Italian Hand Gestures: Meaning & Cultural Charm

Written by
Ernest Bio Bogore

Reviewed by
Ibrahim Litinine
Italian hand gestures represent far more than mere physical expressions; they form a sophisticated non-verbal communication system deeply embedded in Italy's cultural heritage. This comprehensive guide explores the intricate world of Italian gesticulation, examining how these movements enhance communication, their historical context, and their contemporary relevance in Italian society.
The Cultural Backbone of Italian Non-Verbal Communication
When observing Italians in conversation, one quickly notices that verbal communication represents only a fraction of the exchange. The hands take center stage, dancing through the air to convey emotions, emphasize points, and sometimes communicate entire concepts without a single word being spoken.
This gestural communication serves multiple critical functions in Italian interaction:
- It amplifies emotional expression beyond what words alone can convey
- It provides nuance and contextual depth to statements
- It creates rhythmic emphasis that structures conversation
- It maintains cultural continuity through generations
What makes Italian hand gestures particularly fascinating is their codified nature—they aren't random movements but rather a systematic collection of signals with specific meanings recognized throughout Italian society. Understanding these gestures offers profound insight into Italian cultural psychology and social dynamics.
Decoding the Semantic Landscape of Italian Gestures
Italian hand gestures function as a linguistic system with its own grammar and vocabulary. Let's examine some of the most culturally significant gestures and their precise contextual meanings.
1. The Questioning Gesture (Che cosa vuoi?)
When an Italian brings their fingertips together and moves the hand up and down with a slight rotation at the wrist, they're expressing confusion, questioning, or mild frustration. This gesture essentially asks "What do you want?" or "What's going on?" The faster and more pronounced the movement, the greater the emotional intensity behind the question.
2. Culinary Appreciation Gesture (Che squisito!)
The gesture of bringing fingertips to the lips and then moving them outward while making a kissing sound signifies exceptional culinary quality. This expression communicates that something is not merely good but transcendent in its deliciousness. Italians often accompany this with verbal expressions like "Che squisito!" (How exquisite!) or "Da leccarsi i baffi!" (Finger-licking good!).
3. Disinterest Expression (Non mi importa)
To indicate complete disinterest or dismissal, Italians brush their fingers underneath their chin in an outward motion. This gesture conveys that the speaker considers the matter trivial or unworthy of attention. Its directness makes it a powerful signal in conversation that can abruptly redirect discussion.
4. Absence Indication (Non ne ho)
A distinctive gesture formed by extending the index finger while keeping other fingers curled, then rotating the wrist side to side, signifies absence or lack. It clearly communicates "I don't have any" or "There isn't any." This efficient signal eliminates the need for lengthy explanations in contexts ranging from shopping to responding to requests.
5. Affirmation Signal (Va bene)
The internationally recognized "OK" gesture—forming a circle with the thumb and index finger—holds strong significance in Italian culture as well. However, Italians often emphasize this gesture with additional wrist movement or by holding the position longer to reinforce agreement or satisfaction with an arrangement.
6. Summoning Motion (Vieni qui)
Unlike the American beckoning gesture with the palm facing upward, Italians summon others with the palm facing downward, making a scooping motion toward themselves. This subtle difference highlights how even seemingly universal gestures can have cultural variations that reveal deeper cultural patterns.
7. Olfactory Displeasure (Che puzza)
Waving a hand in front of the nose with a grimace effectively communicates that something smells unpleasant. This gesture transcends verbal barriers and clearly conveys disgust at offensive odors without requiring explanation.
8. Ambivalence Indication (Così così)
The Italian "so-so" gesture involves extending the hand with fingers together and rocking it from side to side. This nuanced gesture communicates mediocrity, uncertainty, or moderate satisfaction—conveying complex emotional states that might otherwise require extensive explanation.
9. Hunger Expression (Ho fame)
Tapping the fingertips against the stomach area in a rhythmic pattern universally communicates hunger in Italian gesture vocabulary. This direct, body-referenced movement connects physical sensation with communication in a remarkably efficient manner.
