How Accurate is Google Translate? Testing AI Translation

Written by
Ernest Bio Bogore

Reviewed by
Ibrahim Litinine
Google Translate stands as the world's most widely used translation platform. Launched in 2006, it has evolved dramatically through machine learning advancements, particularly with the implementation of Google Neural Machine Translation (GNMT). But a critical question remains: can automated translation truly rival the nuanced understanding of bilingual humans?
We conducted a comprehensive analysis to determine Google Translate's true capabilities across different languages and content types.
The Translation Accuracy Experiment
As machine translation becomes increasingly integrated into global communication, understanding its limitations is essential. Our analysis examined Google Translate's performance when handling three distinct content categories: literary texts, business communications, and conversational phrases.
For each category, we analyzed translations between English, Spanish, German, and Italian, measuring accuracy, readability, and error frequency. The results reveal important distinctions in how machine translation performs across different contexts.
Accuracy Rates Across Content Types
Our research revealed significant performance variations depending on content type:
Literary texts demonstrated the highest accuracy at 96.35%, with only 0.36 mistakes per 10 words and a readability score of 6.03 out of 10. Business content followed with 94.43% accuracy, showing 0.56 mistakes per 10 words and the highest readability score of 7.40. Most notably, conversational phrases performed substantially worse, achieving only 72.29% accuracy with 2.77 mistakes per 10 words and a moderate readability score of 5.28.
The data clearly demonstrates Google Translate's effectiveness with formal, structured content while struggling significantly with colloquial expressions. This is unsurprising given the algorithmic nature of machine translation, which lacks human contextual understanding and cultural awareness.
The Colloquial Challenge: Google Translate's Biggest Weakness
The most striking finding from our research is Google Translate's difficulty with everyday conversational language. At only 72.29% accuracy for colloquial phrases, it falls dramatically short compared to its performance with more structured content.
When attempting to translate idiomatic expressions like "break a leg" or regional phrases specific to certain countries, Google Translate frequently delivers literal interpretations that miss cultural nuance. For example, when translating the Spanish phrase "ponerse las pilas" (literally "to put in batteries" but meaning "to get one's act together"), Google often produces confusing literal interpretations.
This represents the fundamental limitation of AI translation: the inability to fully grasp human contextual and emotional elements that give language its richness. Machine learning models can analyze patterns but struggle to interpret the uniquely human aspects of communication that vary by region and culture.
Language-Specific Performance: Which Languages Work Best?
Our analysis ranked Google Translate's accuracy across four major European languages:
When translating into English, Google Translate achieved its highest accuracy at 97.18%, with only 0.28 mistakes per 10 words, though readability remained moderate at 5.74 out of 10. Spanish followed closely with 96.58% accuracy, 0.34 mistakes per 10 words, and the highest readability rating of 7.38. German translations showed 94.56% accuracy with 0.54 mistakes per 10 words and a readability score of 6.82. Italian proved most challenging with 94.12% accuracy, 0.59 mistakes per 10 words, and the lowest readability rating at just 4.50 out of 10.
These findings reveal important patterns about how machine translation performs across different language pairs.
English: Google Translate's Strongest Language
Google Translate demonstrates superior performance when translating content into English, with an impressive 97.18% accuracy rate and only 0.28 mistakes per 10 words. This strength likely stems from English's dominance on the internet, providing the AI with substantially more English language data to learn from.
The algorithmic advantage comes from exposure: with English being the most prevalent language online, Google Translate's neural networks have been trained on vastly more English content than other languages. This makes the system functionally closer to an "English native speaker" in its ability to produce natural-sounding output.
However, despite the high accuracy, translations into English received a moderate readability score of 5.74/10, suggesting that while technically correct, the translations don't always capture the natural flow of native expression.
Spanish: Strong Performance with High Readability
Spanish ranked second in our analysis with 96.58% accuracy and only 0.34 mistakes per 10 words. More impressively, Spanish translations received the highest readability rating at 7.38/10, indicating that Google Translate produces not just accurate but naturally flowing Spanish text.
