What is the Past Tense of Cough? [English]

Written by
Ernest Bio Bogore

Reviewed by
Ibrahim Litinine
![What is the Past Tense of Cough? [English]](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcdn.sanity.io%2Fimages%2F147z5m2d%2Fproduction%2Ff15759220479b4b78d5d4c11f2275af6da86dc9e-2240x1260.png&w=3840&q=75)
Language precision matters more than most people realize. When English learners struggle with seemingly simple verbs like "cough," they're not just making minor mistakes—they're revealing fundamental gaps in understanding regular verb patterns that affect their entire communication framework.
The past tense of "cough" is "coughed." This straightforward transformation follows English's most reliable grammatical pattern: adding "-ed" to regular verbs. Why does this matter? Because mastering this single verb opens the door to understanding approximately 70% of English verbs that follow identical conjugation rules.
Understanding Why "Coughed" Follows Regular Verb Patterns
Regular verbs in English operate on predictable systems that native speakers internalize unconsciously. "Cough" exemplifies this pattern perfectly because it demonstrates how phonetic structure influences morphological changes. The verb ends in an unvoiced consonant /f/, which creates specific pronunciation requirements when adding the past tense suffix.
The transformation from "cough" to "coughed" isn't arbitrary—it reflects systematic linguistic principles that govern thousands of English verbs. When you understand why "cough" becomes "coughed," you simultaneously grasp the mechanism behind walked, talked, laughed, and countless other regular verbs.
This systematic approach matters because language acquisition accelerates when learners recognize patterns rather than memorizing individual cases. The verb "cough" serves as a perfect entry point for understanding broader grammatical structures that impact daily communication effectiveness.
Practical Applications of "Coughed" in Context
Effective usage of "coughed" requires understanding temporal relationships and contextual appropriateness. Consider these strategic applications:
Medical and Health Contexts: The patient coughed intermittently throughout the examination, indicating potential respiratory irritation. Here, "coughed" establishes a completed action within a specific timeframe, crucial for medical documentation accuracy.
Social Situations: During the presentation, Marcus coughed deliberately to signal his disagreement without interrupting the speaker. This usage demonstrates intentional action in past narrative, showing how "coughed" can convey non-verbal communication.
Environmental Responses: The construction workers coughed as dust clouds enveloped the site, forcing them to seek protective equipment. This example illustrates involuntary physical responses to external stimuli, a common usage pattern.
Narrative Storytelling: Sarah coughed nervously before delivering her first public speech, her anxiety manifesting in physical symptoms. This application shows how "coughed" can advance character development in storytelling contexts.
Each example demonstrates different semantic functions of the past tense form, from medical reporting to emotional expression. The versatility of "coughed" reflects its importance in accurate English communication across professional and personal contexts.
Advanced Pronunciation Considerations for "Coughed"
Pronunciation accuracy significantly impacts communication effectiveness, particularly with "coughed." The past tense form ends with an unvoiced /t/ sound, not a voiced /d/ sound. This distinction affects listener comprehension and speaker credibility.
The phonetic transformation occurs because "cough" ends with the unvoiced fricative /f/. When adding the "-ed" suffix to verbs ending in unvoiced consonants, English phonology requires the /t/ pronunciation to maintain articulatory efficiency. This pattern extends to other verbs like "laughed" /læft/, "stuffed" /stʌft/, and "roughed" /rʌft/.
Understanding this pronunciation rule prevents common errors that mark speakers as non-native. Many English learners incorrectly pronounce "coughed" with a /d/ ending, creating confusion and reducing communication clarity. The /t/ ending aligns with natural English speech rhythms and demonstrates advanced grammatical competence.
Regional variations in English-speaking countries maintain this /t/ pronunciation consistently. Whether in American, British, Canadian, or Australian English, "coughed" retains the same phonetic characteristics, making this pronunciation rule universally applicable.
Semantic Alternatives and Contextual Variations
While "coughed" serves as the standard past tense form, sophisticated English usage often requires alternative expressions that convey nuanced meanings. These alternatives demonstrate advanced vocabulary control and contextual awareness.
"Cleared throat" Usage: Before announcing the verdict, the judge cleared her throat to ensure everyone's attention. This alternative suggests deliberate preparation rather than involuntary response, adding intentionality to the action.