10. Auditory Clarification Request (Non ho capito)
Cupping the hand behind the ear while leaning slightly forward signals that the person didn't hear or understand what was said. This gesture efficiently requests repetition without interrupting conversation flow with verbal questions.
Regional Variations in Italian Gestural Communication
Italy's rich tapestry of regional cultures extends to its gestural language. The same physical movement can carry dramatically different meanings across regions—a fascinating reflection of Italy's historical development as a collection of distinct city-states and kingdoms before unification.
In Sicily, for instance, certain gestures appear with greater frequency and intensity than in Lombardy. Northern Italian gestural vocabulary tends toward more restrained movements, while southern regions often employ more expansive, elaborate gestures—reflecting broader cultural differences in expressiveness and social interaction norms.
These regional variations demand awareness from travelers and newcomers to avoid potential social misunderstandings. A gesture warmly received in Naples might cause offense in Milan, highlighting the importance of contextual knowledge when navigating Italian non-verbal communication.
The Historical Evolution of Italian Hand Gestures
Italian hand gestures boast a remarkably ancient lineage. Evidence from Ancient Roman art, literature, and rhetorical texts reveals that many contemporary Italian gestures have direct historical antecedents dating back millennia.
Quintilian's "Institutio Oratoria," a first-century CE text on rhetoric, extensively documents hand movements that bear striking resemblance to modern Italian gestures. This historical continuity suggests that gestural communication serves as a living archaeological artifact—preserving cultural patterns across centuries.
Several factors contributed to the particularly rich development of gestural communication in Italy:
- Historical multilingualism in the Italian peninsula before unification
- The need for merchants to communicate across language barriers
- Urban density creating social environments where subtle non-verbal cues had high utility
- Theatrical traditions that emphasized physically expressive performance
This historical perspective reveals that Italian gestures aren't merely contemporary cultural quirks but rather sophisticated communication tools refined across generations.
Italian Gestures in Contemporary Social Contexts
Modern Italian society continues to integrate hand gestures into daily communication across various contexts, though with evolving patterns of usage.
Professional Settings
In contemporary professional environments, Italians typically moderate their gestural expressiveness according to formality levels. Business meetings may feature more restrained gestures, while still incorporating key movements to emphasize points or express agreement. However, as conversations become more animated or passionate about particular topics, gesture frequency and intensity often increase accordingly.
Intergenerational Transmission
Younger Italians continue to acquire and use traditional gestures, though research suggests certain historical gestures are becoming less common. Digital communication and globalization introduce new influences, yet core gestural vocabulary remains remarkably stable across generations—particularly within family contexts where gestures are organically transmitted.
Cross-Cultural Interactions
For international visitors and immigrants to Italy, learning key gestures provides significant social advantages. Recognizing and appropriately responding to common gestures facilitates deeper cultural integration and demonstrates respect for Italian communication norms.
Potential Misinterpretations and Cultural Sensitivity
While Italian gestures enrich communication, they also present potential pitfalls for the uninitiated. Certain gestures carry dramatically different meanings across cultures, creating risk for inadvertent offense.
The "horns" gesture (extending index and pinky fingers while holding others down) represents a prime example. While this might signify enthusiasm at rock concerts in some countries, in Italy it traditionally implies marital infidelity—a highly sensitive accusation. Similarly, the "chin flick" interpreted as dismissiveness in Italy might be meaningless elsewhere.
Context significantly influences appropriate gesture usage. Gestures acceptable among friends might be inappropriate in formal settings or with strangers. Cultural sensitivity requires awareness of these contextual nuances and respectful adaptation to local norms.
The Neurocognitive Dimension of Gestural Communication
Research in cognitive neuroscience reveals fascinating insights into how gestures function cognitively. Italian hand gestures activate specialized neural networks bridging language and motor control centers. Studies demonstrate that gesture processing occurs in brain regions partially overlapping with but distinct from pure language processing areas.