This strong performance may result from Spanish being the second most spoken native language globally and having relatively standardized grammar rules. The abundance of Spanish content online gives Google Translate's algorithms robust training data.
For tourists in Spanish-speaking countries, Google Translate can effectively handle basic communication needs. However, for deeper conversations or professional contexts, the limitations become apparent quickly. When attempting to discuss complex topics or understand regional Spanish variations, Google Translate's capabilities diminish rapidly.
German and Italian: The Challenging Frontier
Google Translate faces its greatest challenges with German and Italian translations. German achieved 94.56% accuracy with 0.54 mistakes per 10 words, while Italian showed slightly lower accuracy at 94.12% with 0.59 mistakes per 10 words.
Most notably, Italian translations received the lowest readability score (4.50/10), indicating that even when translations are technically correct, they often sound unnatural to native speakers due to awkward phrasing and structure.
These challenges stem from linguistic and cultural factors:
- German combines words to form compound nouns and has complex grammatical cases that require contextual understanding to apply correctly.
- Italian contains significant regional variations and nuances that evolved through diverse historical influences across different parts of Italy.
Without deep cultural and linguistic knowledge, accurate translation becomes extraordinarily difficult. As one language expert noted, "The grammar, style and contextual cultural differences between German and English make translation particularly challenging, while Italian varies dramatically by region based on historical and linguistic evolution."
Use Cases: When Google Translate Works (And When It Doesn't)
Understanding Google Translate's strengths and limitations helps determine when it's appropriate to rely on machine translation.
Effective Use Cases
- Reading foreign websites: For basic comprehension of foreign language content, Google Translate provides sufficient accuracy to understand the main points.
- Simple travel communication: Basic questions about directions, ordering food, or reading signs can be handled reasonably well.
- Translating formal documents: Business documents, technical materials, and standardized content generally translate with high accuracy.
Problematic Use Cases
- Literary translation: The subtle nuances, cultural references, and artistic elements of literature require human translation to preserve meaning and style.
- Business negotiations: Complex discussions involving industry terminology, cultural business norms, and nuanced proposals require human translation.
- Medical or legal content: Fields with specialized terminology and where miscommunication could have serious consequences demand professional human translation.
- Colloquial conversation: Daily expressions, slang, humor, and regional phrases often translate poorly or nonsensically.
The Evolution of Machine Translation: Progress and Limitations
Google Translate has undeniably improved since its inception. The shift from statistical machine translation to neural machine translation (NMT) in 2016 marked a significant advancement, enabling the system to process entire sentences rather than fragmented phrases.
Key innovations have included:
- Context-aware translations that consider surrounding words
- Enhanced language detection capabilities
- Offline functionality for mobile users
- Pronunciation assistance and audio output
- Visual translation of signs and text through camera integration
Despite these improvements, fundamental limitations persist. Even the most advanced AI translation lacks:
- Cultural awareness: Understanding cultural contexts, sensitivities, and appropriate expressions.
- Emotional intelligence: Recognizing tone, humor, sarcasm, or emotional nuance.
- Creative interpretation: Making appropriate adaptations when direct translation doesn't convey the intended meaning.
- Ethical judgment: Knowing when certain phrases might be offensive or inappropriate in different contexts.
Machine learning can only approximate these human capacities by analyzing patterns in existing data. It cannot truly understand language the way humans do through lived experience and cultural immersion.
Beyond Google: The Competitive Translation Landscape
While Google Translate dominates the field, other translation technologies offer different strengths:
- DeepL: Often provides more natural-sounding translations for European languages with better contextual understanding.
- Microsoft Translator: Excels in business document translation and integrates well with Microsoft products.
- Baidu Translate: Offers superior performance for Chinese and some Asian languages.
- Yandex Translate: Provides strong capabilities for Russian and Eastern European languages.
The competition continues to drive innovation, though all machine translation services share similar fundamental limitations regarding cultural context and nuance.
Human Translation vs. Machine Translation: The Remaining Gap
For all the technological progress, significant differences persist between human and machine translation:
Human Translation Advantages
- Contextual understanding: Humans grasp implied meanings, connotations, and cultural references.