"Hacked" for Intensity: The patient hacked violently during the night, suggesting a severe respiratory condition requiring immediate attention. "Hacked" implies harsh, repetitive coughing that exceeds normal intensity levels.
"Spluttered" for Surprise: When the interviewer asked the unexpected question, the candidate spluttered momentarily before regaining composure. This alternative conveys sudden, uncontrolled response often accompanied by speech disruption.
"Wheezed" for Breathing Difficulty: The elderly man wheezed as he climbed the stairs, indicating potential respiratory limitations affecting his mobility. "Wheezed" specifically denotes labored breathing often associated with medical conditions.
Each alternative carries distinct connotations that "coughed" alone cannot express. Strategic selection among these options demonstrates linguistic sophistication and precise communication skills that distinguish advanced English users from intermediate learners.
Common Errors and Strategic Corrections
Error patterns in using "coughed" reveal systematic misunderstandings that extend beyond individual verb usage. Addressing these errors strategically improves overall grammatical competence.
Tense Consistency Errors: Incorrect: "Yesterday I cough when the smoke fill the room." Correct: "Yesterday I coughed when the smoke filled the room."
This error demonstrates insufficient understanding of narrative tense consistency. All past events require past tense forms to maintain temporal coherence.
Auxiliary Verb Confusion: Incorrect: "She did coughed during the meeting." Correct: "She coughed during the meeting" or "She did cough during the meeting."
This error occurs when learners incorrectly combine auxiliary verbs with past tense forms. Understanding when auxiliary verbs require base forms prevents this systematic mistake.
Spelling Inconsistencies: Incorrect: "He coft loudly in the library." Correct: "He coughed loudly in the library."
Phonetic spelling attempts often fail because English orthography doesn't consistently represent pronunciation. Memorizing correct spellings prevents written communication errors.
These error patterns indicate deeper grammatical system gaps rather than isolated mistakes. Correcting them requires understanding underlying principles rather than rote memorization.
Advanced Applications in Professional Communication
Professional contexts demand precise verb usage that demonstrates competence and attention to detail. "Coughed" appears frequently in medical documentation, legal testimony, and business reporting where accuracy affects outcomes.
Medical Documentation: "The patient coughed productively during the examination, producing yellow sputum that required laboratory analysis." Medical contexts require specific terminology that distinguishes between cough types and their clinical significance.
Legal Testimony: "The witness coughed repeatedly during cross-examination, potentially indicating nervousness or deception according to behavioral analysts." Legal contexts use physical actions as evidence indicators requiring precise documentation.
Business Meeting Minutes: "The CEO coughed to interrupt the heated discussion between department heads, redirecting attention to quarterly projections." Business documentation captures non-verbal communication that influences meeting dynamics.
Academic Research: "Participants coughed an average of 3.7 times per session when exposed to the controlled irritant, supporting the hypothesis regarding environmental sensitivity." Academic contexts require quantifiable observations using past tense forms.
Professional communication standards expect grammatical accuracy that reinforces credibility. Incorrect verb usage undermines professional authority and reduces communication effectiveness in high-stakes situations.
Morphological Analysis and Pattern Recognition
Understanding "coughed" within broader morphological frameworks accelerates learning efficiency. Regular verbs follow predictable transformation patterns that apply across thousands of English words.
The morpheme "-ed" serves multiple grammatical functions beyond past tense formation. It creates past participles for perfect tense constructions ("has coughed"), passive voice formations ("was coughed up"), and adjectival uses ("the coughed-up substance"). This morphological flexibility demonstrates why mastering regular verb patterns yields disproportionate learning benefits.
Phonological rules governing "-ed" pronunciation follow systematic patterns based on final consonant characteristics. Verbs ending in /t/ or /d/ sounds require an additional syllable (/ɪd/), while voiceless consonants trigger /t/ pronunciation, and voiced consonants produce /d/ sounds. "Cough" ending in voiceless /f/ predictably generates the /t/ pronunciation in "coughed."
This systematic approach contrasts sharply with irregular verb patterns that require individual memorization. Regular verbs like "cough" provide reliable frameworks for understanding English morphology, making them strategic learning priorities for developing fluency.
