French Irregular Verbs: A Complete Guide for Learners

Written by
Ernest Bio Bogore

Reviewed by
Ibrahim Litinine

Irregular verbs stand as one of the most challenging aspects of learning French. Unlike their predictable regular counterparts, these linguistic wildcards follow their own unique conjugation patterns that can frustrate even dedicated language students. Yet mastering these verbs is essential for anyone serious about achieving fluency in French.
French contains approximately 40% irregular verbs among its most commonly used vocabulary—a significant proportion that demands focused attention from learners. The good news? Behind the apparent chaos lies a system of patterns that, once understood, transforms this intimidating aspect of French grammar into a manageable—even fascinating—linguistic challenge.
This guide explores everything you need to know about French irregular verbs: their defining characteristics, common patterns, effective learning strategies, and practical ways to incorporate them into your language practice. Whether you're a beginner struggling with "être" and "avoir" or an intermediate learner looking to refine your command of more complex verbs, you'll find actionable insights to elevate your French proficiency.
What Exactly Are French Irregular Verbs?
To understand irregular verbs, we must first clarify what makes a verb "regular" in French. Regular verbs follow predictable conjugation patterns based on their infinitive endings:
- -er verbs (like "parler" - to speak): The most common and predictable group
- -ir verbs (like "finir" - to finish): The second most common group
- -re verbs (like "vendre" - to sell): The smallest of the three regular groups
When conjugating regular verbs, you simply remove the infinitive ending (-er, -ir, or -re) and add the appropriate ending for the subject and tense.
Irregular verbs, however, break these rules. They may:
- Change their stems unpredictably
- Use unique endings that don't follow standard patterns
- Have completely different forms across different tenses
- Follow no apparent pattern at all
For example, with the regular verb "parler," you form the present tense "I speak" by removing -er and adding -e: "je parle." But with the irregular verb "aller" (to go), "I go" becomes "je vais"—a form that bears little resemblance to its infinitive.
The Most Essential French Irregular Verbs
Some irregular verbs appear so frequently in everyday French that mastering them early will significantly boost your communication abilities. Here are the most fundamental irregular verbs you should prioritize:
Être (to be)
Present tense:
- Je suis
- Tu es
- Il/elle/on est
- Nous sommes
- Vous êtes
- Ils/elles sont
Example: Je suis étudiant. (I am a student.)
Avoir (to have)
Present tense:
- J'ai
- Tu as
- Il/elle/on a
- Nous avons
- Vous avez
- Ils/elles ont
Example: J'ai un chat noir. (I have a black cat.)
Aller (to go)
Present tense:
- Je vais
- Tu vas
- Il/elle/on va
- Nous allons
- Vous allez
- Ils/elles vont
Example: Nous allons au cinéma ce soir. (We are going to the cinema tonight.)
Faire (to do/make)
Present tense:
- Je fais
- Tu fais
- Il/elle/on fait
- Nous faisons
- Vous faites
- Ils/elles font
Example: Je fais mes devoirs tous les soirs. (I do my homework every evening.)
Venir (to come)
Present tense:
- Je viens
- Tu viens
- Il/elle/on vient
- Nous venons
- Vous venez
- Ils/elles viennent
Example: Ils viennent de Paris. (They come from Paris.)
Dire (to say/tell)
Present tense:
- Je dis
- Tu dis
- Il/elle/on dit
- Nous disons
- Vous dites
- Ils/elles disent
Example: Vous dites toujours la vérité. (You always tell the truth.)
Pouvoir (to be able to/can)
Present tense:
- Je peux
- Tu peux
- Il/elle/on peut
- Nous pouvons
- Vous pouvez
- Ils/elles peuvent
Example: Je peux parler trois langues. (I can speak three languages.)
Vouloir (to want)
Present tense:
- Je veux
- Tu veux
- Il/elle/on veut
- Nous voulons
- Vous voulez
- Ils/elles veulent
Example: Elle veut devenir médecin. (She wants to become a doctor.)
Savoir (to know)
Present tense:
- Je sais
- Tu sais
- Il/elle/on sait
- Nous savons
- Vous savez
- Ils/elles savent
Example: Tu sais jouer du piano? (Do you know how to play the piano?)
Devoir (to have to/must)
Present tense:
- Je dois
- Tu dois
- Il/elle/on doit
- Nous devons
- Vous devez
- Ils/elles doivent
Example: Nous devons partir maintenant. (We have to leave now.)
Decoding the Patterns: French Irregular Verb Categories
While irregular verbs don't follow the standard rules, many share similar patterns of irregularity. Understanding these patterns can significantly reduce the memorization burden.
1. Stem-Changing Verbs
Some verbs maintain regular endings but change their stems in certain conjugations. These often fall into predictable subgroups:
E→È verbs: Verbs like "acheter" (to buy) and "lever" (to raise) change their 'e' to 'è' in certain conjugations.
