130+ Spanish Cognates You Should Know

Written by
Ernest Bio Bogore

Reviewed by
Ibrahim Litinine

Learning a new language requires strategic approaches that maximize efficiency and effectiveness. For English speakers venturing into Spanish, there exists a powerful shortcut that instantly expands vocabulary: cognates. These linguistic bridges between languages offer immediate recognition and comprehension, dramatically accelerating the learning curve and providing confidence for new speakers.
What Are Spanish Cognates?
Cognates represent a fascinating linguistic phenomenon where words across different languages share etymological origins, resulting in similar spelling, pronunciation, and meaning. The relationship between English and Spanish proves particularly fruitful in this regard, as both languages draw heavily from Latin roots. This shared ancestry has produced thousands of recognizable cognates that provide English speakers with an immediate Spanish vocabulary advantage.
When you encounter Spanish phrases like "Es importante estudiar la información" or "La música clásica es excelente," you'll likely understand them without prior Spanish study because of cognate recognition. This immediate comprehension represents a significant advantage that strategic learners can leverage.
Cognates function as mental anchors, allowing you to navigate conversations and texts with greater confidence. Rather than memorizing entirely new vocabulary, you can focus on identifying patterns and relationships between words you already know and their Spanish counterparts.
Categories of Spanish-English Cognates
Understanding the systematic nature of cognates helps organize your learning approach. Spanish-English cognates generally fall into three distinct categories:
Perfect Cognates
These words maintain nearly identical spelling and pronunciation across both languages, though Spanish may include accent marks (diacritical marks) for proper pronunciation guidance. The meaning remains consistent across both languages, providing immediate vocabulary recognition.
Near-Perfect Cognates
While maintaining similar meaning, these words feature slight variations in spelling or pronunciation. However, they follow predictable patterns that, once learned, allow you to transform thousands of English words into their Spanish equivalents through simple modifications.
False Cognates
These deceptive pairs appear identical or very similar across languages but carry entirely different meanings. While relatively few in number compared to true cognates, awareness of these "false friends" prevents potentially embarrassing miscommunications.
Perfect Spanish Cognates: Your Instant Vocabulary Boost
Perfect cognates represent the easiest entry point into Spanish vocabulary acquisition. These words require minimal adaptation from English, often differing only in pronunciation or the addition of accent marks. Recognizing common patterns among these words enables you to instantly expand your Spanish lexicon.
Words Ending in -al
The -al ending in English often remains identical in Spanish, creating perfect cognates that transfer directly between languages:
- actual → actual
- animal → animal
- digital → digital
- hospital → hospital
- ideal → ideal
- natural → natural
- professional → profesional
- normal → normal
- legal → legal
- manual → manual
Words Ending in -ar
Similarly, words ending with -ar maintain their form across both languages:
- circular → circular
- familiar → familiar
- muscular → muscular
- particular → particular
- popular → popular
- regular → regular
- similar → similar
- solar → solar
- nuclear → nuclear
- molecular → molecular
Words Ending in -ble
This pattern creates another set of directly transferable vocabulary:
- admirable → admirable
- cable → cable
- double → doble
- flexible → flexible
- horrible → horrible
- impossible → imposible
- terrible → terrible
- visible → visible
- responsible → responsable
- memorable → memorable
Words Ending in -sión
Words ending in -sion in English typically become -sión in Spanish, adding only an accent mark while maintaining their recognizable form:
- compassion → compasión
- comprehension → comprensión
- decision → decisión
- expression → expresión
- illusion → ilusión
- mansion → mansión
- mission → misión
- passion → pasión
- tension → tensión
- vision → visión
Essential Spanish Cognates by Category
Organizing cognates by thematic categories helps contextualize vocabulary within practical usage scenarios, making them more memorable and immediately applicable.