Cognitive Processing and Memory Optimization
Language acquisition research demonstrates that regular verb patterns like "coughed" activate different cognitive processing mechanisms than irregular forms. Regular patterns engage rule-based processing systems that generalize across similar constructions, while irregular forms require associative memory networks.
This cognitive distinction has practical implications for learning strategies. Regular verbs benefit from pattern recognition exercises that emphasize systematic transformations rather than rote memorization. Understanding why "cough" becomes "coughed" creates neural pathways that automatically process similar verbs without conscious effort.
Memory consolidation occurs more efficiently when learners understand underlying principles rather than memorizing isolated examples. The regular pattern demonstrated by "coughed" provides a cognitive framework that accommodates thousands of additional verbs with minimal additional effort.
Strategic learning approaches emphasize pattern recognition over individual word memorization because systematic understanding creates scalable knowledge structures. Mastering "coughed" correctly establishes cognitive templates for processing extensive verb vocabularies efficiently.
Assessment Frameworks for Mastery Verification
Effective language learning requires systematic assessment methods that verify genuine understanding rather than superficial memorization. "Coughed" usage provides multiple assessment opportunities across different skill areas.
Production Assessments: Spontaneous speech samples reveal whether learners automatically apply correct past tense forms under time pressure. Natural conversation contexts test internalized grammar rather than conscious rule application.
Recognition Assessments: Multiple choice exercises isolate specific grammatical knowledge without production demands. These assessments verify understanding of form-meaning relationships independent of pronunciation challenges.
Application Assessments: Contextual usage tasks require learners to select appropriate verb forms based on temporal and semantic requirements. These assessments test practical application rather than theoretical knowledge.
Integration Assessments: Complex communication tasks combine multiple grammatical systems requiring coordinated application of various rules. These assessments verify genuine fluency rather than isolated skill demonstration.
Comprehensive assessment frameworks reveal learning gaps that targeted instruction can address. Understanding assessment implications helps learners focus effort on areas requiring additional development.
Technological Integration and Modern Usage Patterns
Digital communication platforms create new contexts for "coughed" usage that differ from traditional written or spoken formats. Social media, instant messaging, and voice-to-text applications present unique challenges and opportunities for demonstrating grammatical competence.
Voice recognition software requires precise pronunciation of "coughed" to ensure accurate transcription. The /t/ ending becomes crucial for technological interaction, as mispronunciation can result in incorrect text conversion that affects communication clarity.
Autocorrect systems often flag "coughed" incorrectly when users misspell based on phonetic assumptions. Understanding correct spelling becomes essential for efficient digital communication that doesn't require constant correction.
Professional video conferencing and online presentations increase the importance of clear pronunciation and appropriate usage. Remote communication contexts amplify the impact of grammatical errors because visual cues are limited and audio quality affects comprehension.
These technological considerations add practical urgency to mastering "coughed" correctly. Modern communication increasingly relies on technological mediation that requires precise grammatical competence for effective interaction.
Learn Any Language with Kylian AI
Private language lessons are expensive. Paying between 15 and 50 euros per lesson isn’t realistic for most people—especially when dozens of sessions are needed to see real progress.
Many learners give up on language learning due to these high costs, missing out on valuable professional and personal opportunities.
That’s why we created Kylian: to make language learning accessible to everyone and help people master a foreign language without breaking the bank.
To get started, just tell Kylian which language you want to learn and what your native language is
Tired of teachers who don’t understand your specific struggles as a French speaker? Kylian’s advantage lies in its ability to teach any language using your native tongue as the foundation.
Unlike generic apps that offer the same content to everyone, Kylian explains concepts in your native language (French) and switches to the target language when necessary—perfectly adapting to your level and needs.