- J'achète (I buy)
- Tu achètes (You buy)
- Il/elle/on achète (He/she/one buys)
- Nous achetons (We buy)
- Vous achetez (You buy)
- Ils/elles achètent (They buy)
E→É verbs: Verbs like "espérer" (to hope) change their 'e' to 'é' in specific forms.
- J'espère (I hope)
- Tu espères (You hope)
- Il/elle/on espère (He/she/one hopes)
- Nous espérons (We hope)
- Vous espérez (You hope)
- Ils/elles espèrent (They hope)
2. "-IR" Verbs with "-RE" Patterns
Some "-ir" ending verbs adopt conjugation patterns similar to "-re" verbs. Examples include:
- Partir (to leave)
- Dormir (to sleep)
- Sortir (to go out)
Their conjugation follows a distinct pattern:
- Je pars (I leave)
- Tu pars (You leave)
- Il/elle/on part (He/she/one leaves)
- Nous partons (We leave)
- Vous partez (You leave)
- Ils/elles partent (They leave)
3. Verbs with Similar Irregular Patterns
Several groups of verbs share related conjugation patterns:
"-OIR" verbs: Many verbs ending in "-oir" follow similar patterns:
- Voir (to see)
- Recevoir (to receive)
- Pouvoir (to be able to)
"-ENIR" verbs: Verbs ending in "-enir" share conjugation patterns:
- Venir (to come)
- Tenir (to hold)
- Devenir (to become)
"-UIRE" verbs: Verbs like:
- Conduire (to drive)
- Produire (to produce)
- Traduire (to translate)
4. The Complete Irregulars
Some verbs are completely irregular, with forms that must be memorized individually:
- Être (to be)
- Avoir (to have)
- Aller (to go)
- Faire (to do/make)
These foundational verbs have unique conjugations across all tenses and moods.
Strategic Approaches to Mastering Irregular Verbs
Rather than randomly memorizing conjugations, use these strategic approaches to master irregular French verbs more efficiently:
1. Focus on High-Frequency Verbs First
Prioritize the most commonly used irregular verbs: être, avoir, aller, faire, dire, pouvoir, vouloir, savoir, and venir. These appear constantly in everyday French and form the foundation for compound tenses.
2. Learn Verbs in Logical Groups
Instead of tackling random verbs, study those with similar patterns together. For example, learn all the "-enir" verbs as a group (venir, tenir, devenir) to reinforce pattern recognition.
3. Master One Tense at a Time
Start with present tense conjugations before moving to other tenses. The present tense is the most frequently used and serves as the foundation for learning other tenses.
4. Use Mnemonic Devices
Create memory aids for particularly challenging verbs. For instance, to remember the present tense conjugation of "aller" (je vais, tu vas, il va...), you might create a silly sentence or image that helps the forms stick in your memory.
5. Incorporate Verb Drills into Daily Practice
Spend 10 minutes daily drilling irregular verb conjugations. Consistent, spaced repetition is far more effective than occasional marathon study sessions.
6. Leverage Technology
Use spaced repetition apps like Anki or specialized language learning apps that offer conjugation practice.
7. Create Conjugation Tables
Writing out complete conjugation tables by hand creates muscle memory and visual reinforcement of patterns.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Learning irregular French verbs comes with specific challenges. Here's how to address the most common ones:
Challenge 1: Confusing Similar Irregular Verbs
Verbs like "savoir" (to know facts) and "connaître" (to be familiar with) have similar meanings but different conjugations.
Solution: Create comparative charts and practice sentences that highlight the differences. For example:
- Je sais nager. (I know how to swim.)
- Je connais cette ville. (I know this city.)
Challenge 2: Applying Regular Rules to Irregular Verbs
It's tempting to apply regular patterns to irregular verbs, leading to errors like "je *alle" instead of "je vais."
Solution: Practice through frequent exposure and correction. Create flashcards with common error patterns to avoid.
Challenge 3: Remembering Irregular Past Participles
Many learners struggle with irregular past participles needed for compound tenses.
Solution: Create a dedicated study list of irregular past participles:
- Faire → fait
- Voir → vu
- Prendre → pris
- Mettre → mis
Challenge 4: Maintaining Motivation
The sheer number of irregular verbs can feel overwhelming.
Solution: Set small, achievable goals. Perhaps master two irregular verbs per week, complete with all their tenses. Celebrate your progress regularly.
Beyond Memorization: Contextual Learning Techniques
While memorization plays a role in mastering irregular verbs, contextual learning deepens understanding and improves retention.
1. Immersive Reading
Read French texts that naturally incorporate irregular verbs. Children's books, news articles, and graded readers provide accessible exposure.
2. Audio Reinforcement
Listen to French podcasts, songs, and audio lessons. Hearing irregular verbs used naturally strengthens your recognition and recall abilities.
3. Active Speaking Practice
Create sentences using targeted irregular verbs. Practice with language partners or tutors who can provide immediate feedback.