For native Italian speakers, observing culturally familiar gestures triggers stronger neural responses than observing unfamiliar movements, suggesting the brain processes these gestures as meaningful linguistic units rather than arbitrary movements.
This neurocognitive perspective explains why immersive learning—observing and practicing gestures in context—proves more effective than attempting to memorize gestures intellectually. The brain must develop appropriate neural pathways connecting visual recognition, meaning attribution, and motor production.
Practical Acquisition Strategies for Italian Gestures
For those seeking to understand and appropriately use Italian gestures, several evidence-based approaches yield effective results:
Immersive Observation
Spend time in authentic Italian social environments—cafés, markets, public squares—observing natural gesture usage in context. Pay attention to:
- Which gestures appear most frequently
- How intensity varies across contexts
- The correlation between verbal and non-verbal elements
- Age and regional differences in gesture usage
Contextual Practice
Rather than practicing gestures in isolation, incorporate them into conversational practice. Begin with basic, widely-used gestures like agreement, questioning, and appreciation. Practice these in appropriate contexts until they feel natural rather than performative.
Cultural Verification
Confirm your understanding of gestures with native Italians before using them extensively. What seems clear from observation might carry nuances or contextual limitations not immediately apparent to outsiders.
Gradual Integration
Introduce gestures progressively into your communication repertoire, beginning with universally acceptable gestures before attempting more culturally specific or potentially sensitive movements.
The Global Influence of Italian Gestural Communication
Italian gestures have achieved remarkable international recognition, becoming cultural emblems that transcend borders. Films, television programs, and even advertising frequently reference iconic Italian gestures, sometimes perpetuating stereotypes but also celebrating this distinctive aspect of Italian cultural heritage.
In multicultural urban centers worldwide, certain Italian gestures have been adopted into broader gestural vocabularies, particularly in food-related contexts and emotional expressions. This cultural diffusion demonstrates the communicative power and appeal of these movements beyond their original context.
The global fascination with Italian gestural communication reflects broader appreciation for Italy's expressive cultural contributions. The gestures embody values of emotional authenticity, conversational engagement, and social connection that resonate across cultural boundaries.
The Future of Italian Hand Gestures in a Digital Era
As communication increasingly occurs in digital spaces, Italian gestural tradition faces new challenges and opportunities. Video communication platforms preserve the visual component essential for gestures, but limit the three-dimensional and spatial qualities that give many gestures their full impact.
Emoji and GIF communication incorporates simplified versions of some traditional Italian gestures, creating digital approximations of gestural communication. The "Italian hand" emoji 🤌 represents perhaps the most recognized digital translation of an Italian gesture, though it flattens the dynamic nature of actual gestural communication.
Despite these technological mediations, the embodied nature of Italian gestural communication ensures its continued relevance. The deep integration of these movements into Italian cultural identity and social interaction suggests they will adapt to new contexts rather than disappear.
Learn Any Language with Kylian AI
Private language lessons are expensive. Paying between 15 and 50 euros per lesson isn’t realistic for most people—especially when dozens of sessions are needed to see real progress.
Many learners give up on language learning due to these high costs, missing out on valuable professional and personal opportunities.
That’s why we created Kylian: to make language learning accessible to everyone and help people master a foreign language without breaking the bank.
To get started, just tell Kylian which language you want to learn and what your native language is
Tired of teachers who don’t understand your specific struggles as a French speaker? Kylian’s advantage lies in its ability to teach any language using your native tongue as the foundation.
Unlike generic apps that offer the same content to everyone, Kylian explains concepts in your native language (French) and switches to the target language when necessary—perfectly adapting to your level and needs.
This personalization removes the frustration and confusion that are so common in traditional language learning.
Choose a specific topic you want to learn
Frustrated by language lessons that never cover exactly what you need? Kylian can teach you any aspect of a language—from pronunciation to advanced grammar—by focusing on your specific goals.
Avoid vague requests like “How can I improve my accent?” and be precise: “How do I pronounce the R like a native English speaker?” or “How do I conjugate the verb ‘to be’ in the present tense?”