Food and Dining
- banana → banana
- chocolate → chocolate
- fruit → fruta
- restaurant → restaurante
- salad → ensalada
- menu → menú
- vegetable → vegetal
- cereal → cereal
- dessert → postre
- ingredient → ingrediente
Daily Life
- bank → banco
- doctor → doctor
- family → familia
- hospital → hospital
- organize → organizar
- study → estudiar
- telephone → teléfono
- university → universidad
- office → oficina
- apartment → apartamento
Leisure Activities
- celebrate → celebrar
- music → música
- photography → fotografía
- sport → deporte
- television → televisión
- cinema → cinema
- festival → festival
- concert → concierto
- theater → teatro
- park → parque
Travel
- airport → aeropuerto
- hotel → hotel
- passport → pasaporte
- reserve → reservar
- tourist → turista
- visit → visitar
- destination → destinación
- excursion → excursión
- transportation → transportación
- souvenir → souvenir
Near-Perfect Spanish Cognates: Recognizing Patterns
Near-perfect cognates follow predictable transformation patterns. Learning these patterns allows you to convert thousands of English words into their Spanish equivalents through simple modifications.
Words Ending in -ct Changing to -cto
- act → acto
- insect → insecto
- contact → contacto
- correct → correcto
- effect → efecto
- perfect → perfecto
- conflict → conflicto
- product → producto
- project → proyecto
- aspect → aspecto
Words Ending in -ic Changing to -ico
- alcoholic → alcohólico
- allergic → alérgico
- athletic → atlético
- automatic → automático
- basic → básico
- electric → eléctrico
- exotic → exótico
- fantastic → fantástico
- scientific → científico
- toxic → tóxico
Words Ending in -id Changing to -ido
- fluid → fluido
- rapid → rápido
- solid → sólido
- valid → válido
- stupid → estúpido
- liquid → líquido
- vivid → vívido
- humid → húmedo
- splendid → espléndido
- morbid → mórbido
Words Ending in -y Changing to -ia
- academy → academia
- agency → agencia
- energy → energía
- history → historia
- memory → memoria
- photography → fotografía
- technology → tecnología
- therapy → terapia
- industry → industria
- economy → economía
Words Ending in -ant Changing to -ante
- abundant → abundante
- distant → distante
- elegant → elegante
- important → importante
- instant → instante
- vacant → vacante
- tolerant → tolerante
- dominant → dominante
- brilliant → brillante
- constant → constante
Words Ending in -ary Changing to -ario
- canary → canario
- diary → diario
- extraordinary → extraordinario
- glossary → glosario
- imaginary → imaginario
- necessary → necesario
- ordinary → ordinario
- primary → primario
- salary → salario
- vocabulary → vocabulario
Words Ending in -ate Changing to -ar
- accelerate → acelerar
- calculate → calcular
- celebrate → celebrar
- communicate → comunicar
- coordinate → coordinar
- create → crear
- decorate → decorar
- illuminate → iluminar
- operate → operar
- terminate → terminar
Words Ending in -ous Changing to -oso
- ambitious → ambicioso
- contagious → contagioso
- curious → curioso
- delicious → delicioso
- famous → famoso
- furious → furioso
- generous → generoso
- glorious → glorioso
- mysterious → misterioso
- religious → religioso
Words Ending in -ence Changing to -encia
- adolescence → adolescencia
- audience → audiencia
- coincidence → coincidencia
- competence → competencia
- difference → diferencia
- excellence → excelencia
- intelligence → inteligencia
- presence → presencia
- science → ciencia
- violence → violencia
Words Ending in -ment Changing to -mento
- argument → argumento
- cement → cemento
- department → departamento
- document → documento
- element → elemento
- instrument → instrumento
- moment → momento
- ornament → ornamento
- segment → segmento
- treatment → tratamiento
Words Ending in -tion Changing to -ción
- abbreviation → abreviación
- acceleration → aceleración
- attention → atención
- cancelation → cancelación
- collection → colección
- direction → dirección
- exception → excepción
- identification → identificación
- information → información
- invitation → invitación
Verb Cognates: Action Words That Transfer Easily
Beyond nouns and adjectives, many verbs also function as cognates, particularly those ending in -ate in English, which typically transform to -ar endings in Spanish. Understanding these patterns allows you to quickly expand your verbal expression:
- activate → activar
- collaborate → colaborar
- demonstrate → demostrar
- evaluate → evaluar
- motivate → motivar
- participate → participar
- regulate → regular
- stimulate → estimular
- tolerate → tolerar
- negotiate → negociar
Cognate Pronunciation Variations: Speaking Authentically
While cognates offer written recognition, pronunciation differences remain important for authentic spoken Spanish. Key pronunciation differences to master include:
- Spanish vowels maintain consistent sounds, unlike English variable vowels
- The letter 'r' requires a rolled/trilled pronunciation in Spanish
- Stress patterns often differ, with Spanish typically stressing the penultimate syllable
- Diacritical marks (accent marks) in Spanish indicate exceptions to standard stress patterns
These pronunciation differences explain why Spanish speakers might not immediately understand cognates when pronounced with an English accent. Mastering authentic Spanish pronunciation transforms written recognition into spoken communication success.