- Adaptability: Human translators can rework content to maintain the spirit of the original while making it natural in the target language.
- Cultural sensitivity: Professional translators understand cultural norms and can avoid potential misunderstandings or offense.
- Specialized knowledge: Human translators with subject expertise can accurately translate field-specific terminology.
Machine Translation Advantages
- Speed: Instantaneous translation of large volumes of text.
- Cost: Free or low-cost compared to professional human translation.
- Accessibility: Available 24/7 from any connected device.
- Language breadth: Support for over 100 languages, including many with limited professional translator availability.
The Future of Translation Technology
As AI continues to advance, several trends are emerging:
- Multimodal translation: Integrating text, speech, and visual elements for more comprehensive translation experiences.
- Personalized translation: Systems that learn individual user preferences and specialized vocabulary over time.
- Real-time conversation translation: Increasingly fluid translation of live conversations through earbuds and other wearable technology.
- Domain-specific models: Translation systems trained on specialized content for fields like medicine, law, or technical documentation.
Despite these advancements, the fundamental limitations of machine translation will likely persist. AI can approximate human understanding through increasingly sophisticated pattern recognition, but true comprehension of cultural context, emotional subtlety, and creative expression remains uniquely human.
Practical Applications: Making the Most of Google Translate
While acknowledging its limitations, Google Translate remains a valuable tool when used appropriately:
Best Practices for Using Google Translate
- Use simple, clear language: Avoid idioms, slang, or complex sentence structures when inputting text.
- Verify important translations: For critical communications, have a native speaker review machine-translated content.
- Provide context: When possible, translate complete sentences or paragraphs rather than isolated words or phrases.
- Be aware of sensitive content: Exercise caution when translating culturally sensitive, legal, or medical information.
- Compare multiple sources: For important translations, compare results from different translation services.
Learning Languages in the Age of AI Translation
Despite Google Translate's convenience, learning languages remains valuable for several reasons:
- Deeper cultural understanding: Language learning provides insights into cultural perspectives and worldviews.
- Cognitive benefits: Research shows language learning improves memory, problem-solving, and multitasking abilities.
- Professional advantage: Bilingual professionals often command higher salaries and access more opportunities.
- Authentic connections: Speaking someone's language creates more meaningful personal and professional relationships.
- Independence from technology: Language skills function without requiring internet connectivity or devices.
For those committed to language learning, technology serves best as a supplement rather than a replacement for traditional learning methods. The most effective approach combines language courses, conversation practice with native speakers, immersive experiences, and judicious use of translation tools.
Learn Any Language with Kylian AI
Private language lessons are expensive. Paying between 15 and 50 euros per lesson isn’t realistic for most people—especially when dozens of sessions are needed to see real progress.
Many learners give up on language learning due to these high costs, missing out on valuable professional and personal opportunities.
That’s why we created Kylian: to make language learning accessible to everyone and help people master a foreign language without breaking the bank.
To get started, just tell Kylian which language you want to learn and what your native language is
Tired of teachers who don’t understand your specific struggles as a French speaker? Kylian’s advantage lies in its ability to teach any language using your native tongue as the foundation.
Unlike generic apps that offer the same content to everyone, Kylian explains concepts in your native language (French) and switches to the target language when necessary—perfectly adapting to your level and needs.