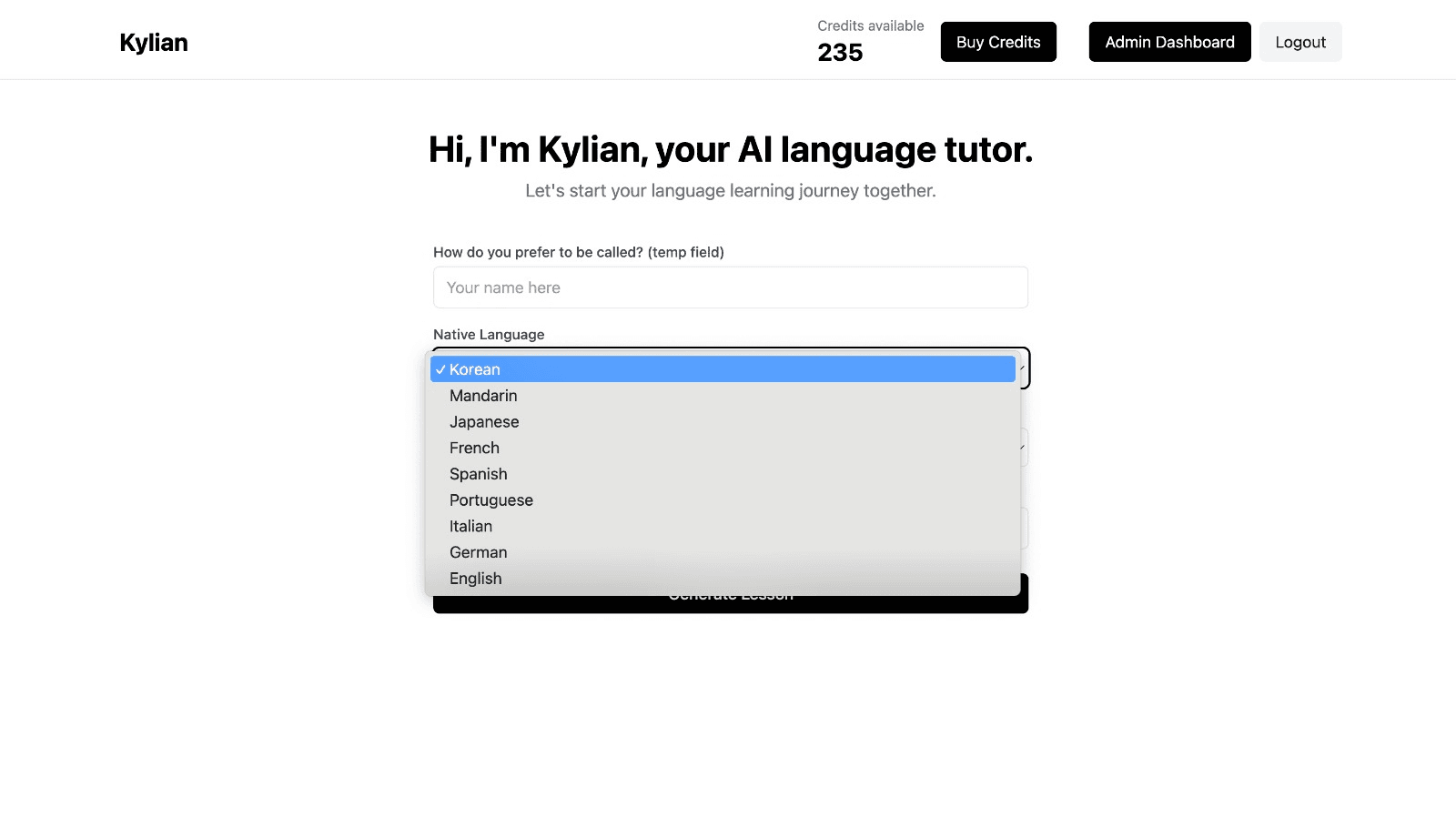
This personalization removes the frustration and confusion that are so common in traditional language learning.
Choose a specific topic you want to learn
Frustrated by language lessons that never cover exactly what you need? Kylian can teach you any aspect of a language—from pronunciation to advanced grammar—by focusing on your specific goals.
Avoid vague requests like “How can I improve my accent?” and be precise: “How do I pronounce the R like a native English speaker?” or “How do I conjugate the verb ‘to be’ in the present tense?”