False Cognates: Avoiding Common Traps
False cognates (also called "false friends") represent a small but important subset of word pairs that appear similar but carry different meanings. Awareness of these potential pitfalls prevents miscommunication:
- "Embarazada" means "pregnant," not "embarrassed" (which is "avergonzado/a")
- "Constipado" means "having a cold," not "constipated" (which is "estreñido/a")
- "Éxito" means "success," not "exit" (which is "salida")
- "Asistir" means "to attend," not "to assist" (which is "ayudar")
- "Carpeta" means "folder," not "carpet" (which is "alfombra")
- "Librería" means "bookstore," not "library" (which is "biblioteca")
- "Actual" means "current," not "actual" (which is "real" or "verdadero")
- "Sopa" means "soup," not "soap" (which is "jabón")
- "Sensible" means "sensitive," not "sensible" (which is "sensato")
- "Realizar" typically means "to perform/carry out," not "to realize" (which is "darse cuenta")
Understanding these distinctions prevents potential confusion or embarrassment in conversation. While cognates offer tremendous learning advantages, these exceptions require specific attention.
Cognitive Benefits of Learning Through Cognates
Beyond practical vocabulary acquisition, cognate awareness offers deeper cognitive benefits for language learners:
Pattern Recognition Development
Recognizing cognate patterns strengthens neural pathways related to linguistic pattern identification, a skill that transfers to other areas of language learning and cognitive processing.
Etymological Understanding
Exploring cognates naturally introduces learners to word origins and the historical relationships between languages, creating deeper understanding of linguistic evolution.
Memory Enhancement
Connecting new vocabulary to familiar words creates stronger memory associations, improving both retention and recall compared to memorizing isolated vocabulary.
Confidence Building
The immediate comprehension provided by cognates offers psychological reinforcement that accelerates learning motivation and reduces language anxiety, particularly for beginners.
Strategic Application of Cognate Knowledge
Maximizing the advantage of cognates requires intentional learning strategies:
Pattern Mastery
Focus on learning transformation patterns rather than individual words. The ability to convert -tion to -ción or -ant to -ante allows you to transform thousands of words instantly.
Thematic Grouping
Organize cognates into functional categories relevant to your communication needs. Travel-related cognates prove immediately useful for travelers, while academic cognates benefit students.
Context Integration
Practice cognates within authentic sentences and conversations, not as isolated vocabulary. This contextual learning reinforces proper usage and meaning associations.
False Cognate Awareness
Create specific study sessions focused on false cognates, particularly those relevant to your communication contexts, to prevent recurring miscommunications.
Advanced Cognate Recognition: Beyond the Basics
As your Spanish proficiency advances, subtler cognate relationships become apparent:
Historical Sound Shifts
Understanding systematic sound changes between Latin-derived languages reveals less obvious cognates:
- Spanish 'h' often corresponds to English 'f': "hijo" (son) relates to "filial"
- Spanish 'll' often corresponds to English 'cl': "llave" (key) relates to "clave" and "clavis"
Root Word Recognition
Identifying Latin and Greek roots allows you to recognize cognates even when prefixes and suffixes differ:
- "Responsabilidad" and "responsibility" share the root "respons-"
- "Transformación" and "transformation" share the root "transform-"
Professional Field Terminology
Specialized professional fields often contain near-complete cognate vocabularies:
- Medical terminology: "cardiovascular," "neurológico," "diagnóstico"
- Scientific terms: "fotosíntesis," "gravitacional," "molecular"
- Technical vocabulary: "electromagnético," "calibración," "hidráulico"
Technological Tools for Cognate Learning
Modern language learning can leverage technology specifically for cognate mastery:
Spaced Repetition Systems
Specialized flashcard applications using algorithms that prioritize challenging words while reinforcing cognate patterns maximize learning efficiency.