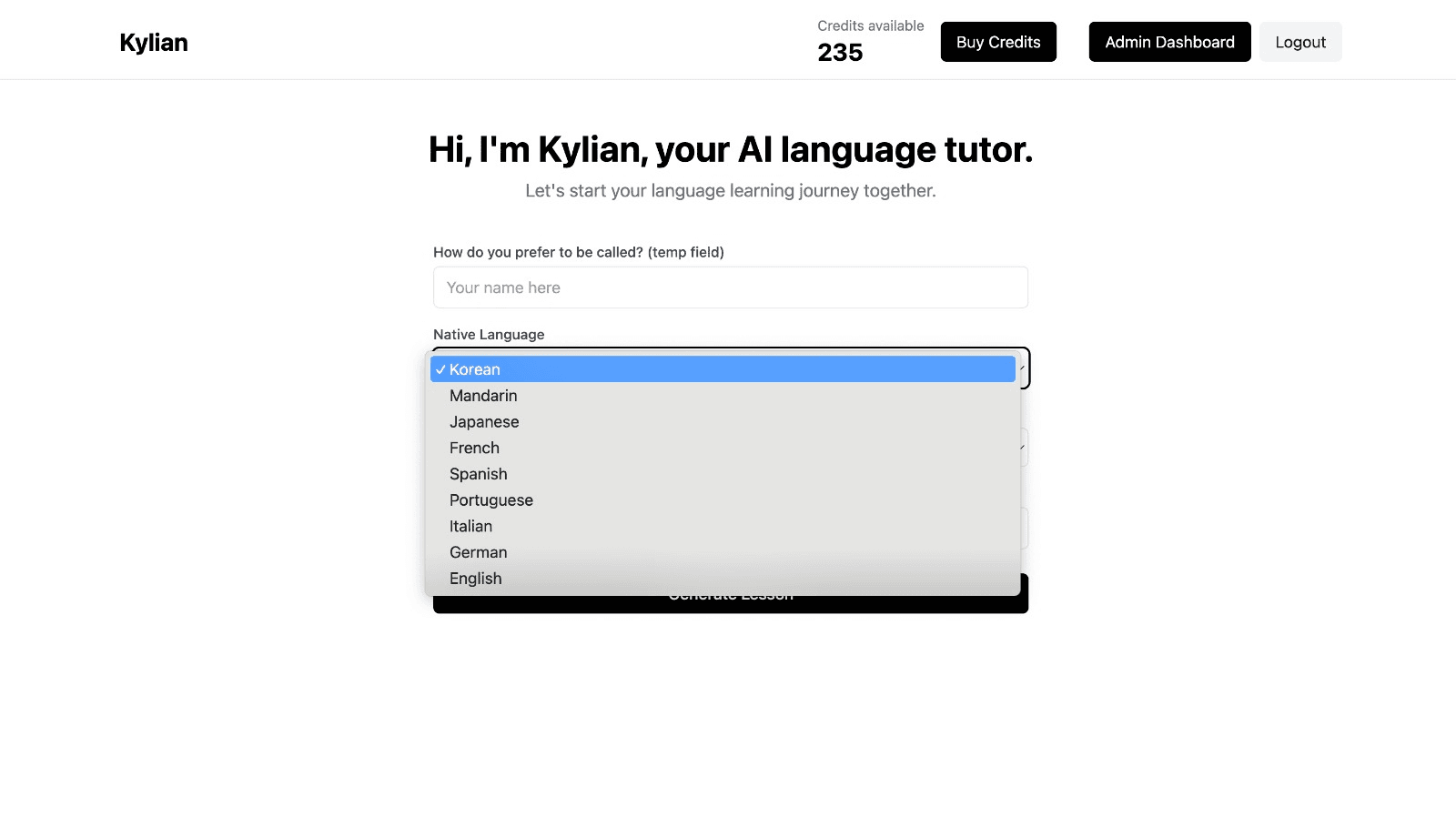
This personalization removes the frustration and confusion that are so common in traditional language learning.
Choose a specific topic you want to learn
Frustrated by language lessons that never cover exactly what you need? Kylian can teach you any aspect of a language—from pronunciation to advanced grammar—by focusing on your specific goals.
Avoid vague requests like “How can I improve my accent?” and be precise: “How do I pronounce the R like a native English speaker?” or “How do I conjugate the verb ‘to be’ in the present tense?”