4. Error Analysis
When you make mistakes with irregular verbs, analyze the errors. Understanding why you made a particular mistake helps prevent repetition.
5. Create Verb Stories
Construct short stories that incorporate multiple irregular verbs. For example: "Je suis allé au marché hier. J'ai vu mon ami Pierre. Il m'a dit qu'il voulait faire du shopping. Nous avons pu trouver des vêtements intéressants."
Mastering Tenses: Irregular Verbs Across Time
Once you've built a foundation with present tense irregular verbs, expand your mastery to other crucial tenses:
Past Tense (Passé Composé)
Many irregular verbs use "avoir" as their auxiliary verb, but some key verbs use "être":
- Aller → Je suis allé(e) (I went)
- Venir → Elle est venue (She came)
- Naître → Ils sont nés (They were born)
Others have irregular past participles:
- Boire → J'ai bu (I drank)
- Lire → Tu as lu (You read)
- Voir → Nous avons vu (We saw)
Future Tense (Futur Simple)
Several irregular verbs have unique stems in the future tense:
- Être → Je serai (I will be)
- Avoir → Tu auras (You will have)
- Aller → Il ira (He will go)
- Venir → Nous viendrons (We will come)
Conditional Mood
The conditional mood generally uses the same stem as the future tense:
- Être → Je serais (I would be)
- Faire → Tu ferais (You would do)
- Vouloir → Elle voudrait (She would want)
Digital Resources for Mastering Irregular Verbs
Take advantage of these digital resources to enhance your irregular verb mastery:
- Conjugation apps that allow you to practice on the go
- Interactive websites with conjugation exercises and quizzes
- YouTube channels dedicated to French grammar explanations
- Online flashcard systems with pre-made irregular verb decks
- Language exchange platforms where you can practice with native speakers