Parallel Texts
Dual-language reading materials highlight cognates in context, strengthening recognition while providing authentic usage examples.
Cognate-Focused Applications
Several language learning platforms now offer specific cognate-recognition exercises designed to accelerate vocabulary acquisition through pattern identification.
Contextualizing Cognates in Real-World Communication
The ultimate goal of cognate learning extends beyond recognition to functional communication:
Conversational Integration
Practice incorporating newly identified cognates into your speaking practice, focusing on authentic pronunciation while leveraging familiar meanings.
Reading Comprehension Acceleration
Use cognate recognition as a reading comprehension strategy, identifying familiar words first to establish context before addressing unfamiliar vocabulary.
Writing Confidence
When composing in Spanish, begin with cognate-rich sentences to build confidence before incorporating more challenging vocabulary.
Learn Any Language with Kylian AI
Private language lessons are expensive. Paying between 15 and 50 euros per lesson isn’t realistic for most people—especially when dozens of sessions are needed to see real progress.
Many learners give up on language learning due to these high costs, missing out on valuable professional and personal opportunities.
That’s why we created Kylian: to make language learning accessible to everyone and help people master a foreign language without breaking the bank.
To get started, just tell Kylian which language you want to learn and what your native language is
Tired of teachers who don’t understand your specific struggles as a French speaker? Kylian’s advantage lies in its ability to teach any language using your native tongue as the foundation.
Unlike generic apps that offer the same content to everyone, Kylian explains concepts in your native language (French) and switches to the target language when necessary—perfectly adapting to your level and needs.
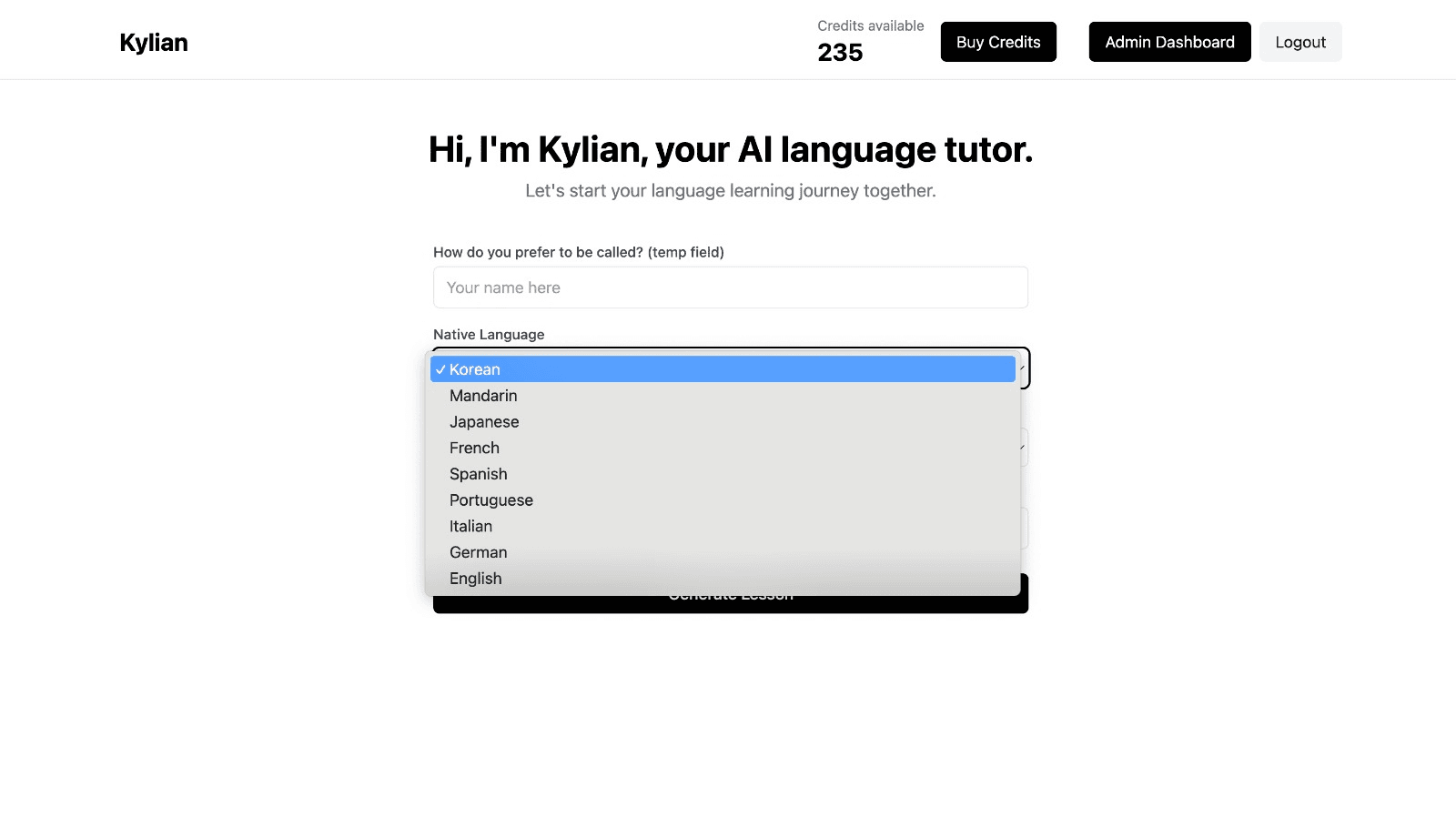
This personalization removes the frustration and confusion that are so common in traditional language learning.
Choose a specific topic you want to learn
Frustrated by language lessons that never cover exactly what you need? Kylian can teach you any aspect of a language—from pronunciation to advanced grammar—by focusing on your specific goals.
Avoid vague requests like “How can I improve my accent?” and be precise: “How do I pronounce the R like a native English speaker?” or “How do I conjugate the verb ‘to be’ in the present tense?”
With Kylian, you’ll never again pay for irrelevant content or feel embarrassed asking “too basic” questions to a teacher. Your learning plan is entirely personalized.
Once you’ve chosen your topic, just hit the “Generate a Lesson” button, and within seconds, you’ll get a lesson designed exclusively for you.
Join the room to begin your lesson
The session feels like a one-on-one language class with a human tutor—but without the high price or time constraints.
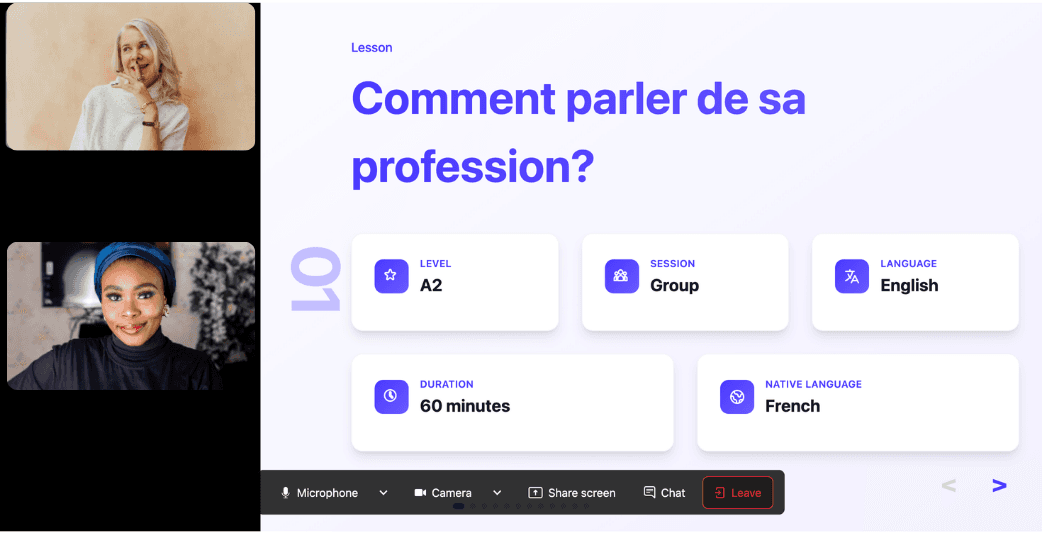
In a 25-minute lesson, Kylian teaches exactly what you need to know about your chosen topic: the nuances that textbooks never explain, key cultural differences between French and your target language, grammar rules, and much more.