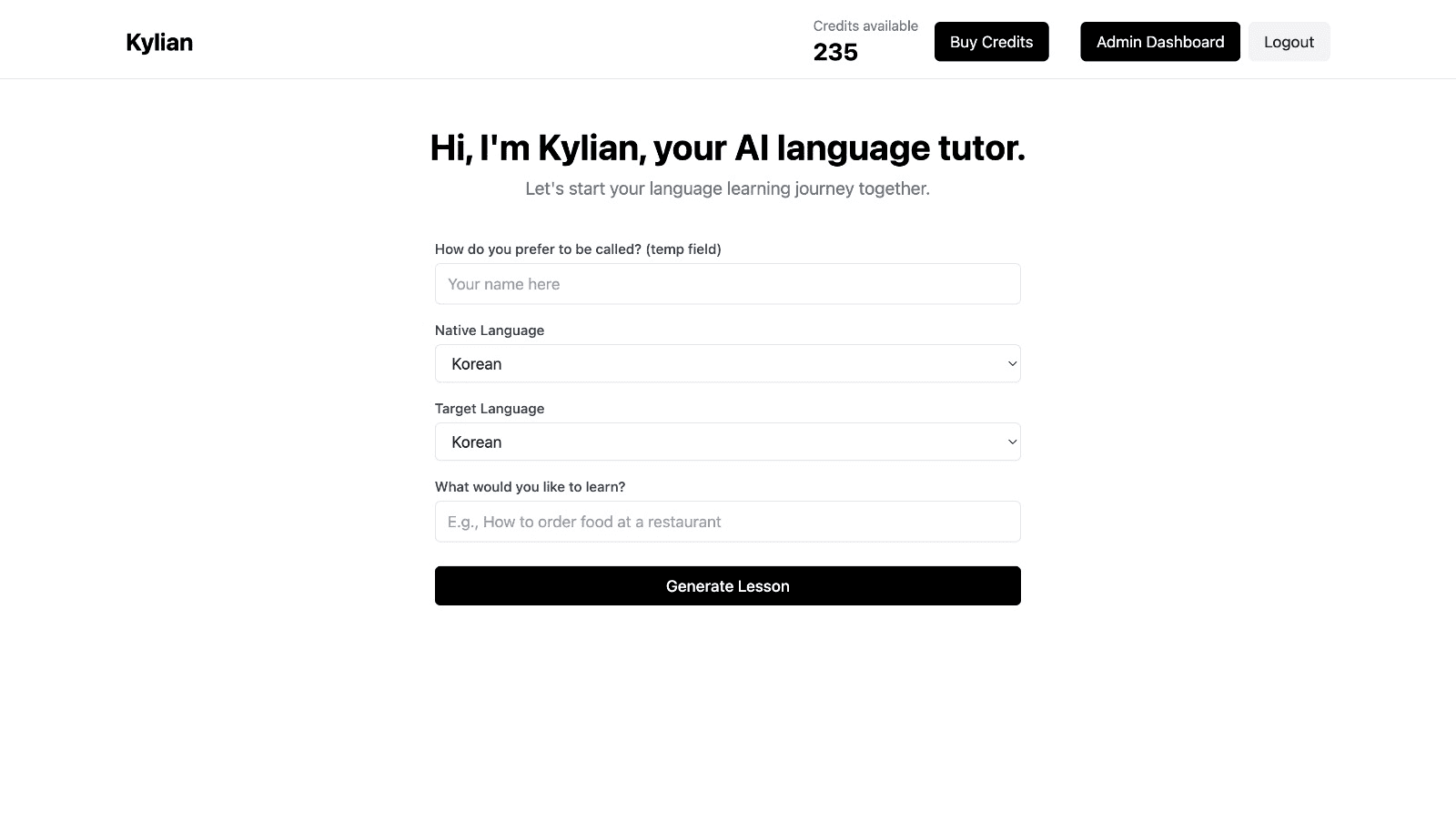
With Kylian, you’ll never again pay for irrelevant content or feel embarrassed asking “too basic” questions to a teacher. Your learning plan is entirely personalized.
Once you’ve chosen your topic, just hit the “Generate a Lesson” button, and within seconds, you’ll get a lesson designed exclusively for you.
Join the room to begin your lesson
The session feels like a one-on-one language class with a human tutor—but without the high price or time constraints.