Advanced Insight: The Historical Reasons Behind Irregular Verbs
Understanding why irregular verbs exist can help you approach them with curiosity rather than frustration.
French irregular verbs typically have Latin origins and were among the most commonly used verbs even in ancient times. Their frequent usage preserved older conjugation patterns that regular verbs eventually abandoned through standardization. What appears as irregularity today is often a linguistic fossil—a glimpse into earlier forms of the language.
For example, the strange conjugation of "être" derives from multiple Latin verbs (esse, stare, and sedere) that merged over centuries of language evolution.
This historical perspective reminds us that irregular verbs aren't arbitrary complications but living artifacts of language history.
Developing a Personalized Mastery Plan
The most effective approach to conquering French irregular verbs is one tailored to your learning style, goals, and available time. Here's how to develop your personalized mastery plan:
- Assess your current knowledge - Which irregular verbs do you already know? Which cause the most trouble?
- Set specific, measurable goals - Perhaps "Master the present tense of 10 essential irregular verbs by the end of the month."
- Create a study schedule - Consistency trumps intensity. Fifteen minutes daily is more effective than three hours once a week.
- Track your progress - Keep a record of mastered verbs and those still giving you trouble.
- Incorporate regular review sessions - Revisit previously learned verbs to prevent forgetting.
- Seek feedback - Work with teachers or language partners who can correct your usage.
Learn Any Language with Kylian AI