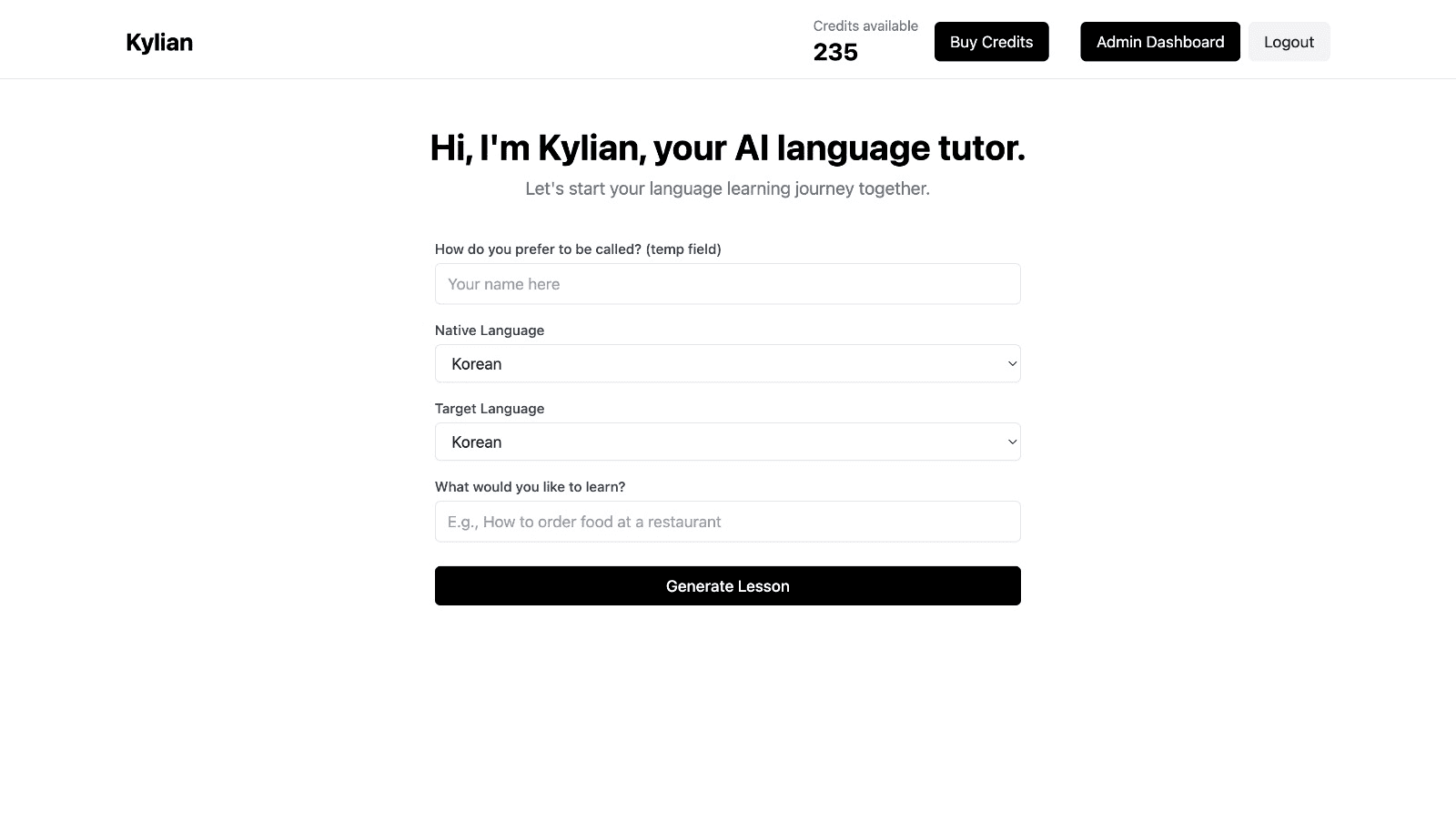
With Kylian, you’ll never again pay for irrelevant content or feel embarrassed asking “too basic” questions to a teacher. Your learning plan is entirely personalized.
Once you’ve chosen your topic, just hit the “Generate a Lesson” button, and within seconds, you’ll get a lesson designed exclusively for you.
Join the room to begin your lesson
The session feels like a one-on-one language class with a human tutor—but without the high price or time constraints.