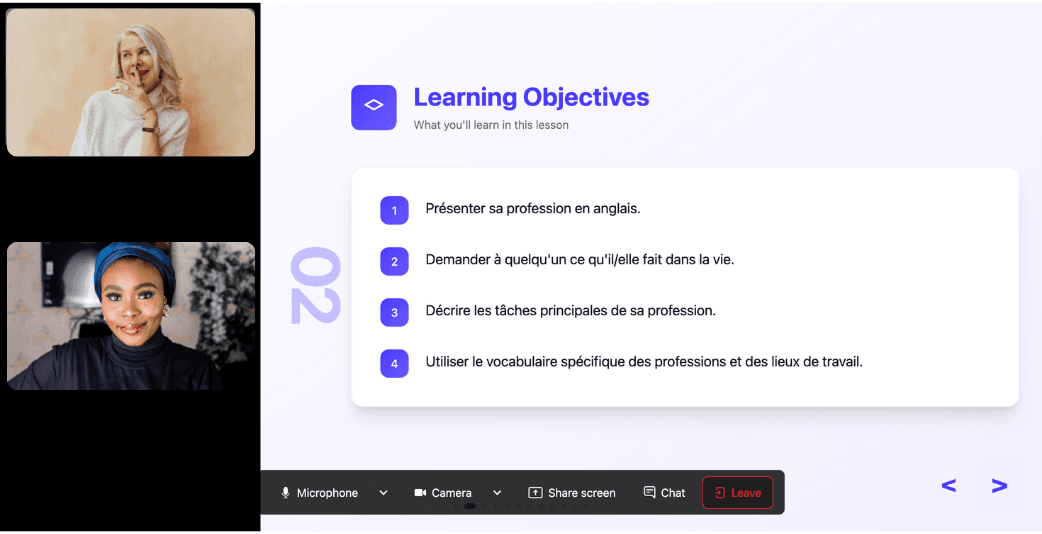
Ever felt frustrated trying to keep up with a native-speaking teacher, or embarrassed to ask for something to be repeated? With Kylian, that problem disappears. It switches intelligently between French and the target language depending on your level, helping you understand every concept at your own pace.