With Kylian, you’ll never again pay for irrelevant content or feel embarrassed asking “too basic” questions to a teacher. Your learning plan is entirely personalized.
Once you’ve chosen your topic, just hit the “Generate a Lesson” button, and within seconds, you’ll get a lesson designed exclusively for you.
Join the room to begin your lesson
The session feels like a one-on-one language class with a human tutor—but without the high price or time constraints.
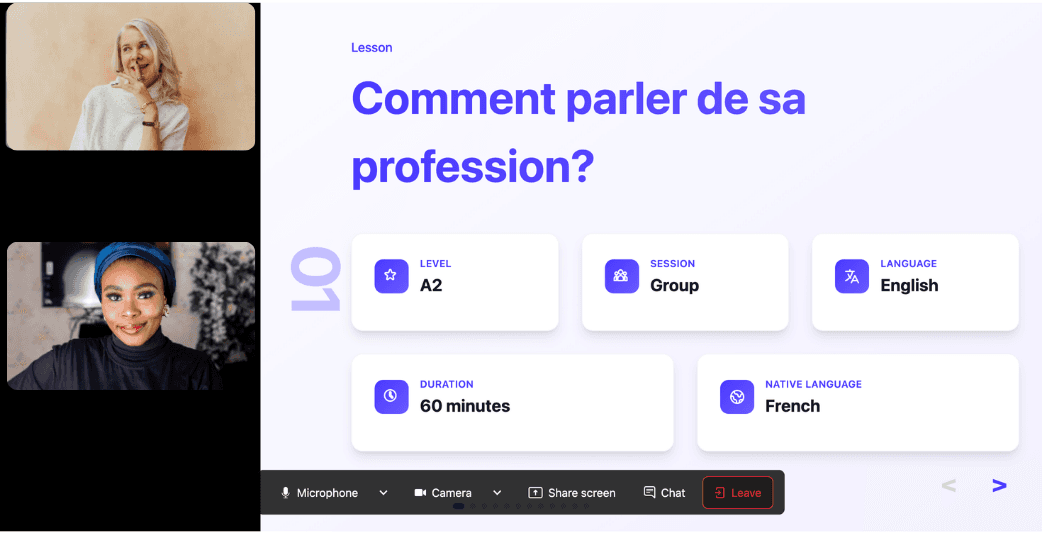
In a 25-minute lesson, Kylian teaches exactly what you need to know about your chosen topic: the nuances that textbooks never explain, key cultural differences between French and your target language, grammar rules, and much more.
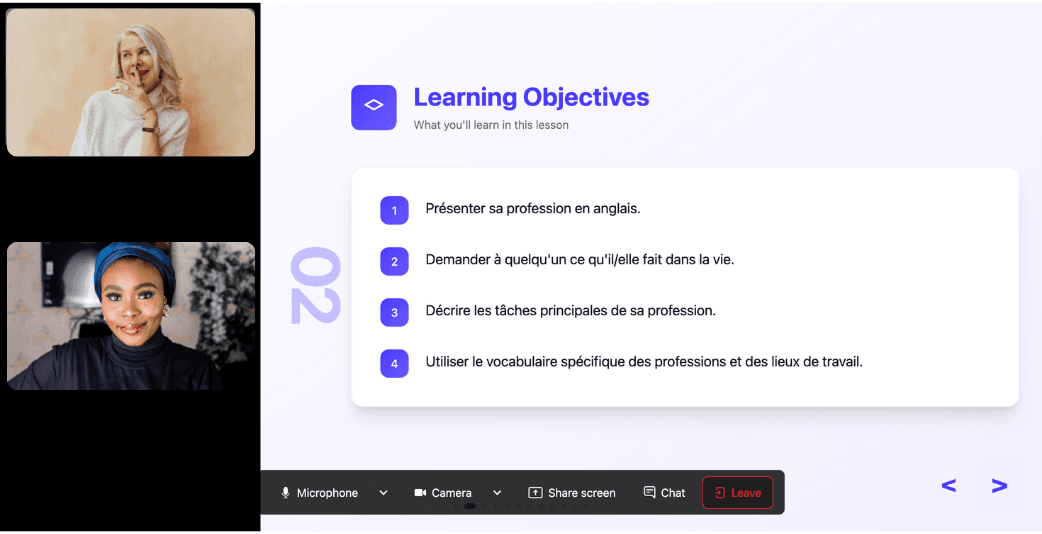
Ever felt frustrated trying to keep up with a native-speaking teacher, or embarrassed to ask for something to be repeated? With Kylian, that problem disappears. It switches intelligently between French and the target language depending on your level, helping you understand every concept at your own pace.