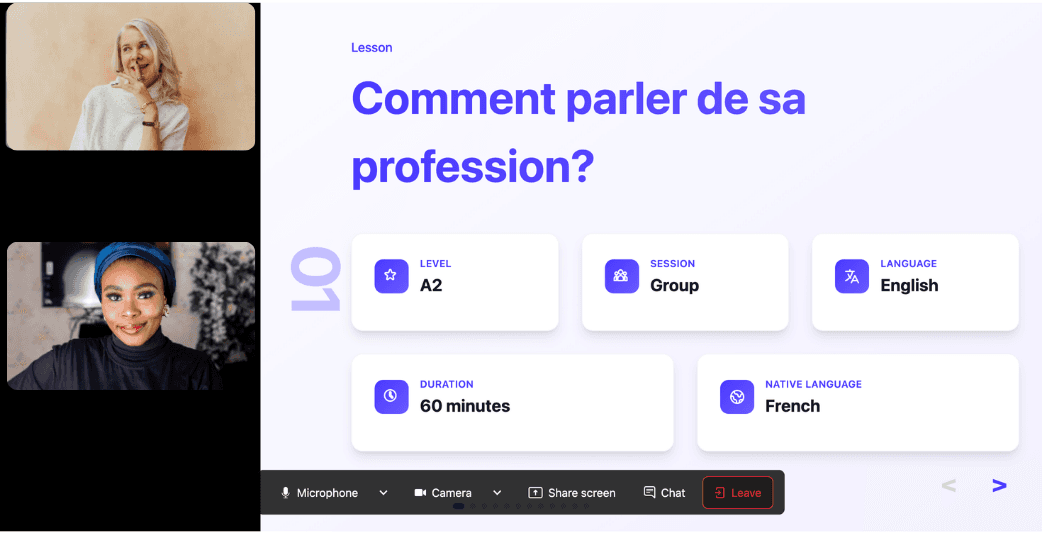
In a 25-minute lesson, Kylian teaches exactly what you need to know about your chosen topic: the nuances that textbooks never explain, key cultural differences between French and your target language, grammar rules, and much more.
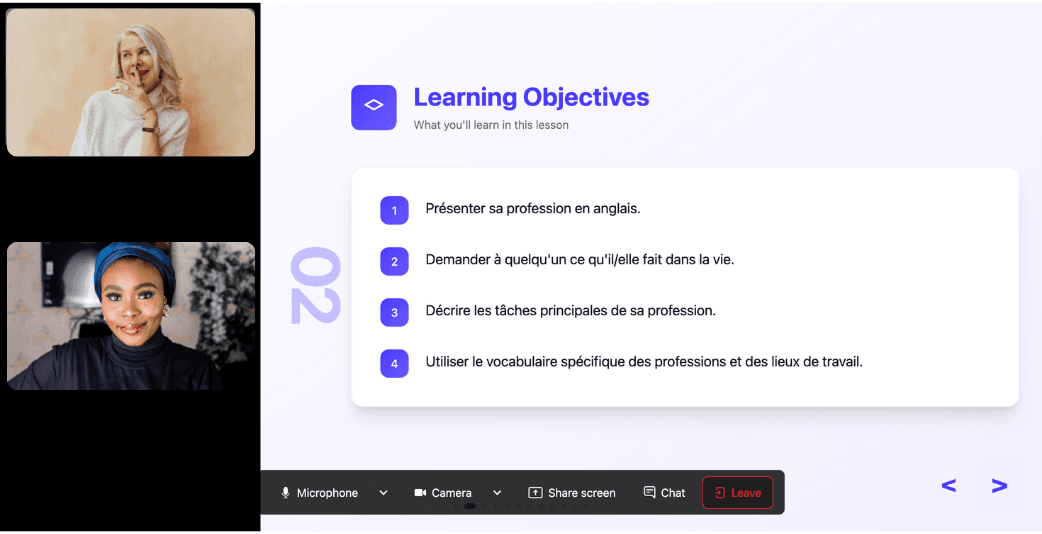
Ever felt frustrated trying to keep up with a native-speaking teacher, or embarrassed to ask for something to be repeated? With Kylian, that problem disappears. It switches intelligently between French and the target language depending on your level, helping you understand every concept at your own pace.