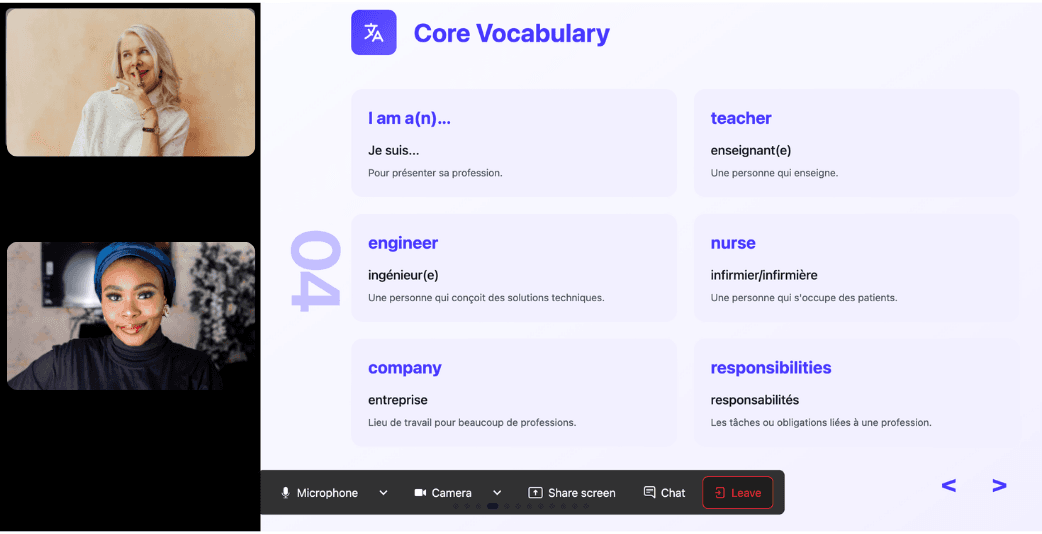
During the lesson, Kylian uses role-plays, real-life examples, and adapts to your learning style. Didn’t understand something? No problem—you can pause Kylian anytime to ask for clarification, without fear of being judged.
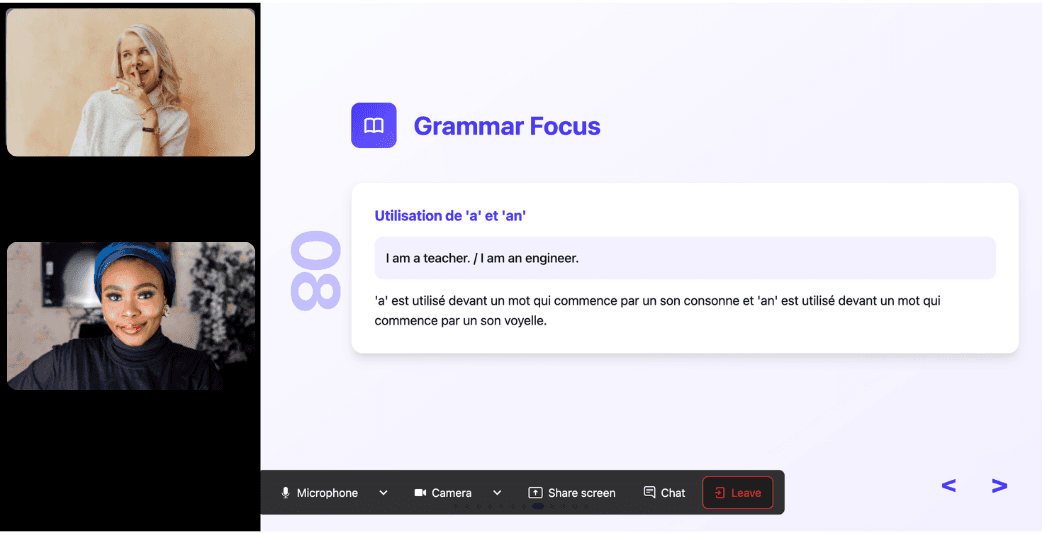
Ask all the questions you want, repeat sections if needed, and customize your learning experience in ways traditional teachers and generic apps simply can’t match.