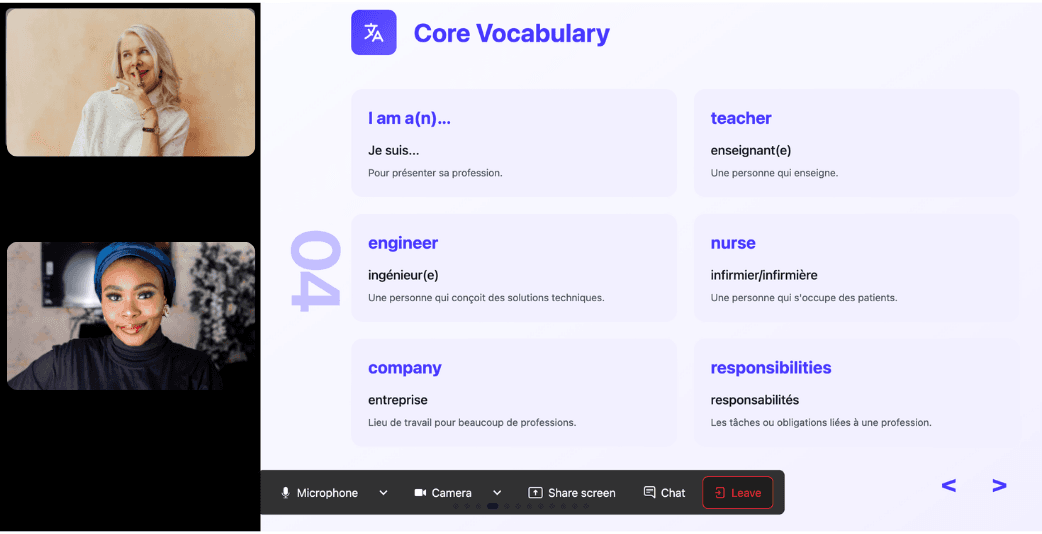
During the lesson, Kylian uses role-plays, real-life examples, and adapts to your learning style. Didn’t understand something? No problem—you can pause Kylian anytime to ask for clarification, without fear of being judged.
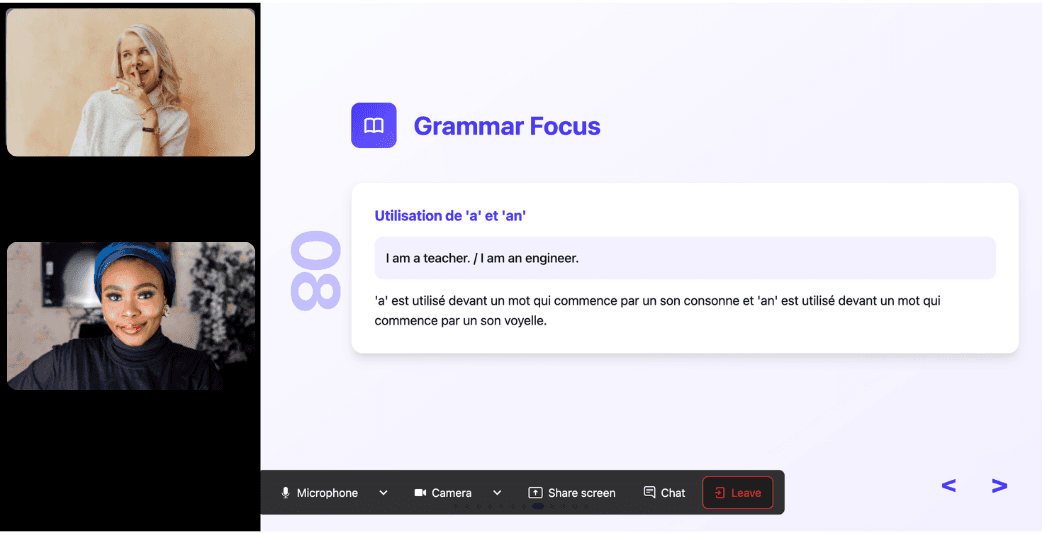
Ask all the questions you want, repeat sections if needed, and customize your learning experience in ways traditional teachers and generic apps simply can’t match.