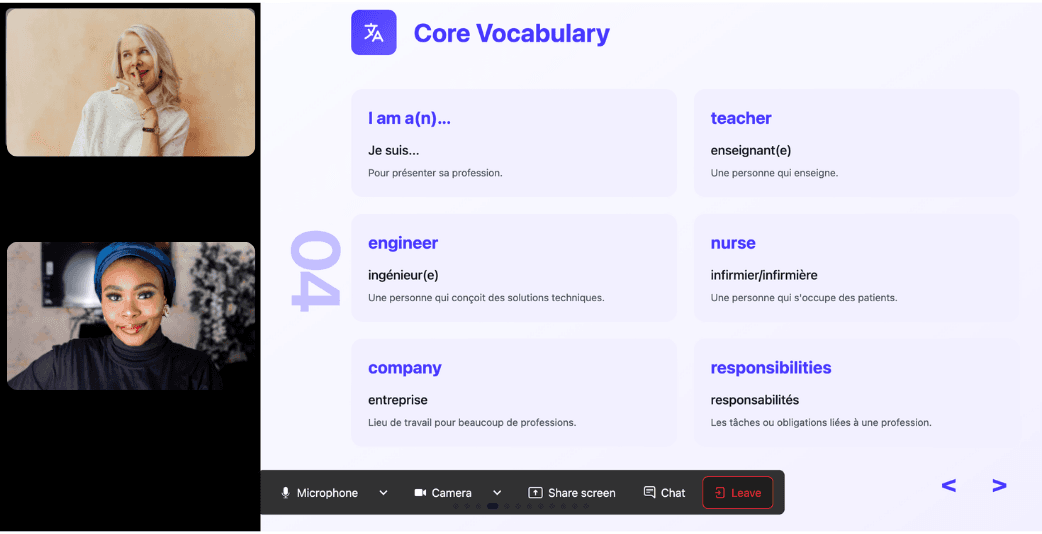
During the lesson, Kylian uses role-plays, real-life examples, and adapts to your learning style. Didn’t understand something? No problem—you can pause Kylian anytime to ask for clarification, without fear of being judged.
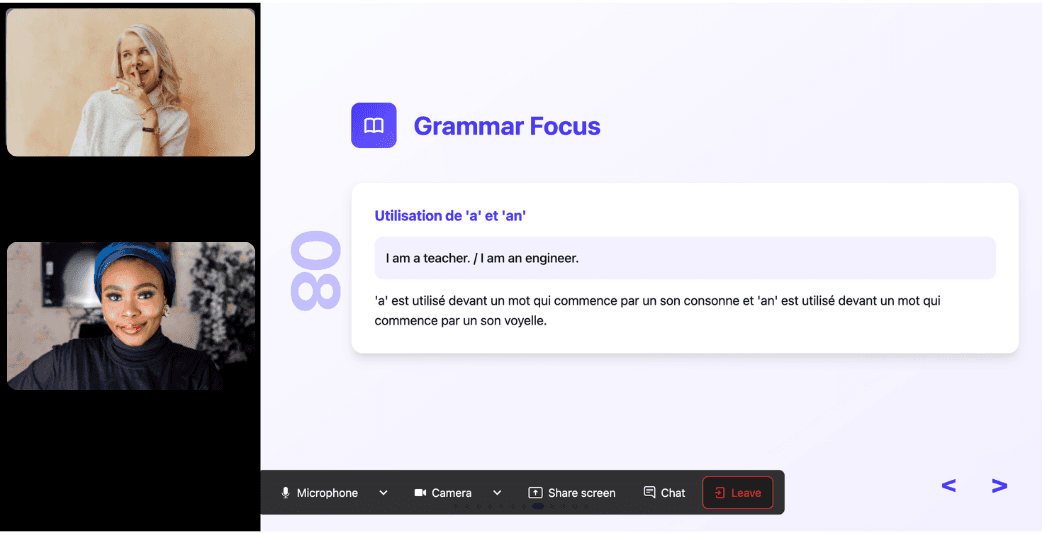
Ask all the questions you want, repeat sections if needed, and customize your learning experience in ways traditional teachers and generic apps simply can’t match.