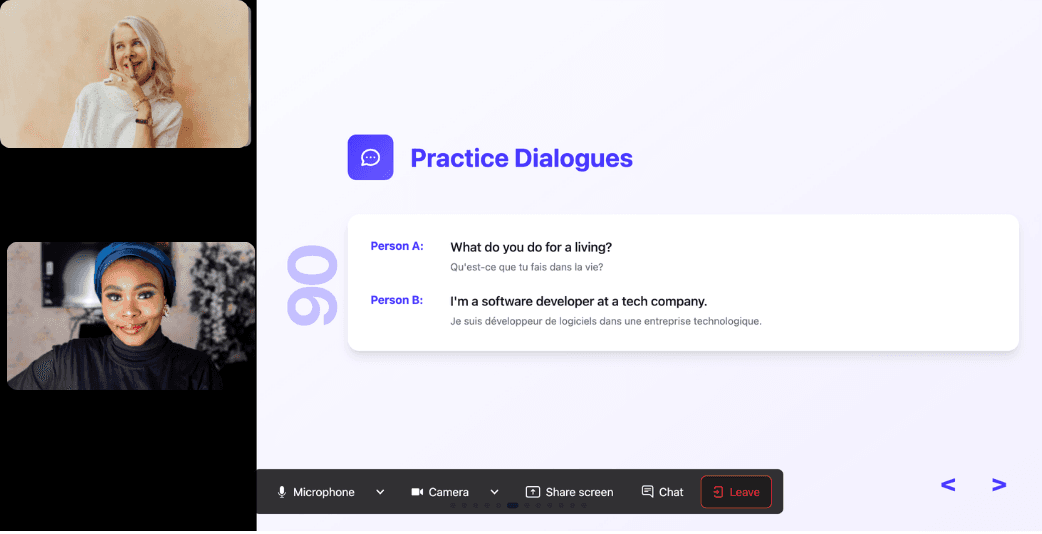
With 24/7 access at a fraction of the cost of private lessons, Kylian removes all the barriers that have kept you from mastering the language you’ve always wanted to learn.
Similar Content You Might Want To Read

Hawaiian Family Vocabulary: Learn Family Member Names
Understanding family-related vocabulary in Hawaiian offers profound insights into cultural values and relational structures in Hawaiian society. The Hawaiian language reflects a rich perspective on family connections that extends beyond nuclear relationships, embracing community ties and ancestral bonds.

How to Learn French Fast: A Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners
French—often called the language of love—carries an undeniable elegance, particularly in its melodic sounds. However, its grammatical complexities, inconsistent spelling patterns, and numerous rule exceptions can intimidate beginners. If you've ever dreamed of conversing with locals in Paris or working for a French organization, you might wonder if achieving proficiency requires years of dedication. The reality? With strategic learning approaches and consistent practice, you can reach basic conversational proficiency in mere months. This guide examines evidence-based methods to accelerate your French learning journey, with actionable steps to implement today. Let's begin!

Whose' vs. 'Who's': Learn the Difference Easily
In the landscape of commonly confused words in English, the "whose" versus "who's" dilemma ranks high among native and non-native speakers alike. These homophones—words that sound identical but differ in meaning, spelling, and usage—create persistent confusion in written communication. Much like their problematic cousins "there/their/they're" and "it's/its," these terms follow distinct grammatical rules that, once understood, eliminate the potential for error. This comprehensive guide dissects the fundamental differences between "whose" and "who's," providing actionable strategies to distinguish between them in various contexts. By the end of this article, you'll possess the knowledge to deploy these terms with confidence and precision.

How to Learn English by Yourself: Your Path to Fluency
English stands as the most widely studied second language globally. With an abundance of learning materials, self-proclaimed language hacks, and supportive online communities at your disposal, the path to English proficiency has never been more accessible. But for those needing to learn English efficiently, what approach yields the most effective results? This guide offers a methodical approach to mastering English independently. We'll examine proven techniques for accelerating your progress, explain the science behind their effectiveness, and identify the essential resources for achieving fluency.

300 Common English Words & How to Learn Them Fast
The daunting task of learning English often begins with the overwhelming realization that there are over 100,000 word families to master. Adding to this challenge, the language continuously expands with approximately three new words daily. However, linguistic research reveals something remarkable: with just the 300 most frequently used words in English, you can understand roughly 65% of all written material. This insight transforms the seemingly impossible journey into a manageable endeavor.

14 Most Effective Ways to Learn Spanish as an Adult
Learning Spanish as an adult presents unique challenges compared to childhood language acquisition. While children absorb languages effortlessly through exposure, adults often approach learning with analytical mindsets that can actually hinder fluency. The good news? By leveraging evidence-based learning strategies that prioritize immersion and practical application, adults can achieve Spanish proficiency efficiently. This guide explores proven methodologies that work specifically for adult learners, focusing on immersion-based techniques that research has consistently demonstrated to be superior to traditional grammar-heavy approaches.