Private language lessons are expensive. Paying between 15 and 50 euros per lesson isn’t realistic for most people—especially when dozens of sessions are needed to see real progress.
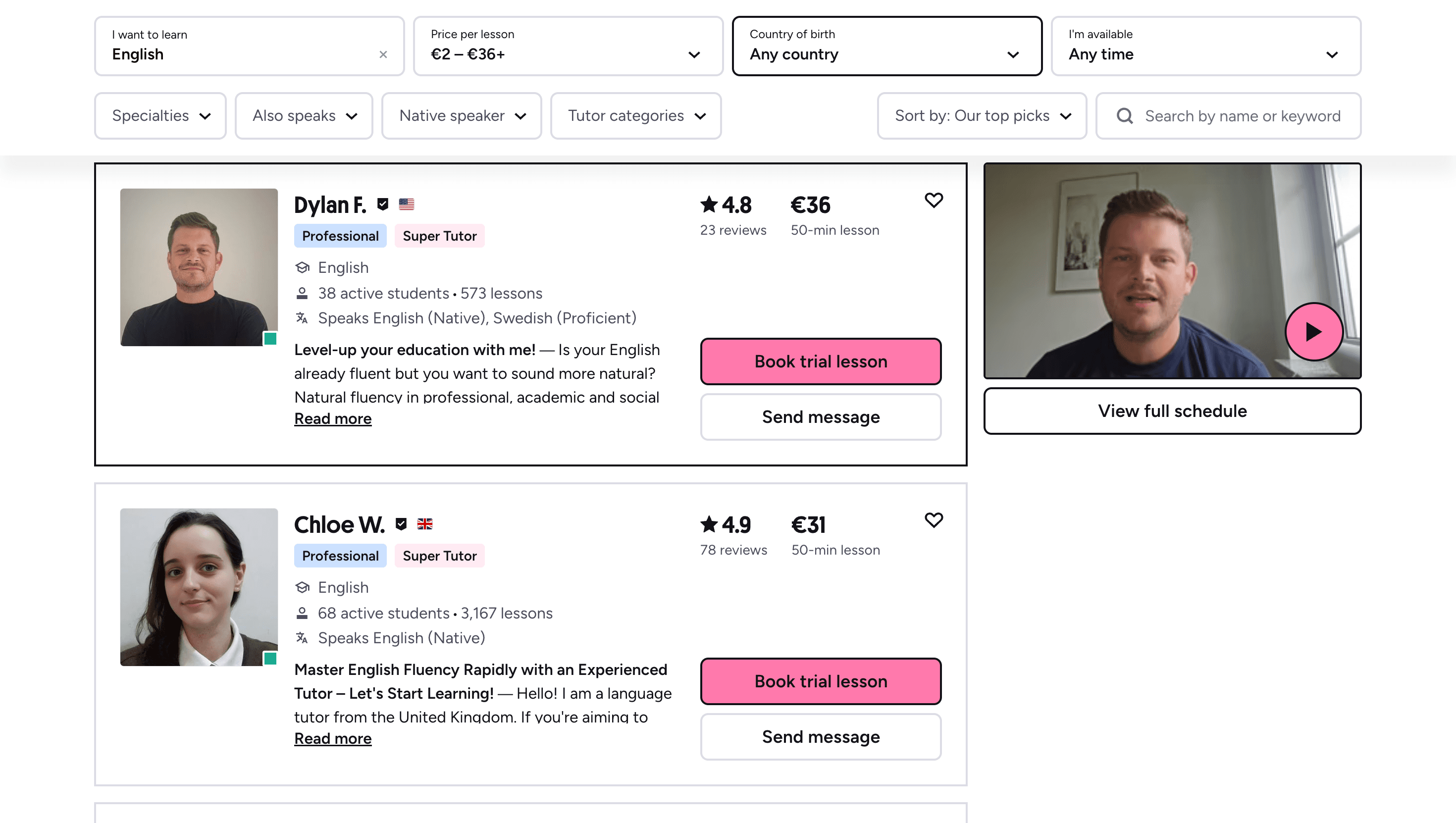
Many learners give up on language learning due to these high costs, missing out on valuable professional and personal opportunities.
That’s why we created Kylian: to make language learning accessible to everyone and help people master a foreign language without breaking the bank.
To get started, just tell Kylian which language you want to learn and what your native language is
Tired of teachers who don’t understand your specific struggles as a French speaker? Kylian’s advantage lies in its ability to teach any language using your native tongue as the foundation.
Unlike generic apps that offer the same content to everyone, Kylian explains concepts in your native language (French) and switches to the target language when necessary—perfectly adapting to your level and needs.
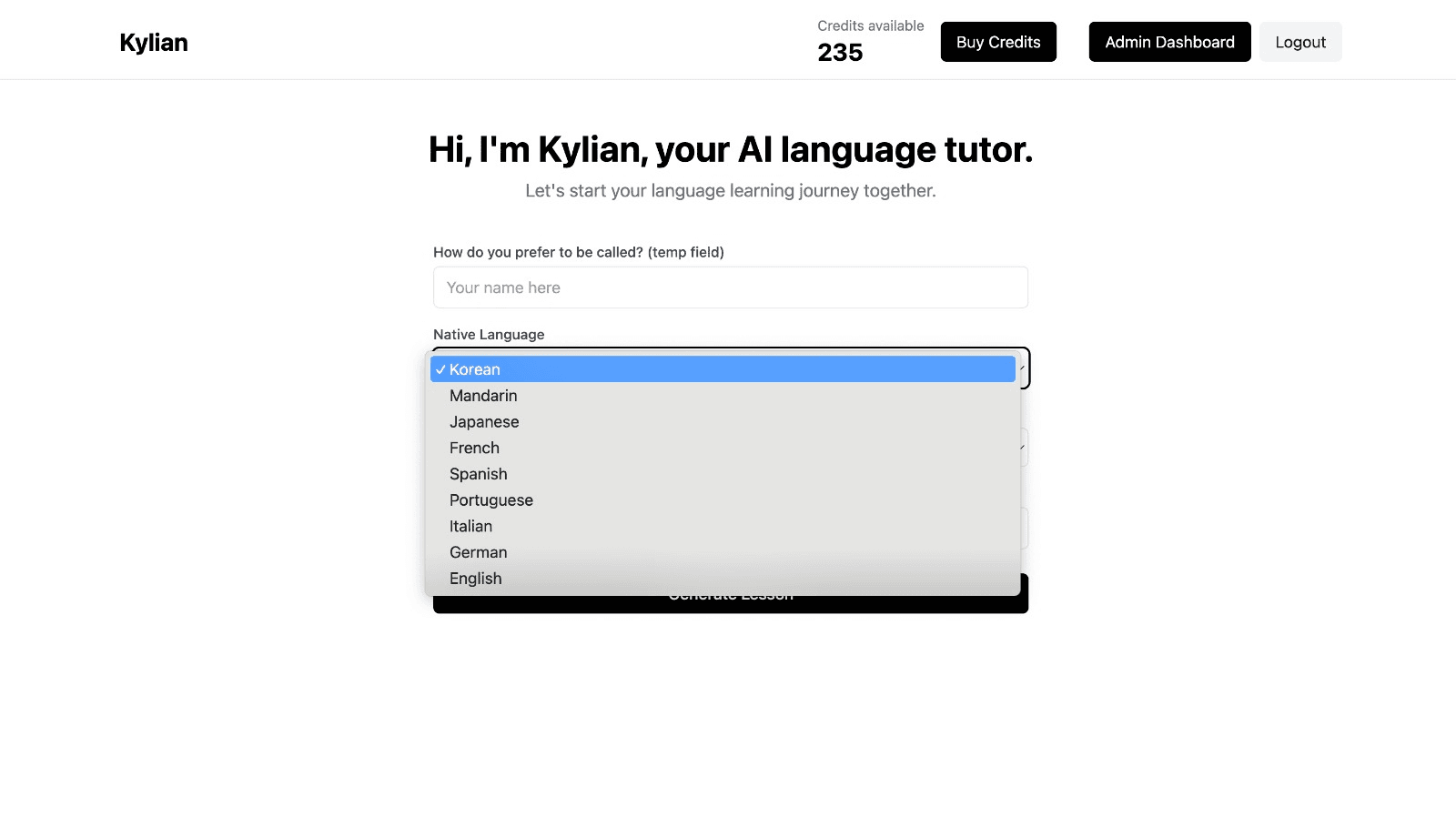
This personalization removes the frustration and confusion that are so common in traditional language learning.
Choose a specific topic you want to learn
Frustrated by language lessons that never cover exactly what you need? Kylian can teach you any aspect of a language—from pronunciation to advanced grammar—by focusing on your specific goals.
Avoid vague requests like “How can I improve my accent?” and be precise: “How do I pronounce the R like a native English speaker?” or “How do I conjugate the verb ‘to be’ in the present tense?”
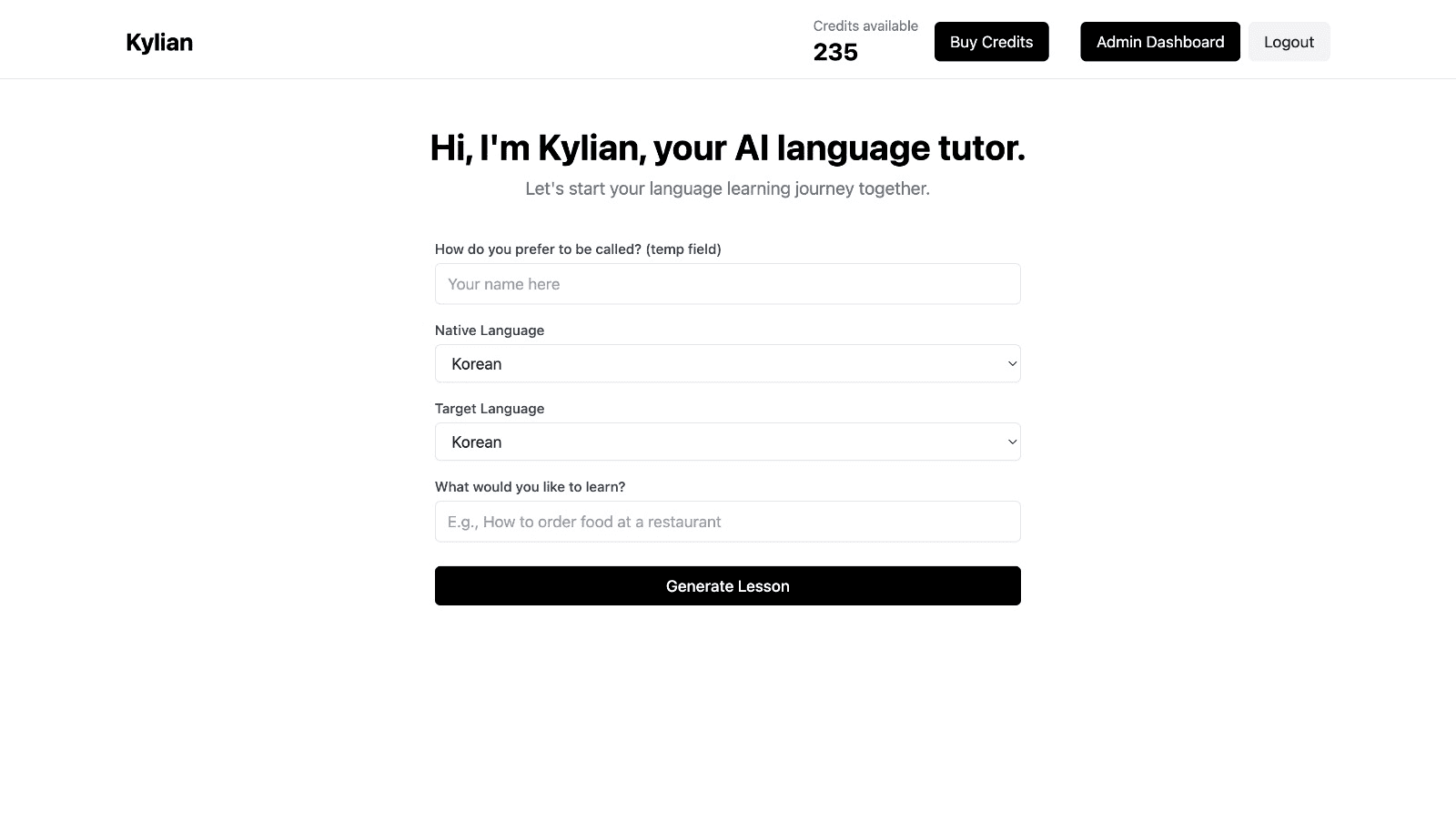
With Kylian, you’ll never again pay for irrelevant content or feel embarrassed asking “too basic” questions to a teacher. Your learning plan is entirely personalized.