With 24/7 access at a fraction of the cost of private lessons, Kylian removes all the barriers that have kept you from mastering the language you’ve always wanted to learn.
Similar Content You Might Want To Read

Sports Vocabulary Every Spanish Learner Needs to Know
Learning a language isn't just about mastering grammar rules and memorizing vocabulary lists. It's about acquiring the tools to connect with others in meaningful ways. For many Spanish learners, sports provide an exceptional gateway to authentic conversations and cultural immersion. Understanding sports terminology in Spanish opens doors to discussions that transcend linguistic barriers, creating opportunities for genuine connection. The importance of sports vocabulary extends far beyond the playing field. These terms form part of everyday conversations, news headlines, and cultural references. By mastering this specific lexicon, you're not just learning isolated words—you're gaining access to a vibrant aspect of Spanish-speaking cultures worldwide. This comprehensive guide will equip you with the essential sports vocabulary in Spanish, enabling you to discuss everything from basketball matches to Olympic competitions with confidence and fluency.

Types of Questions in English: A Comprehensive Guide
Feeling overwhelmed by the multitude of question structures in English? You're not alone. Many language learners find themselves intimidated by the seemingly endless variety of question formats they need to master. Rather than focusing on the sheer number of question types, let's approach this systematically. English, with its rich linguistic flexibility, offers multiple ways to express inquiries—and understanding these patterns can significantly enhance your communication skills. This guide breaks down 16 essential question types in English (with practical examples) and demonstrates how mastering them can make your language skills more versatile and natural.

Reflexive Verbs in Spanish: A Comprehensive Guide
Learning a language requires mastering its core grammatical structures. Among these, reflexive verbs in Spanish represent a fundamental concept that dramatically enhances fluency and authenticity in conversation. This comprehensive guide offers clear explanations, actionable strategies, and contextual examples to help you incorporate reflexive verbs naturally into your Spanish communication. Let's explore this crucial element of Spanish grammar to elevate your language proficiency.

Abbreviation for Highway in English: Complete Guide
When navigating road systems across English-speaking countries, understanding highway abbreviations becomes essential for efficient travel planning and communication. The abbreviation "Hwy" stands as the most common shorthand for "highway" in English, though regional variations exist throughout different countries. These abbreviations serve a critical purpose in cartography, GPS systems, address formatting, and everyday navigation instructions. The standardization of highway abbreviations emerged from practical necessity - the need to convey information concisely on road signs, maps, and in written directions while maintaining clarity. This standardization varies between countries like the United States, Canada, Australia, and the United Kingdom, each with their own established systems reflecting local transportation infrastructure development. For travelers, commuters, and transportation professionals alike, mastering these abbreviations isn't merely a convenience but often a necessity for navigating complex road networks. The purpose of this comprehensive guide is to explore the various abbreviations for highways across English-speaking regions, their appropriate usage contexts, and the historical evolution that has shaped these standardized communication systems.

Describing Graphs, Charts & Diagrams in Presentations
The ability to effectively communicate data through visual elements transforms ordinary presentations into compelling narratives. When you master the vocabulary and techniques for describing graphs, charts, and diagrams in English, you position yourself not just as a presenter, but as an authoritative guide who can translate complex information into accessible insights. For non-native English speakers, this skill becomes particularly crucial—whether you're preparing for high-stakes business presentations or standardized language assessments like the IELTS, where data visualization interpretation frequently appears. The following comprehensive guide will equip you with the precise terminology and structured approach necessary to articulate visual data with confidence and clarity.

A Guide to the Italian Alphabet & Letter Pronunciation
Learning a new language begins with understanding its foundational elements. The Italian alphabet serves as the cornerstone of language acquisition, establishing a framework upon which more complex linguistic skills are built. This guide offers a comprehensive breakdown of the Italian alphabet, its pronunciation, and the phonetic patterns that make Italian one of the most melodic languages in the world.