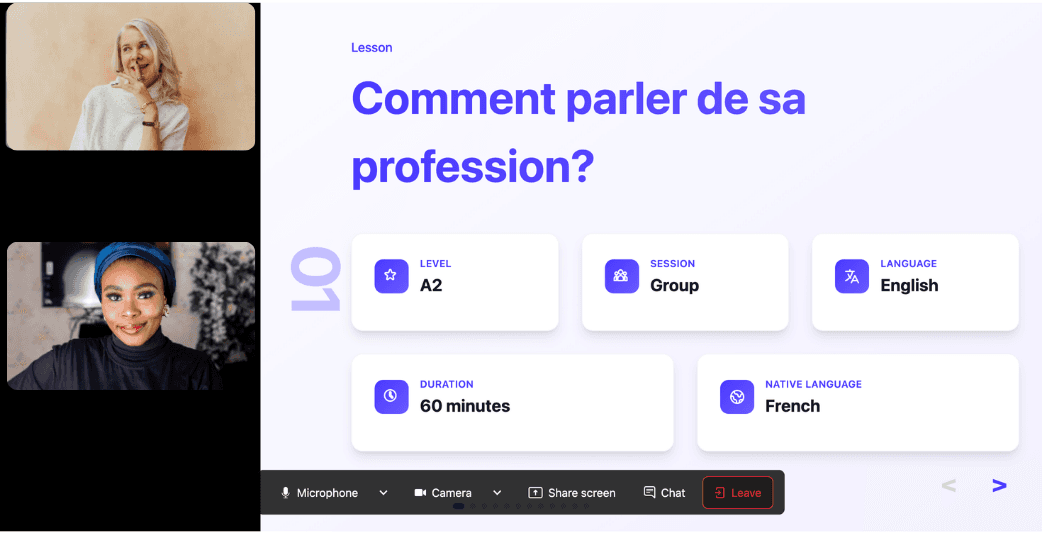
In a 25-minute lesson, Kylian teaches exactly what you need to know about your chosen topic: the nuances that textbooks never explain, key cultural differences between French and your target language, grammar rules, and much more.
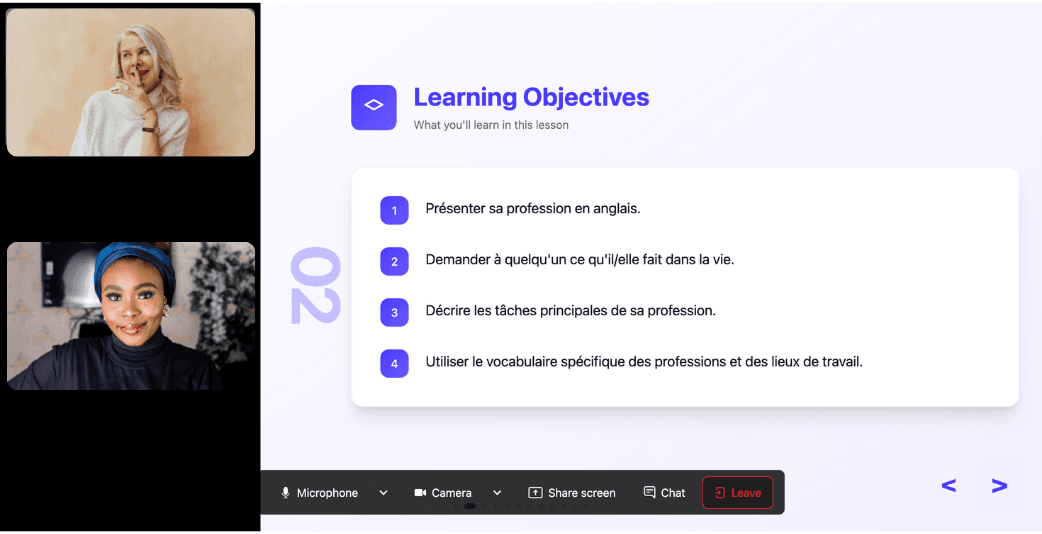
Ever felt frustrated trying to keep up with a native-speaking teacher, or embarrassed to ask for something to be repeated? With Kylian, that problem disappears. It switches intelligently between French and the target language depending on your level, helping you understand every concept at your own pace.