Once you’ve chosen your topic, just hit the “Generate a Lesson” button, and within seconds, you’ll get a lesson designed exclusively for you.
Join the room to begin your lesson
The session feels like a one-on-one language class with a human tutor—but without the high price or time constraints.
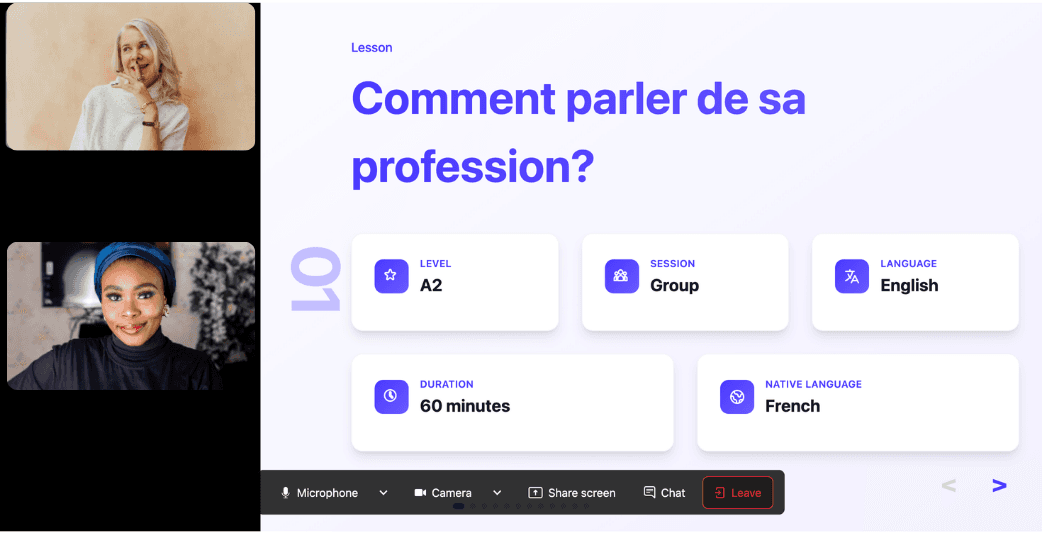
In a 25-minute lesson, Kylian teaches exactly what you need to know about your chosen topic: the nuances that textbooks never explain, key cultural differences between French and your target language, grammar rules, and much more.
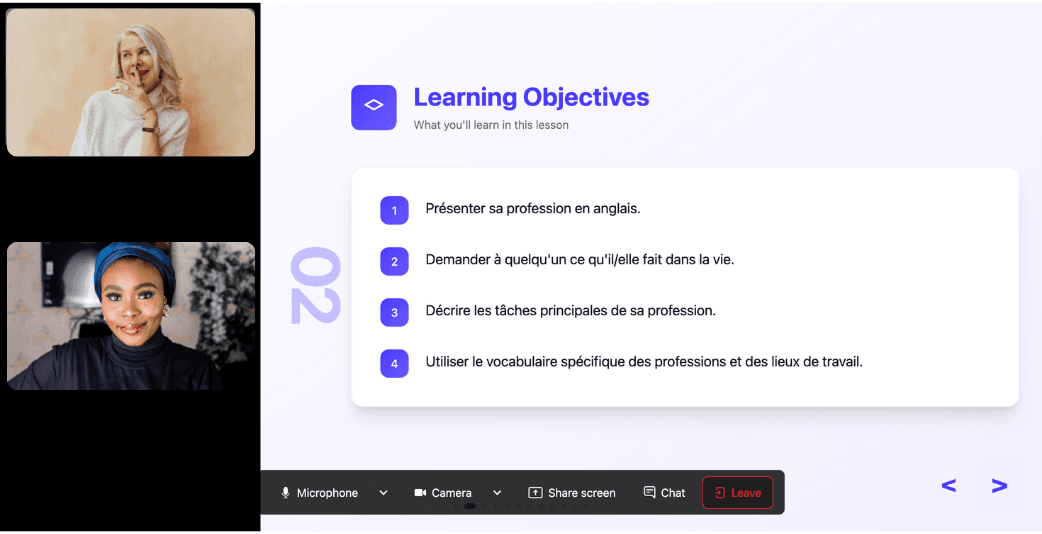
Ever felt frustrated trying to keep up with a native-speaking teacher, or embarrassed to ask for something to be repeated? With Kylian, that problem disappears. It switches intelligently between French and the target language depending on your level, helping you understand every concept at your own pace.
