that empowers informed decision-making. When faced with a question like "what percent of 80 is 60?" many people experience momentary confusion despite the apparent simplicity. This hesitation reveals a common gap in mathematical fluency that affects countless individuals across educational levels. In this comprehensive guide, I'll break down the fundamental concepts behind percentage calculations, provide multiple solution methods for finding what percent of 80 is 60, and equip you with practical techniques to handle similar questions with confidence. By understanding the underlying principles rather than memorizing formulas, you'll develop the critical thinking skills necessary for mathematical reasoning in real-world situations.

How to Learn French Fast: A Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners
French—often called the language of love—carries an undeniable elegance, particularly in its melodic sounds. However, its grammatical complexities, inconsistent spelling patterns, and numerous rule exceptions can intimidate beginners. If you've ever dreamed of conversing with locals in Paris or working for a French organization, you might wonder if achieving proficiency requires years of dedication. The reality? With strategic learning approaches and consistent practice, you can reach basic conversational proficiency in mere months. This guide examines evidence-based methods to accelerate your French learning journey, with actionable steps to implement today. Let's begin!

Spanish Numbers: Master Counting from 0 to 100 and Beyond
Learning to count in Spanish unlocks a fundamental aspect of the language that you'll use daily. Once you understand the key patterns, Spanish numbers become remarkably straightforward to master. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about counting from 0 to 100 and beyond, including the critical differences between cardinal and ordinal numbers.

13 Essential Ways to Say Thank You in Italian
Learning how to say "thank you" in a foreign language is one of the first steps toward meaningful communication. In Italian culture, expressing gratitude appropriately is essential to building relationships and navigating social situations with finesse. Unlike English, which often relies on a single expression with varying intonation, Italian offers numerous phrases to convey appreciation in different contexts. The beauty of the Italian language lies in its ability to express subtle differences in formality, intensity, and relationship through carefully chosen expressions of gratitude. Whether you're a beginner just starting your language journey or an intermediate learner looking to refine your conversational skills, mastering these expressions will significantly enhance your ability to connect with Italian speakers.

Whose' vs. 'Who's': Learn the Difference Easily
In the landscape of commonly confused words in English, the "whose" versus "who's" dilemma ranks high among native and non-native speakers alike. These homophones—words that sound identical but differ in meaning, spelling, and usage—create persistent confusion in written communication. Much like their problematic cousins "there/their/they're" and "it's/its," these terms follow distinct grammatical rules that, once understood, eliminate the potential for error. This comprehensive guide dissects the fundamental differences between "whose" and "who's," providing actionable strategies to distinguish between them in various contexts. By the end of this article, you'll possess the knowledge to deploy these terms with confidence and precision.