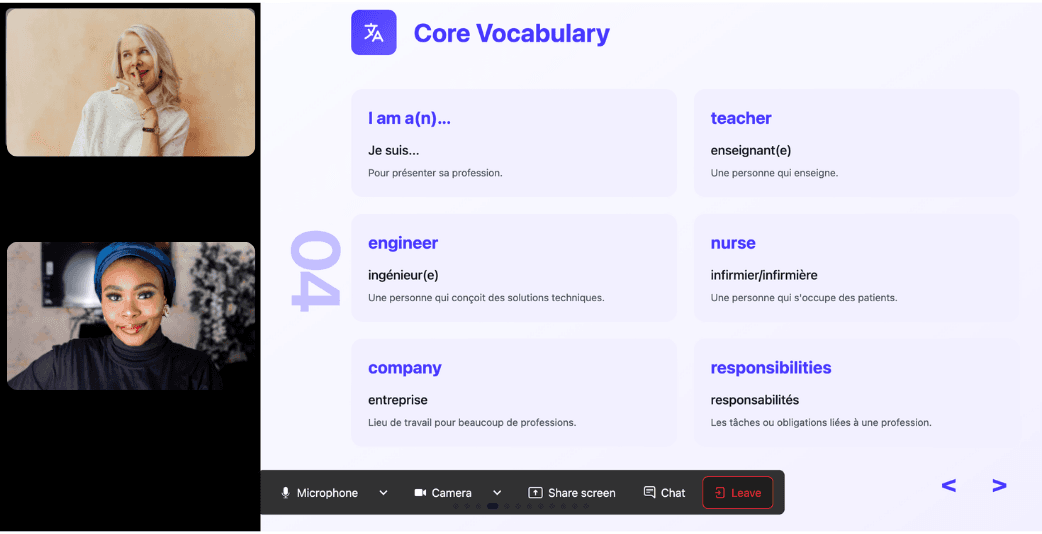
During the lesson, Kylian uses role-plays, real-life examples, and adapts to your learning style. Didn’t understand something? No problem—you can pause Kylian anytime to ask for clarification, without fear of being judged.
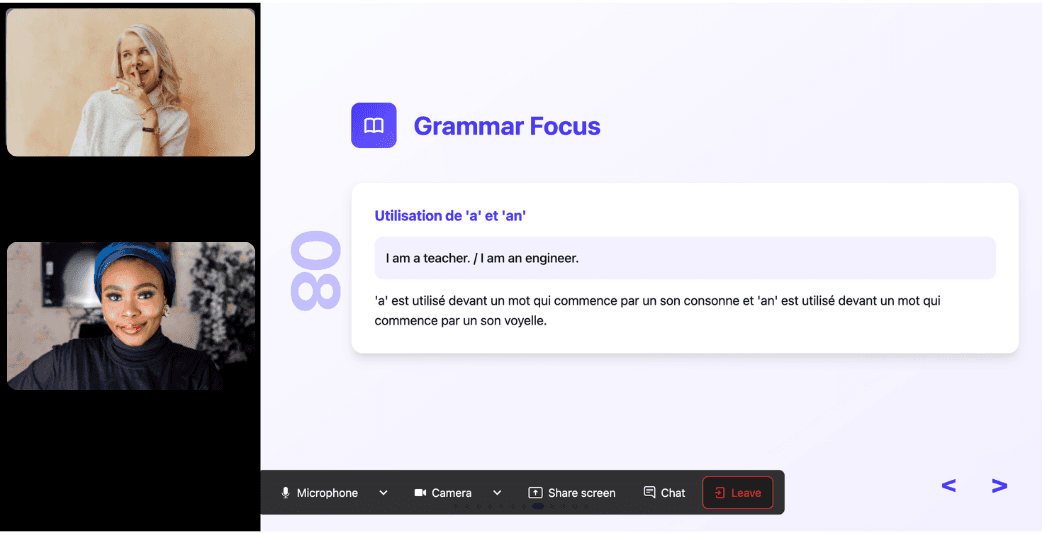
Ask all the questions you want, repeat sections if needed, and customize your learning experience in ways traditional teachers and generic apps simply can’t match.