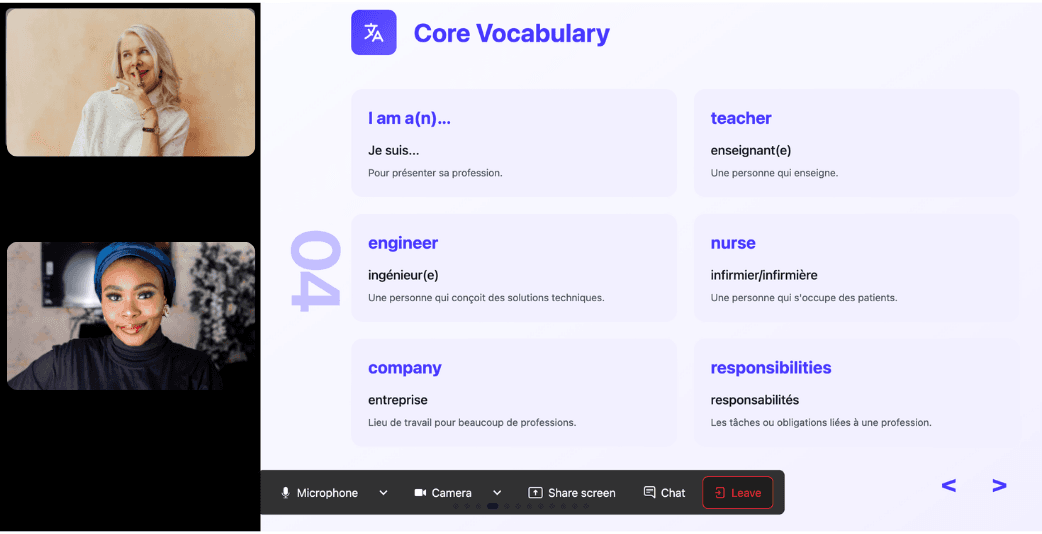
During the lesson, Kylian uses role-plays, real-life examples, and adapts to your learning style. Didn’t understand something? No problem—you can pause Kylian anytime to ask for clarification, without fear of being judged.
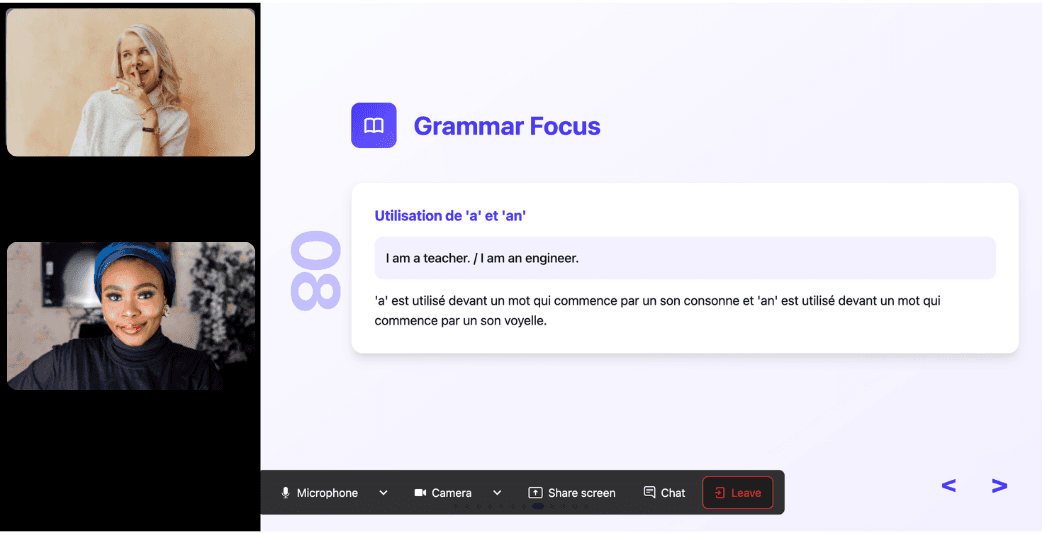
Ask all the questions you want, repeat sections if needed, and customize your learning experience in ways traditional teachers and generic apps simply can’t match.