With 24/7 access at a fraction of the cost of private lessons, Kylian removes all the barriers that have kept you from mastering the language you’ve always wanted to learn.
Similar Content You Might Want To Read

Better Ways to Say "I Like" and "I Don't Like" in English
Do you find yourself repeatedly using the same phrases to express your preferences? The ability to articulate what you enjoy or dislike with precision and variety not only enriches your conversations but also demonstrates language proficiency. This article explores alternative expressions to the common "I like" and "I don't like" statements, providing you with a diverse vocabulary arsenal to communicate your preferences more effectively.

The Worst Passive-Aggressive Phrases in American English
In a culture where direct confrontation is often avoided, passive-aggressive communication thrives. It manifests through subtle jabs, intentional silence, and phrases that sound innocuous but carry undertones of hostility. Our recent survey of over 1,200 Americans reveals not only which phrases Americans find most passive-aggressive but also who tends to use them and where they're most prevalent.

17 Most Common Text Abbreviations in English: Decoded
In today's digitally-driven world, text message abbreviations have become an essential component of modern communication. These shorthand expressions not only streamline our digital conversations but also create a shared linguistic framework among English speakers worldwide. For anyone navigating English-language digital spaces—whether you're learning the language or simply trying to decode what your teenager just sent you—understanding these abbreviations is increasingly vital.

30 Spanish Tongue Twisters to Perfect Your Pronunciation
Spanish tongue twisters (or "trabalenguas") offer an entertaining yet effective way to improve your pronunciation skills. These challenging phrases combine similar sounds in sequences that require focus, concentration, and practice to pronounce correctly. From beginners to advanced learners, tongue twisters can help you master specific Spanish sounds that might not exist in your native language. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore a collection of Spanish tongue twisters organized by difficulty level, complete with pronunciations, translations, and explanations of the specific sounds they help you practice.

The Useful Guide to Saying "Thank You" in Portuguese
In the realm of language acquisition, mastering expressions of gratitude stands as a fundamental milestone. When venturing into Portuguese-speaking territories—whether the bustling streets of Lisbon or the vibrant beaches of Rio de Janeiro—knowing how to properly express thanks transcends mere politeness; it establishes meaningful connection. The Portuguese language, like many Romance languages, incorporates nuanced ways to express gratitude that vary depending on context, relationship, and even the speaker's gender identity. This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted approaches to saying "thank you" in Portuguese, equipping you with practical knowledge for authentic interactions.
![50 Essential Spanish Words for Beginners [+ Translation]](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcdn.sanity.io%2Fimages%2F147z5m2d%2Fproduction%2F4f4eb1df25a5c2b15e1dcfed1009d2edb7db9a64-2240x1260.png%3Frect%3D175%2C0%2C1890%2C1260%26w%3D600%26h%3D400&w=3840&q=75)
50 Essential Spanish Words for Beginners [+ Translation]
Speaking even just a few words of Spanish can significantly enhance your travel experience in Spanish-speaking countries. While you'll undoubtedly encounter locals who speak English, making an effort to communicate in their native language demonstrates respect and friendliness that opens doors to more authentic connections. Let's explore 50 fundamental Spanish words and phrases that will help you navigate conversations with confidence during your travels.