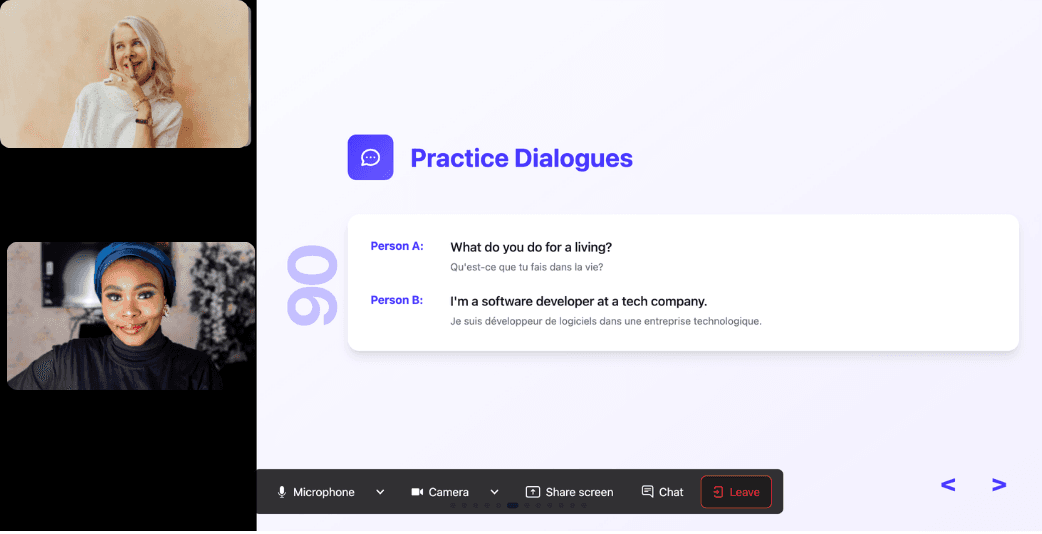
With 24/7 access at a fraction of the cost of private lessons, Kylian removes all the barriers that have kept you from mastering the language you’ve always wanted to learn.
Similar Content You Might Want To Read

Your Complete Guide to Days of the Week in French
Learning how to say and use the days of the week in French is a fundamental step toward language fluency. Whether you're scheduling business meetings, making weekend plans with friends, or simply trying to understand when a shop is open, mastering these seven essential words will dramatically improve your everyday communication skills. This comprehensive guide explores everything you need to know about the French days of the week—from pronunciation and etymology to grammatical rules and cultural contexts. We'll also examine common phrases and expressions that will help you sound more natural when discussing time and schedules in French.

The Essential Guide to Saying "Thank You" in French
In every culture worldwide, expressing gratitude represents a fundamental social cornerstone. Yet in France, the art of saying "thank you" transcends mere politeness—it embodies an essential cultural practice deeply woven into daily interactions. Understanding the nuances of French gratitude expressions doesn't just prevent social faux pas; it demonstrates cultural literacy and respect that French speakers deeply value. This comprehensive guide examines the various expressions of gratitude in French across formal, casual, and written contexts. We'll analyze when and how to deploy each phrase effectively, examine crucial cultural context, and highlight common mistakes to avoid.

Mastering the French Passé Composé: A Strategic Guide
Effective communication in any language hinges on expressing when actions occurred. French offers several past tenses, but none more crucial for everyday communication than the passé composé. This tense serves as the foundation for discussing completed actions in French, making it an essential milestone for language learners. Let's examine why this tense matters, how to construct it properly, and how to implement it efficiently in your French language practice.

Portuguese Numbers: The Complete Guide for Language Learners
Numbers form the foundation of practical communication in any language. Whether you're shopping at a market in Lisbon, scheduling a meeting in Rio de Janeiro, or simply discussing statistics with Portuguese-speaking colleagues, mastering numbers is essential. This comprehensive guide covers everything from basic counting to expressing complex numerical concepts in Portuguese.

9 Different Ways to Say Congratulations in French
There's something profoundly human about celebrating achievements. When we witness someone's success, our instinct is to acknowledge it—to participate in their moment of triumph. This shared experience transcends cultural boundaries, though the expressions we use vary widely across languages. French, with its melodic cadence and rich cultural heritage, offers a particularly elegant array of congratulatory expressions. These phrases do more than convey basic sentiments; they reflect the nuances of French culture and social interactions. This guide explores multiple ways to express congratulations in French, equipping you with the vocabulary to celebrate authentically in any context—from professional achievements to personal milestones, formal occasions to casual encounters.

French Alphabet: Mastering Letter Pronunciation
Learning to pronounce the French alphabet correctly establishes the foundation for mastering French pronunciation. When you understand how individual letters sound, you gain the ability to pronounce new words with confidence and develop a more authentic accent. This comprehensive guide breaks down everything you need to know about French alphabet pronunciation, from basic letter sounds to the nuances of accent marks.