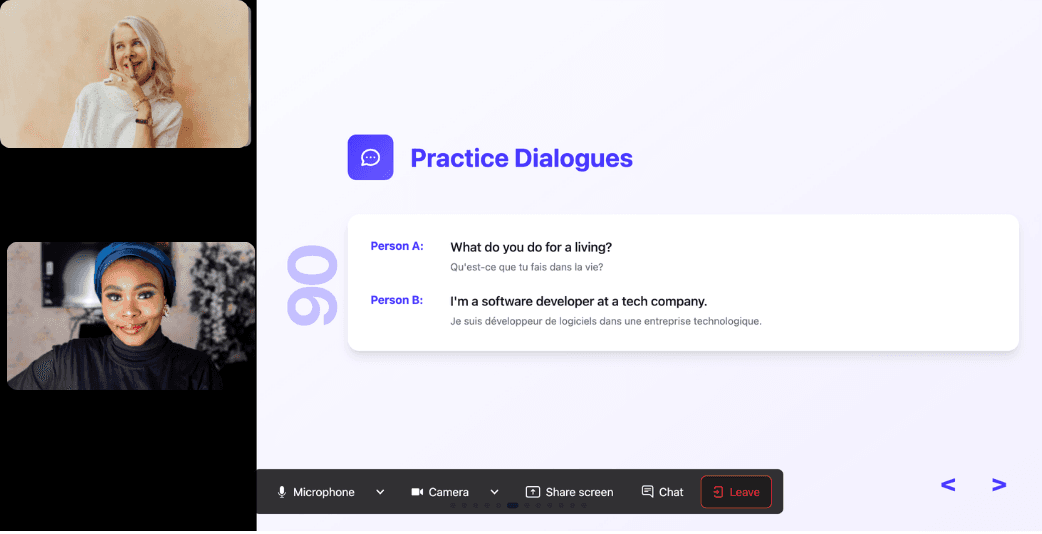
With 24/7 access at a fraction of the cost of private lessons, Kylian removes all the barriers that have kept you from mastering the language you’ve always wanted to learn.
Similar Content You Might Want To Read

English Tutoring Rates: What You Should Actually Pay
With approximately 1.45 billion speakers worldwide, English has become the global lingua franca for business, education, and international communication. This widespread adoption creates an enormous demand for quality English instruction, but many prospective learners struggle with a fundamental question: how much should they actually pay for English lessons? The market for English tutoring is diverse and complex, with prices typically ranging from $15 to $50 per hour. However, understanding what drives these price differences empowers you to make smarter decisions about your language learning investment. This comprehensive guide examines the critical factors that influence English tutoring rates, helping you determine a reasonable budget for your specific learning needs.

How to Learn Chinese for Beginners: 9 Effective Steps
Learning Mandarin Chinese might seem daunting at first, but with the right approach, it becomes a rewarding journey. This comprehensive guide breaks down the process into manageable steps, helping you establish an effective learning routine regardless of your ultimate goal—whether it's basic conversation or professional fluency.

14 Main Steps for Moving to Japan: Expat Guide
Relocating to Japan represents a transformative opportunity that combines professional advancement with cultural immersion. This comprehensive guide examines the critical steps required to successfully transition to this dynamic East Asian nation, addressing everything from financial planning to cultural integration.

How to Say "Happy Birthday" in German: Complete Guide
Ever wondered how to express birthday wishes in German? Learning to say "Happy birthday" in German isn't just about memorizing a phrase—it's about embracing a cultural tradition that reveals the warmth and depth of German celebrations. This guide will equip you with essential German birthday vocabulary, pronunciation tips, and cultural insights that will help you connect authentically with German speakers during their special day.

Whose' vs. 'Who's': Learn the Difference Easily
In the landscape of commonly confused words in English, the "whose" versus "who's" dilemma ranks high among native and non-native speakers alike. These homophones—words that sound identical but differ in meaning, spelling, and usage—create persistent confusion in written communication. Much like their problematic cousins "there/their/they're" and "it's/its," these terms follow distinct grammatical rules that, once understood, eliminate the potential for error. This comprehensive guide dissects the fundamental differences between "whose" and "who's," providing actionable strategies to distinguish between them in various contexts. By the end of this article, you'll possess the knowledge to deploy these terms with confidence and precision.

How to Learn English by Yourself: Your Path to Fluency
English stands as the most widely studied second language globally. With an abundance of learning materials, self-proclaimed language hacks, and supportive online communities at your disposal, the path to English proficiency has never been more accessible. But for those needing to learn English efficiently, what approach yields the most effective results? This guide offers a methodical approach to mastering English independently. We'll examine proven techniques for accelerating your progress, explain the science behind their effectiveness, and identify the essential resources for achieving fluency.